Epithelial Cell Abnormality – Everything You Need To Know About

- Epithelium
- 28 Sep 2023
Overview
Healthy Epithelial Cells
Epithelial cells are an important part of the human body, but they can sometimes change in bizarre ways. This can cause concerns with your health. There could be a genetic cause, an external cause, or a social cause. Symptoms vary, but they can include blood that can’t be explained, growths, lumps, or pain that won’t go away.

Is your skin or mucous tissue going through strange changes right now? Are you worried about what might cause epithelium cell problems and what will work to fix them? Look no further, because we’re going to learn everything we can about this common illness that affects millions of people around the world.
So, don’t wait. Take care of your health and talk to a doctor about any worries or questions you have. Your health is important! Don’t discount the power of bad epithelium cells. They’re the rebels that mess up the body’s perfectly planned balance.
Epithelial Cell
Epithelial Cell: What is it?
Epithelial cells 1 Epithelial Cell | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health are a type of cell that make up the epithelium, which is a tissue that covers the outer part of many organs, spaces, and structures in the body.
Epithelial tissue acts as a filter to keep things out, helps with absorption and release, and is very important for keeping different body systems healthy and working. Epithelial cells are found in the skin, the breathing system, the digestive system, the urine system, and other places.
Here are a few important features about epithelial cells:
Cellular Arrangement:
- Epithelial cells are close together and make smooth layers. There is usually very little or no connection between them. Tight joints are special features that link them together in a close way.
Shape of the Cell:
- Epithelial cells can be squamous, which means they are flat and look like scales, cuboidal, which means they look like cubes, or columnar, which means they are tall and rectangular. Most of the time, the form of the cells matches the role of the tissue they are in.
Function:
- Epithelial cells form a shield that keeps germs, dangerous substances, and damage from getting to the organs below. They can also help with intake, release, and feeling what’s going on around them.
Polarity:
- Epithelial cells are polarized, which means that different parts of the cell have different jobs. The apical surface faces the outside world or a body space. It may have microvilli or cilia, which are special structures. A basement membrane holds the bottom surface to the flesh below it.
Types of epithelium:
- Based on how they are built and what they do, there are different types of epithelium. For example, simple squamous epithelium lines blood vessels and air sacs in the lungs, while stratified squamous epithelium makes up the top layer of the skin.
Variations:
- Some epithelial cells are changed so that they can do specific jobs. For example, goblet cells are specialized epithelial cells that make mucus in the gut and breathing systems.
Cancer:
- As was said in the last answer, epithelial cells can change in strange ways. These changes can be anything from small problems to major diseases like cancer. Regular tests and checkups with a doctor can help find and treat these problems.
Abnormality
Epithelial Cell Abnormality: What is it?
An abnormality of an epithelial cell 2 Epithelial Cell Abnormality| Researched based study from National Institutes of Health is any change from the normal look, shape, or action of an epithelial cell. Epithelial cells are known as the backbone of epithelial tissues. If these cells aren’t working right, it could be a sign of inflammation, an infection, precancerous changes, or even cancer.
When epithelial cells are looked at under a microscope, some differences may be seen, some of these things can be:
- Changes in the size and shape of cells: Epithelial cells may get bigger, smaller, more curved, or have a different form than they would normally.
- Disorganized Arrangement: The way epithelial cells are usually arranged in layers can get messed up, giving the skin a messy look.
- Increased ratio of nuclei to cytoplasm: In abnormal cells, the nucleus, which houses the genes, may look bigger than the cytoplasm.
- Nuclear Abnormalities: If the form, size, or pattern of coloring of the cell nucleus isn’t right, it can be a sign of deeper problems.
- Increased cell division: Epithelial cells can divide quickly and out of control, which is a sign that is often linked to cancer.
- Hyperplasia: It is when the number of epithelial cells grows, which makes the tissue thicker.
- Dysplasia: Changes in the size, shape, and organization of cells that are not normal and can be a sign of a precancerous disease.
- Metaplasia: It is when one type of epithelial cell changes into a different type. This could be a sign of tissue damage or inflammation.
- Carcinoma in situ: It is a severe form of dysplasia that affects the whole epithelium but hasn’t spread to deeper organs yet.
