Vitamin B3 and its health benefits

- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
What is vitamin B3?
Vitamin B3 (niacin) is a water-soluble vitamin essential for our body’s functioning. It is one of the eight types of B vitamins. The primary function of the vitamin B3 is to produce the coenzymes; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) required for the body’s numerous biochemical reactions linked to deriving energy from food 1Overview| Researched based study from Nih.gov

Facts
Facts about vitamin B3
- Vitamin B3 is water soluble; the body cannot store it
- The excess vitamin B3 not required by the body is excreted in urine
- The two chemical forms of vitamin B3 are nicotinamide (niacinamide) and nicotinic acid
- Our body can get vitamin B3 through foods or from the amino acid tryptophan found in animal foods
- Vitamin B3 act as an antioxidant and helps in DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) synthesis and DNA repair
- A severe lack of vitamin B3 causes a disease life-threatening disease called pellagra (skin disease with the mental problem)
- Vitamin B3 supplements are available commercially as tablet or capsule forms of niacin, nicotinamide or inositol hexaniacinate 2Facts| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Sources
Sources of vitamin B3
Animal sources
- Fish
- Swordfish
- Tuna
- Poultry
- Red meat
- Beef liver
- Beef
- Pork
- Chicken breast
- Turkey breast
- Brewer’s yeast
- Egg
Plant sources
- Beets
- Green vegetables
- Fortified bread and cereals
- Brown rice
- Legumes
- Sunflower seed
- Nuts
- Bananas
- Potato 3Sources| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage
Dosage of vitamin B3 in the different age groups
As per recommended dietary allowance, the doses per day for different age groups are as follows-
Dosage for infants
- Between 0 to 6 months-2 mg
- Between 7 months and 1year-4mg
Dosage for children
- Between 1 to 3 years-6mg
- Between 4 to 8 years-8mg
- Between 9to 13 years-12 mg
Dosage for adolescents and adults
- Men (14 years and above)-16mg
- Women (14 years and above) -14mg
Dosage for adults (above 19 years)
- Pregnant women-18mg
- Nursing mothers-17mg 2Dosages Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Maximum Doses for adults above 19 years without adverse health effect-35mg
It is to be noted that for ages above seven months, niacin is calculated in milligrams of NE (niacin equivalent), and 1 NE is equal to 1mg of niacin or 60 mg of tryptophan amino acid 1Dosage| Researched based study from Nih.gov
Biological role
Biological functions of vitamin D3
- It helps maintain homeostasis( maintaining the body’s internal stability) of the body.
- It helps in gene expression(DNA instruction converted to protein) and apoptosis(the natural process of cell death)
- It helps function the NAD-requiring enzymes(proteins speeding up a chemical reaction) and processes.
- It also plays a role in cell signalling(the process in which cells communicate with other body cells or the external environment 4Biological role| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Benefits
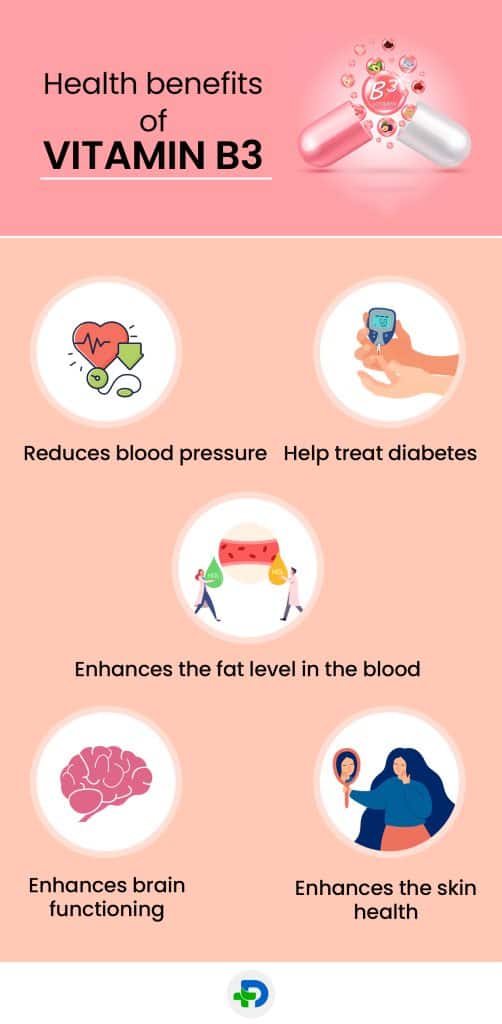
Health benefits of vitamin B3
Reduces blood pressure
- Vitamin B3 releases chemicals (prostaglandins) that widen the blood vessels
- It decreases blood pressure and It helps improve the blood flow 5Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Help treat diabetes
In Type 1 diabetes, the body damages the healthy insulin-secreting cells of the pancreas.
- Niacin help protect the healthy insulin cells from getting attacked
- It lowers the chance of type 1 diabetes
- It also helps reduce the high cholesterol in Type 2 diabetes patients 6Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhances the fat level in the blood
Vitamin B3 improves the level of good cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol)
- It decreases the levels of bad cholesterol(low-density lipoprotein(LDL)cholesterol)
- It decreases triglyceride(common body fat) levels 7Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhances brain functioning
Our brain needs niacin for cognitive health
- Niacin helps prevent damage to the brain cells .
- It helps in proper brain functioning 8Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhances the skin health
- Niacin help prevent the skin from the harmful effects of the sun .
