Calcium : An Important Mineral

- Calcium
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
About Calcium
The mineral calcium is essential for several processes in the body, like developing and maintaining strong bones, proper muscle functioning, proper blood circulation, etc. Although studies on calcium have mainly concentrated on bone health, recent studies stress other health outcomes. 1Overview | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov The bulk of the calcium stored by the body is in the teeth and bones. The body can better absorb calcium with vitamin D. As a person ages, calcium concentrations decrease.

Functions
Biological Functions of Calcium
Calcium is responsible for several biological processes, some of which include the following:
- Healthy bone maintenance – Helps build bones and gives strength to them.
- Healthy teeth – Plays a major role in healthy teeth formation and maintenance.
- Muscle function – Aids in the contraction and relaxation of muscles.
- Heart beat – Helps the heart to beat in a regular rhythm. 1Biological role | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Nervous system – Aids in the transmission of nerve signals from the brain to various body parts.
- Blood – Helps in the clotting of blood and wound healing. Additionally, intracellular calcium in vascular smooth muscle cells, vasoconstriction, and changes in vascular volume help the blood arteries transport blood throughout the body and control blood pressure. 1Biological role | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Hormones – Assists in the release of hormones and other substances.
Benefits

Health Benefits
Calcium is frequently taken by people to treat the following conditions:
- Heart issues – Arrhythmias brought on by hyperkalemia (high levels of blood potassium) can be reversed by intravenously (IV) administering calcium gluconate. 2Benefits | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Bone problems in adults – The two bone diseases osteoporosis (brittle/weak bones) and Osteomalacia (soft bones) can be improved and fractures can be avoided with calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
- Bone problems in children – Calcium and vitamin D tablets may be used to treat Osteomalacia in children.
- Prevents tooth loss – Supplements high in calcium and vitamin D help older people avoid tooth loss.
- Indigestion – Calcium carbonate when taken orally as an antacid works well for reducing indigestion.
- Kidney – People with kidney failure can manage high phosphate levels in their blood by taking calcium carbonate or calcium acetate. 2Benefits | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Hypocalcemia – Low calcium levels in the blood can be treated and prevented by taking calcium tablets.
- Bone density loss – Oral calcium and vitamin D supplementation appears to slow the loss of bone density in individuals who take corticosteroids for an extended period.
- Hyperparathyroidism – When a person has kidney failure and elevated parathyroid hormone levels, calcium helps in lowering their parathyroid hormone levels.
- High blood pressure – Calcium may help in slightly lowering the blood pressure.
- PMS (Premenstrual syndrome) – Getting enough calcium through food and supplements appears to greatly lessen mood swings, bloating, food cravings, and discomfort. 3Benefits | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- During pregnancy – Taking calcium supplements raises the baby’s bone mineral density, lowers the chance of high blood pressure (pre-eclampsia) associated with pregnancy and preterm birth, and promotes the bone health of both mothers and their unborn children. 4Benefits | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Colorectal cancer – Calcium appears to lower the chance of developing this disease. However, those with low vitamin D levels and those who are obese do not appear to profit from calcium supplements.
Dosage
Dietary requirement
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) refers to the quantity that should be consumed each day. (RDA). 5Dosage | Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov The following are the dietary calcium requirements:
(Note: Mg = milligrams)
In infants
- 0 to 6 months of age – 200 mg/day.
- 7 to 12 months – 260 mg/day.
In children and adolescents (RDA)
- 1 to 3 years – 700 mg/day.
- 4 to 8 years – 1000 mg/day.
- 9 to 18 years – 1300 mg/day.
In adults (RDA)5Dosage | Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- 19 to 50 years – 1000 mg/day.
- 51 to 70 years – Men – 1000 mg/day; Women – 1200 mg/day.
- Over 71 years – 1200 mg/day.
In pregnant and breastfeeding mothers
- 14 to 18 years – 1300 mg/day.
- 19 to 50 years – 1000 mg/day.
An everyday diet should provide people with all the calcium they require.
For adults aged 19 to 50, 2,500 mg of calcium per day is the suggested upper limit. The upper limit for people 51 years and older is 2,000 mg.
Sources
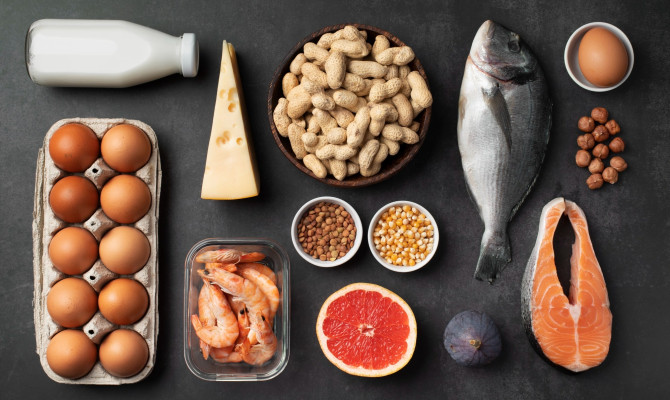
Sources of Calcium
Since our bodies cannot make calcium, we must obtain it from other sources.
Food sources
- Dairy products – Milk, yogurt, cheese, etc. 6Sources | Researched based study from Nih.gov
- Vegetables – green leafy vegetables like okra, spinach, curly kale, broccoli, and Chinese cabbage.
- Fruits – citrus fruit juices fortified.
- Nuts and seeds – almonds, sesame seeds, chia seeds. 7Sources | Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Fishes – Sardines, salmons, etc.
- Calcium-fortified food and beverage – soy products, cereals, fruit juices, milk substitutes, etc.
Supplements
- In addition to calcium carbonate, calcium gluconate, calcium lactate, and calcium citrate are also available as calcium supplements.
- A physician can suggest the best choice based on the patient’s needs, preferences, and any health issues they may have, as well as whether they are currently taking any medications.
Side effects
Side effects of Calcium overdose
If a person consumes more calcium than 1500 mg per day, they may experience adverse effects like,8Side effects | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Abdomen pain.
- Diarrhea.
- Flatulence.
- Constipation.
- Nausea.