The clinical importance depends a lot on how odd something is and where it is found. More medical tests, like biopsies, genetic studies, and images, are often done to find out what the abnormalities are and what they might mean.
If an abnormality in the epithelial cells is found, doctors will decide what to do next. Depending on the specific results and the patient’s medical background, this may include close tracking, more testing, treatment, or intervention. Regular screenings and talks with health care workers are important for finding health problems early and treating them correctly.
Causes
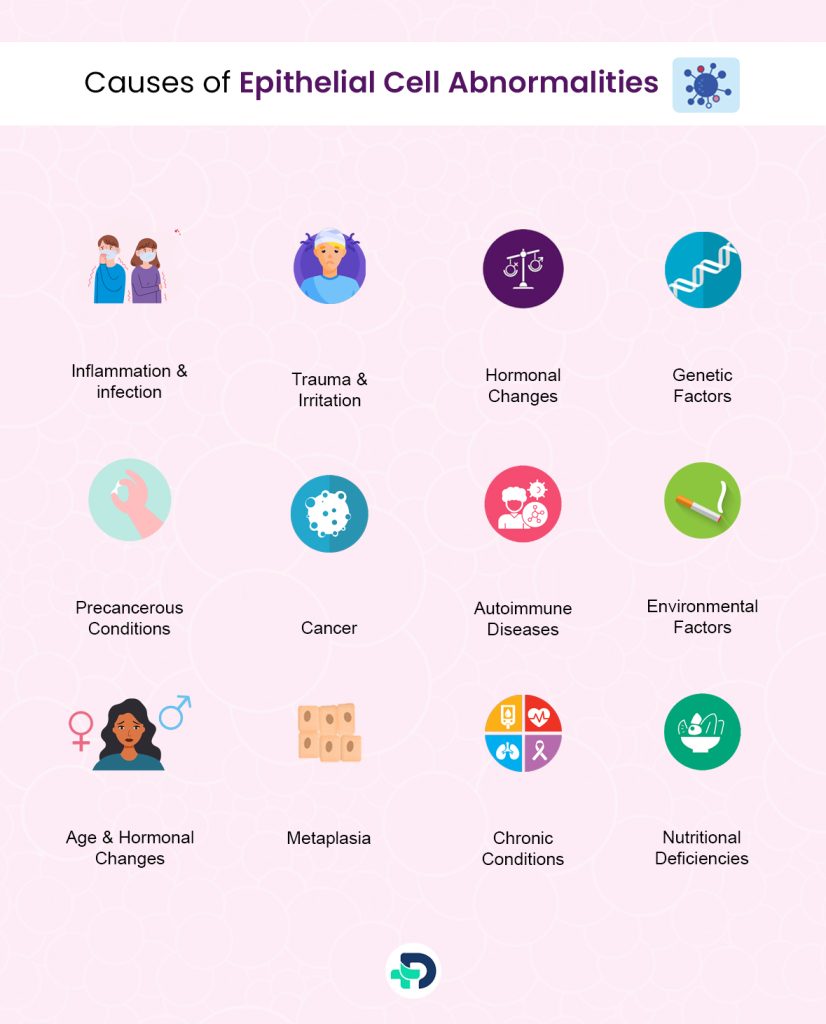
Causes of Epithelial Cell Abnormalities
Epithelial cell problems can be caused by a wide range of things, from harmless and easily fixed conditions to more important problems. Here are some of the most common reasons why epithelial cells don’t behave as they should:
Inflammation and infection:
- Long-term inflammation can change the way epithelium cells look and how they work. When bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites cause an illness, the body’s reaction is to change the cells.
Trauma and Irritation:
- A physical injury, contact to chemicals, or long-term inflammation can change the epithelium cells in the area.
Hormonal Changes:
- Hormonal changes, like those that happen during pregnancy or because of some medical conditions, can affect epithelial cells, especially in the reproductive system.
Genetic Factors:
- Genetic mutations can cause epithelial cells to grow and change in ways that aren’t normal. This can rise the chance of diseases and cancers.
Precancerous Conditions:
- Conditions like dysplasia, which is when cells grow in the wrong way, can lead to cancer. When epithelial cells aren’t working right, it could mean that a person is more likely to get cancer.
