What is Esophagitis: Symptoms, Types, Treatment and Prevention

- Esophagitis
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Esophagitis?
Esophagitis is a medical term that refers to the inflammation or injury to the esophagus, a tube that transports food from one’s mouth to the stomach.1Overview| Researched based study from Cancer.gov Acid reflux, viral or bacterial infections, or adverse drug reactions are the most frequent causes. It could result in pain, chest pain, and nausea. If left untreated, Esophagitis can harm this lining and impair its ability to transport food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
This article will go through the many types of Esophagitis and the symptoms, diagnosis, therapy, prevention, complications, and prognosis.

Symptoms
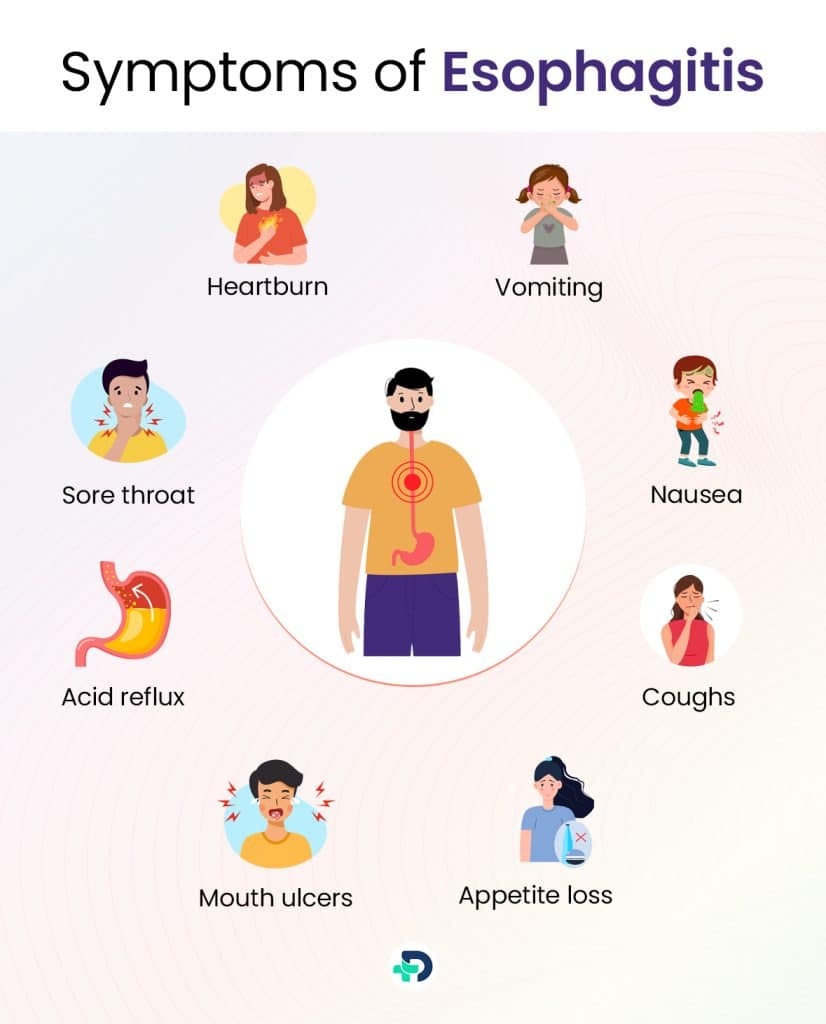
Esophagitis symptoms
The following are some typical esophagitis signs and symptoms:
- Difficult and painful swallowing
- Food trapped in the throat
- Heartburn 2Symptoms| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Sore throat
- Vomiting
- Acid reflux
- Nausea
- Appetite loss
- Mouth ulcers
- Coughs
- Hoarseness
- Regurgitation of food
Symptoms of esophagitis in children
The following symptoms should be reported to a medical expert right away if you or your child experience them:
- Chest pain
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive vomiting (Especially if there is fresh blood in it)
- Dark stool 3Symptoms| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
Either beneath the breastbone in the chest or throat, esophagitis pain may feel heavy, severe, or burning and may worsen just after meals or while lying down.4Symptoms| Researched based study from Harvard.edu
Please visit a doctor if the signs and symptoms do not go away within a few days or get worse over time.
Types
Esophagitis types
Esophagitis can be one of the following forms depending on the cause, including:
- Reflux or erosive Esophagitis
- Infection esophagitis
- Pill induced Esophagitis
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
- Radiation-induced Esophagitis
Reflux or erosive Esophagitis
- Caused by an esophageal mucosal irritation induced by a condition in which stomach contents regularly overflow into the esophagus, mouth, larynx, or lungs.
- One of the illnesses that healthcare personnel see most frequently is reflux esophagitis. 5Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Heartburn and acid reflux are two common symptoms of reflux esophagitis.
Infection esophagitis
- Fungi, yeast, viruses, or bacteria can cause Infectious Esophagitis.