Adults aged 19 to 50 have an upper limit (UL) of 2500 mg, and those over 50 have a UL of 2000 mg. There is a greater possibility of experiencing severe side effects if a person takes more than this each day as follows:8Side effects | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Kidney stones.
- Dry mouth.
- Disorientation.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- Heart attack. 8Side effects | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Sometimes death.
Deficiency
Deficiency of Calcium
Calcium deficiency may result in the following
- Reduced bone strength – Osteoporosis or brittle bones, resulting in easy fractures.
- Osteomalacia – Both adults and children may experience bone softening. This occurs when there is a calcium shortage in addition to a vitamin D deficiency.9Deficiency | Researched based study from Nih.gov
- Dental problems – like excess tooth decay, tooth loss, and bone loss in the jaws.
- Mental problems – confusion, memory loss, hallucination, and depression.
- Tingling and numbness in the cheeks, feet, and hands. 9Deficiency | Researched based study from Nih.gov
- Heart problems – abnormal heart rhythms.
- Muscular problems – like cramps, and pain.
- Poor nail health – Weak and brittle nails.
- Consistent pain in the joints.
- Coarse hair and skin diseases.
- Seizure
People at risk of deficiency
The following may increase the risk of having low calcium levels:
- People with lactose intolerance or vegans who refrain from consuming milk or other dairy items.
- Smokers – Compared to non-smokers, smokers absorb less calcium from their stomachs.
- Eating disorders – like anorexia or bulimia.
- Postmenopausal women – there may be decreased ability to absorb and hold onto calcium. Fragile bones may develop over time.
- Digestive disorders – like inflammatory bowel disease or celiac disease can affect calcium absorption.
- The body may excrete more calcium in people who ingest large amounts of sodium or protein.
- Individuals with Vitamin D deficiency, phosphate deficiency, or parathyroid hormone deficiency.
- Some surgical procedures, including removing the stomach.
- Long-term usage of corticosteroids or laxatives.
- Increased consumption of caffeine or alcohol.
- An excessive intake of magnesium.
- People with kidney failure.
- Some cancer.
Precautions
Precautions while taking Calcium
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding mothers – Higher amounts of calcium could make the infant more prone to seizures. Do not forget to take into account the overall calcium consumption from both dietary and supplemental calcium sources.
- Children – Children should not consume more calcium than what they need each day, just enough to meet their needs.
- Achlorhydria (low amounts of stomach acids) – Those who have this condition are recommended to take calcium supplements with meals as they will absorb less calcium if taken on an empty stomach.
- Conditions like parathyroid gland disorders and sarcoidosis – may show elevated levels of blood calcium and one should refrain from taking calcium supplements as these can lead to even higher calcium levels.
- Kidney disorders – Calcium supplementation by people with kidney diseases can lead to excessive calcium levels.
- Stroke – Those who have had a stroke may be more likely to acquire dementia if they take calcium supplements for five or more years.
Without a doctor’s advice, it is not recommended to use calcium supplements if an individual has a heart condition or bone tumors.
Interactions
Interactions of Calcium
Certain medications may interact or interfere with calcium supplements. Here are a few instances:
- Dolutegravir – Dolutegravir’s effects get diminished by taking calcium at the same time. Dolutegravir should be given either two hours before or six hours following calcium ingestion to prevent this interaction. 10Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Elvitegravir – The effects of elvitegravir may be lessened by taking calcium along with it. Elvitegravir should be given two hours before or two hours after calcium to prevent this interaction. 11Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Levothyroxine – a thyroid hormone, is used to treat thyroid tumors and hypothyroidism. When consumed within 4 hours of a calcium carbonate supplement, levothyroxine is poorly absorbed. 12Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Quinolone antibiotics – such as ciprofloxacin, gemifloxacin, and moxifloxacin, are poorly absorbed if consumed within 2 hours of a calcium supplement. 6Interactions | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Outlook
Outlook
It is justified to put forth the effort necessary to follow calcium intake guidelines as it could have a positive impact on an individual’s health. It’s critical to maintain a good calcium intake balance, making sure a person does not get too little or too much calcium each day. This will help them stay healthy and will also help them avoid health problems due to deficiencies or side effects.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Calcium Intake and Health | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
The effect of calcium gluconate in the treatment of hyperkalemia| Health Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effect of calcium on premenstrual syndrome: A double-blind randomized clinical trial | Health benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Calcium: A Nutrient in Pregnancy | Benefits
-
Medline Plus
Calcium in diet | Dosage
-
National Institutes of Health
Calcium-Fact Sheet for Consumers | Sources | Interactions
-
Cleveland Clinic
22 Calcium-Rich Foods | Sources
-
National Library of Medicine
The good, the bad, and the ugly of calcium supplementation: a review of calcium intake on human health | Side effects
-
National Institutes of Health
Calcium-Fact Sheet for Health professional | Deficiency
-
National Library of Medicine
Pharmacokinetics of Dolutegravir When Administered With Mineral Supplements in Healthy Adult Subjects | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
HIV Viral Rebound Due to a Possible Drug–Drug Interaction between Elvitegravir/Cobicistat/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Alafenamide and Calcium-Containing Products | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Calcium carbonate | Interactions