Cancer:
- Epithelial cells that change into cancerous cells can cause cancer. Different sorts of carcinomas may result from this, depending on the type of tissue that is harmed.
Autoimmune Diseases:
- Autoimmune diseases can cause the immune system to attack epithelial cells, which can damage them and make them behave in unusual ways.
Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke, certain chemicals, and radiation can change the way epithelial cells work, which can lead to cancer.
Age and Hormonal Changes:
- Age and hormonal changes, like menopause, can change the way epithelial cells look and how they work.
Metaplasia:
- In metaplasia, one type of epithelial tissue changes into a different type. This is often caused by long-term pain or inflammation.
Chronic Conditions:
- Conditions that last for a long time, like gastric reflux disease (GERD), can cause discomfort and changes in the epithelial cells of the area that is affected.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
- If you don’t get enough food, the shape and function of your cells, including epithelium cells, can change.
Immunodeficiency:
- When the immune system is weak, diseases that damage epithelial cells can spread more easily.
Even though these are some common reasons, it’s important to remember that the exact causes can change based on where the epithelial tissue is, the person’s health history, and other things. If you think you have epithelial cell problems or have been told you do, it’s important to talk to a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis, the right treatment, and personalized advice.
Symptoms
Signs & Symptoms of Epithelial Cell Abnormalities
The signs and symptoms of abnormal epithelial cells can vary based on where the affected tissue is and what is causing it. Even in the early stages, not all problems with epithelial cells will show up as signs.
But if any of the following signs and symptoms are present, it could mean that something is wrong with the epithelial cells:
Changes in the skin:
- Sores, bumps, or changes in scars.
- Wounds or sores that get worse.
- Spots on the face that change color, size, or shape.
Respiratory system:
- Coughing or wheezing
- Difficulty in Breathing
- Coughing up blood.
- Hoarse voice .
Digestive system:
- Continual stomach pain or soreness.
- Changes in bowel, like diarrhea, constipation, or blood in your stools.
- Trouble eating
- Heartburn that doesn’t go away.
Blood in the urine (Urinary Tract):
- Changes in frequency or urgency to pee.
- Pain or trouble while urinating.
Problems with the reproductive system:
- spotting or blood between periods.
- Changes in the vaginal discharge.
- Pain in the pelvis.
- Breast tissue changes.
Mouth:
- Sores, lumps, or white or red spots.
- Trouble swallowing or a sore throat that won’t go away.
Eyes:
- Changes in vision.
- Redness or discomfort of the eyes.
Nasal cavity:
- Nasal stuffiness or bleeding.
- Changes in the ability to smell.
Gastrointestinal tract:
- Pain or soreness in the stomach.
- Change in appetite.
- Weight loss for no clear reason.
Genital and Anal regions:
- Skin color changes in the groin or anal areas.
- Itching, pain, or burning.
It’s important to remember that many of these symptoms can be caused by things other than abnormal epithelial cells, like infections, inflammation, or harmless growths. But if you have symptoms that don’t go away or are weird, you need to see a doctor to get a good review and diagnosis. Better results can be observed with early diagnosis and the right medical care.
Types
Types of Epithelial Cell Abnormalities:
Epithelial cell abnormalities can show up in different ways based on where and what the damaged tissue does 3 Types | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health . These problems can range from minor changes to more serious ones that need medical help. Here are some types of abnormal epithelial cells and the symptoms that go with them:
Hypertrophy:
- Increased cell growth and division, which leads to thickness of the tissue.
- Signs: The cells may be closer together and more crowded than usual.
Metastasis:
- This is when one type of epithelial cell transforms into another type.
- Characteristics: Cells that have been changed may look and work differently than regular cells.
Diffuse dysplasia:
- Cells that grow and mature in a way that isn’t normal and could lead to cancer.
- Cells can be different sizes, shapes, and ways of being organized, and their nuclei can also be different.
Precancerous :
- This is a severe form of dysplasia in which abnormal cells are present but haven’t spread to other parts of the body.
- There are abnormal cells all the way through the epithelium.
SIL (Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion):
- This is when squamous cells on surfaces like the cervix grow in a way that isn’t normal.
- It Can be mild (dysplasia) or serious (severe dysplasia or cancer in situ).