- It helps prevent skin cancer 9Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Deficiency
Deficiency symptoms of vitamin B3
Niacin deficiency symptoms may include 1Deficiency| Researched based study from Nih.gov
- Headache
- Extreme tiredness
- Feeling of hopelessness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Skin rash
- Rough skin appearance
- Bright red colored tongue
- Burning sensation in the mouth
- Difficulty in clearing bowels
- Diarrhea
- Weakening of memory
- Appetite loss
- Circulatory problem
Severe vitamin B3 deficiency symptoms
- Amnesia (total memory loss of past events and inability to store new memories in the brain)
- Confused mental state (delirium)
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Emotionless
- Abnormal thinking
- Hallucination(misperception)
- Misperceptions (wrong interpretation) 1Deficiency| Researched based study from Nih.gov.
Causes
Causes of vitamin B3 deficiency
Deficiency of Vitamin B3 may occur in following conditions
Chronic Alcoholism
- Excess alcohol intake reduces the body’s ability for essential nutrient absorption It interferes the absorption of vitamin B 3 10Causes| Researched based study from Siencedirect.com
Malnutrition (undernutrition)
Malnutrition is due to insufficient minerals and vitamins, including vitamin B3 and other nutrients. It develops due to
- Unbalanced dietary intake 10Causes| Researched based study from Siencedirect.com
- Overconsumption or little consumption of certain nutrients
Anti Tuberculosis Drugs
- Patient taking Second line drugs(Ethionamide, 6-mercaptopurine) for the treatment of T.B are highly susceptible for B 3 deficiency10Causes| Researched based study from Siencedirect.com
Carcinoid syndrome
- It is a condition due to slow-growing cancer cells in the stomach it converts the diet tryptophan to serotonin instead of vitamin B3 and leads to vitamin B3 deficiency 10Causes| Researched based study from Siencedirect.com.
Toxicity
Vitamin B3 overdose results into
- Skin Flush
- Diarrhea
- Digestive problem
- Stomach abscess (boil)
- Liver problem
- Muscle damage
- Decreases glucose tolerance (ability to dispose of excess glucose from the body) 11Toxicity | Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
- Heart rate problem
- Low blood pressure
- Eye problem 11Toxicity| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Interactions
Interaction of Vitamin B3
Alcohol (ethanol)
Consuming Vitamin B3 and alcohol together may causes
- Increase skin itchiness and flushing (skin redness)
- Increases the risk of liver damage .13Interactions | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Aspirin
- A high dose of aspirin reduces the body’s ability to get rid of excess vitamin B3 .
- It increases the body’s Vitamin B3 concentration and increases the risk of side effects .
Anticoagulants (medicines to slow the blood clotting process)
- Vitamin B3 slows down blood clotting .
- Taking vitamin B3 and anticoagulants together increases the risk of bleeding.13Interactions | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Tetracycline antibiotics
Vitamin B3 should not be taken at the same time as tetracycline.
- It reduces the absorption capacity and minimizes the medicine’s effectiveness
- Moreover, all vitamin B complex medicines act similarly and should not be consumed together with tetracycline medicines.
Blood pressure medication
Vitamin B3 lowers the blood pressure in our bodies taking vitamin B3 and blood pressure medication together
- It further decreases the blood pressure
- It causes light-headedness and fainting
Cholesterol-lowering medication
Bile acid sequestrants (cholesterol-lowering medication) when taken together with vitamin B3
- It decreases the body’s vitamin B3 absorption capacity and decreases its health benefits 13Interactions | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org.
- Such medications are consumed keeping a time gap of around 6 hours
Diabetes medication
- Vitamin B3 consumed in large doses causes a hike in the body’s sugar level
- Vitamin B3 and diabetes medication taken together decrease the medicine’s sugar-lowering effect.12Interactions | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Nicotine patches
- Vitamin B3 occasionally causes light-headedness and skin flush .
- Taking vitamin B3 and nicotine patch together increases the episodes of skin flush and light-headedness .
Allopurinol (gout medicine)
- Vitamin B3 in large doses worsens gout(a type of arthritis disease) by decreasing the medicine’s effect .
Isoniazid
- Isoniazid is a medicine to treat tuberculosis causes vitamin B3 deficiency by reducing its absorption from intestine and also its endogenous synthesis .12Interactions | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Statins
- Taking vitamin B3 and statins together enhances the risk of muscle damage .
Thyroid medicines
- Vitamin B3 decreases the thyroid hormone levels .
- Taking vitamin B3 and thyroid medicines together decreases the effects of the thyroid medication 12Interactions | Researched based study from Nih.gov .
Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin B3 is an essential vitamin of the Vitamin B complex family required by each body part.
- Vitamin B3 can be consumed through a well-balanced diet .
- Vitamin B3 or their supplements are to be consumed under the supervision of a physician .
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Niacin-Fact Sheet for Health Professionals | Overview | Dosage
-
National Library of Medicine
B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy--A Review | Facts | Dosage
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin B3 | Sources
-
National Library of Medicine
Minireview Exploring the Biological Cycle of Vitamin B3 and Its Influence on Oxidative Stress: Further Molecular and Clinical Aspects | Biological role
-
National Library of Medicine
Primary and secondary prevention of Type 1 diabetes | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effect of niacin on lipids and glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled clinical trials | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Role of Niacin in Current Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Nicotinamide riboside restores cognition through an upregulation of proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α regulated β-secretase 1 degradation and mitochondrial gene expression in Alzheimer's mouse models
-
National Library of Medicine
A Phase 3 Randomized Trial of Nicotinamide for Skin-Cancer Chemoprevention | Benefits
-
Science Direct
Niacin | Causes
-
Science Direct
Glucose Tolerance | Toxicity
-
National Institutes of Health
Niacin-Fact Sheet for Consumers | Interactions
-
Mayo Clinic
Niacin | Interactions