- It can affect anyone, but it is more likely to strike someone with a compromised immune system.6Types| Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Pill-induced Esophagitis
- Esophageal mucosal damage brought on by drugs like NSAIDs, antibiotics, acetaminophen, chemotherapy drugs, etc., is known as drug-induced Esophagitis and often refers to a direct toxic action of the offending agent on the esophageal mucosa.7Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
- The precise cause of EoE is unclear, according to researchers.
- They believe it is an immune/allergic reaction to foods or environmental factors such as dust mites, animal dander, pollen, and fungi.
- Specific genes may cause eoE.8Types| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
Radiation-induced Esophagitis
- Esophageal inflammation brought on by radiation is known as radiation esophagitis.
- People who get radiation cancer therapy, most frequently for breast, lung, and other lymphomas, often experience radiation esophagitis as a side effect.9Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Risk
Who are at risk?
The chance of having Esophagitis can be raised by the following factors:
- A history of allergies or Esophagitis in the family
- Smoking cigarettes
- Alcohol consumption10Risk| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Being obese
- Pregnancy
- Older age
- Frequent vomiting
- Spinal cord injury
- Chest surgery
- A history of allergies
- Weakened immunity
- Excessively huge or fatty meal
- After eating, lying down right away
- Chest radiation treatment.
- Scleroderma is an autoimmune condition.11Risk| Researched based study from Cedar-sinai.org
- Ingesting a tablet without enough or any water.
- Immune disorders, such as HIV/AIDS or some types of cancer.
- Some medications include beta blockers, NSAIDs, antibiotics, and nitrates.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Esophagitis
The diagnosis of Esophagitis involves a medical history, questions about personal habits, and family history, followed by a physical examination and a few diagnostic tests, including:
- Imaging tests – X-rays or a barium swallow may be used to visualize the esophagus and detect abnormalities.
- Endoscopy – to inspect the esophagus.12Diagnosis| Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicne.org
- Biopsy – A small sample of esophageal tissue is collected and analyzed for inflammation or infection.
- Allergy test – Some tests may be carried out to determine whether the patient is allergic to one or more allergens. An exclusion diet, blood test, or skin prick test can be necessary. 13Diagnosis| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Treatment
Treatment of Esophagitis
Esophagitis treatment approach is based on the underlying cause and may include the following options:
- Medications
- Lifestyle changes
Medications
- Medicines to reduce stomach acid production – like antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), can help reduce acid production and alleviate symptoms of Esophagitis caused by reflux.14Treatment| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
- Drugs to fight inflammation – Doctors may recommend swallowing a liquid steroid formula for eosinophilic Esophagitis. Without creating the same adverse effects as taking pills, the mixture coats the esophagus of the user and soothes irritation.
- Medicines to fight infections – may include antifungal, anti-viral, or anti-bacterial drugs to treat Esophagitis caused by fungi, viruses, or bacteria.
Lifestyle changes
- Refrain from using tobacco products and consuming alcohol, which might aggravate your symptoms by irritating your throat.
- Identify and cut out the foods that irritate, cause acid reflux, or cause allergic reactions. Consuming a soft or watery diet to reduce esophageal irritation as it heals.
- Discuss changing esophagitis-causing drugs with your doctor, or consider shifting to a liquid form.
- And if you must take a tablet, always use water to swallow it.
- Eat smaller meals more frequently, particularly at dinner, to lessen acid reflux. Avoid lying down immediately after eating.4Treatment| Researched based study from Harvard.edu
Prevention
Prevention of Esophagitis
To prevent Esophagitis, individuals can take the following measures:
- Maintain a healthy weight and avoid obesity.
- To lower the risk of oral infections, practice good oral hygiene.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Manage underlying conditions like GERD or eosinophilic Esophagitis through lifestyle modifications and medications.
- When consuming pills or drugs, use water to swallow.
Complications
Complications of Esophagitis
If left untreated, Esophagitis can lead to complications, including:
- Bleeding
- Aspiration pneumonitis
- Esophageal strictures 15Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Barrett’s esophagus
- Laryngitis
- Perforation
Prognosis
Prognosis of Esophagitis
The symptoms can be reduced and the prognosis improved with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, most cases of Esophagitis start getting healed. However, the full recovery from Esophagitis can take three to six weeks. The underlying reason and the way the individual responds to treatment will determine the long-term prospects. If you experience persistent symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Cancer Institute
esophagitis | Overview
-
Medline Plus
Esophagitis | Symptoms
-
Cleveland Clinic
Melena (Black Stool) | Symptoms
-
Harvard Health Publishing
Esophagitis | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Reflux Esophagitis | Types
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Infectious Esophagitis | Types
-
National Library of Medicine
Drug-Induced Esophagitis | Types
-
Medline Plus
Eosinophilic Esophagitis | Types
-
National Library of Medicine
Radiation Esophagitis | Types
-
Mayo Clinic
Esophagitis | Risk factors
-
Cedars-Sinai
Esophagitis | Risk factors
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Esophagitis | Diagnosis
-
Mayo Clinic
Eosinophilic esophagitis | Diagnosis
-
Mount Sinai
Esophagitis | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Esophagitis | Complications