- Depending on how probable it is that they may cause cancer, they are divided into different categories. After SIL is found, a doctor or nurse will generally suggest a colposcopy or biopsy to find out how dangerous the cell is.
Atypical Hyperplasia:
- This means that there are too many cells with distortion.
- Cells look abnormal, but they are not dangerous. This is called a precancerous state.
Adenomas:
- This is a benign tumor of glandular tissue that can cause cells to grow in the wrong way.
- The tumor has cells that are different from regular salivary cells.
Papilloma:
- This is a harmless growth that sticks out from the surface of epithelial cells.
- Cells may be a little abnormal, but that doesn’t mean they are harmful.
Squamous Cell Cancer:
- It is A cancerous growth composed of squamous epithelial cells.
- Tumor cells may invade nearby tissues and spread to other areas of the body.
Cancer of the Adenocarcinoma:
- It is A cancerous growth made up of swollen epithelial cells.
- Invading adjacent organs, tumor cells have the potential to spread to other bodily regions.
- This is a rare type of cancer that affects glandular cells instead of squamous cells. It is related to squamous cell cancer. When squamous cell cancer is found, doctors usually order more tests to find out how far along the cancer is. Only then do they start treatment.
Basal Cell Cancer:
- The basal cells of the epidermis are the site of origin for this typical kind of skin cancer.
- Usually looks like a slow-growing, swollen, shiny bump with a hole in the middle.
Melanomas:
- This is a cancerous growth that starts in the cells of the skin that make colour, called melanocytes.
- Itt can be very active and spread to other parts of the body.
Epithelial Cell Abnormality in Cervix:
Cervical dysplasia is another name for when abnormal cells are found on the cervix.
A Pap test can find abnormal epithelial cells and cancer of the cervix.
Pap Smear
What is a Pap Smear?
- In the 1920s, a gynecologist named George Papanicolaou came up with the Pap test, also called the Pap smear 4 Pap Smear | Researched based study from American Cancer Society .
- During his study, Papanicolaou found that the normality of epithelial cells in smears from the vagina and cervix looked different when looked at under a microscope. His finding showed that tumor cells can be found in women before they show any signs.
- The Pap test is now a standard part of a woman’s regular physical exam.
- It assists medical professionals in monitoring any cells that are precancerous or cancerous on the cervix that can develop into cervical cancer.
A Pap Smear test can give one of three results: Normal,Unclear or Abnormal
- Normal: It means that no cell changes or signs of cancer were found.
- Unclear: When it’s not clear, a Pap test is often needed again. This means that your cells might be a little bit off, which could be caused by a vaginal or sexually transmitted infection, a change in hormones, or a bad test.
- Abnormal: An abnormal pap test means that some changes were found in the cells of the cervix. It does not mean you have cervical cancer, but you must get checked out more.
Abnormal Pap test results:
The Pap test is a screening test that tells you if something is wrong in different ways. The following table shows, from least to most severe, how bad these results are:
| Degree of severity | Pap test result |
| 0 | Normal |
| 1 | ASC-US |
| 2 | LSIL |
| 3 | ASC-H |
| 4 | HSIL |
| 5 | AIS |
| 6 | Squamous carcinoma |
Breakdown of an Abnormal Result:
Here is a list of Pap test results 1 Pap Smear Results | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health from that are not normal:
ASC-US stands for Atypical Squamous Cells of Unknown Significance:
- This is the most common negative Pap test result. ASC-US means that the cervix’s squamous cells don’t look right. Most likely, this is caused by an HPV virus. Most of the time, the cells go back to normal on their own, but your doctor will probably want to keep an eye on them just to be safe.
Atypical Glandular Cells (AGC):
- This finding is different from the others because it is about glandular cells, not squamous cells. These glandular cells make the mucus in the cervix and the mucus in the uterus.
- An AGC test shows that there are problems with the glandular cells of the cervix, which makes it possible that there are precancerous or cancerous cells. More tests and keeping an eye on things will be suggested.
Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (LSIL):
- This means you have mild cervical dysplasia, which is a form of abnormal tissue that could be the first sign of cancer. Most likely, an HPV virus caused these changes. Most of the time, these differences go back to normal over time, but they need to be watched. This could also be called CIN 1, which stands for cervical intraepithelial cancer.
(ASC-H) Atypical Squamous Cells:
- Another type of odd cell that is likely to be HSIL is atypical squamous cells. To know for sure, more tests need to be done.
High-grade Intraepithelial Squamous Lesions (HSIL):
- This finding shows that the dysplasia is mild to serious. There is an HPV illness that is getting worse and spreading. Even though this is not cancer yet, if it is not treated, it is more likely to develop into cancer.
- With the right kind of help and care, it might go back to normal. A CIN 2 or 3 would be right for this.
In Situ Adenocarcinoma (AIS):
- This means that an advanced disease was found that has a high chance of turning into cancer if it is not treated. At this point, it is very important to stop cervical cancer from getting worse. This would be a CIN 3 situation.
Squamous Carcinoma:
- If a test for squamous carcinoma shows cancer, the person has cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma, a form of cancer, is to blame for 80% of all cervical malignancies.
- At this point, the precancerous cells have turned into cancer and need more treatment, such as surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or other immunotherapies.
- Squamous is not a very common finding. Women who get regular Pap tests will find changes in their cervical cells before they turn into cancer. It is very rare that they will get to this stage without knowing it.
How do you treat cervical cells that aren’t normal?
- Depending on how bad the problem is, your doctor will tell you to watch it or get treatment. Most treatments include excisional and ablative procedures in which cervical tissue is cut out or burned away.
- The most popular excisional methods are Loop electrosurgical excision process (LEEP) and Conization. LEEP gets rid of abnormal cells by sending an electric current through a tiny wire loop.
- Conization takes out a piece of the cervix in the shape of a cone that has abnormal cells. The most popular ablative methods are cryotherapy and laser.
What is epithelial cell abnormality in pregnancy?
Epithelial cell abnormalities in pregnancy can refer to a number of changes or flaws that can be seen in the epithelial cells of certain organs during pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman’s hormones change, her body changes, and her immune system changes. All of these things can cause these changes.
Even though many of these changes are standard and to be expected, some of them may be strange and need to be checked out by a doctor. Here are just a few:
Epithelial changes in the cervix:
- As a result of changes in hormones, the cervix changes during pregnancy. Some of these changes are an increase in the number of salivary cells and small changes to the structure.
- During regular cervical checks (Pap smears) for pregnant women, changes in the epithelium of the cervix, such as squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL) or unusual glandular cells, are often found.
- These results may need more testing, but they are often taken care of with follow-up care after pregnancy.
Changes in the breast epithelial cells:
- During pregnancy, the breast tissue changes a lot to get ready for breastfeeding. Epithelial cells that line the milk ducts multiply, and the ducts can get bigger.
- In some cases, these changes can lead to growths or lumps that are harmless, like fibroadenomas or cysts, which may need to be watched or treated.
Changes in the vaginal epithelium:
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause changes in the vaginal epithelium. This could lead to more vaginal flow and changes in the pH level of the vaginal fluid.
- Epithelial changes could also be caused by infections or irritations in the vaginal area.
Changes in the skin’s cells:
- Due to changes in hormones, pregnancy can cause changes to the skin, such as melasma (darkening of the skin) or the appearance of stretch lines. There could also be growths on the skin or changes in scars, which might need to be looked at.
As part of routine pregnancy care, epithelial cell changes are watched for and dealt with if there are any worries about the mother or baby’s health.
Does epithelial cell abnormality mean cancer?
- No, defects in epithelial cells do not always mean cancer. Epithelial cell defects are changes in how the cells look, how they are built, or how they act.
- The cells that line the outside of the body’s organs and tissues are known as epithelial cells.
- Some defects in epithelial cells are linked to precancerous or cancerous conditions, but many of them are harmless and may be caused by illnesses, inflammation, hormonal changes, or other things.
- It’s important to know that epithelial cells can go through a range of changes, from small ones that can be fixed to more major ones that could be signs of a pre-cancerous state or cancer. Healthcare workers use different medical tests and reviews to figure out what’s wrong and what it means.
Epithelial cell abnormality but hpv negative:
There are many things that can lead to abnormal epithelial cells. Although it’s not the only one, the human papillomavirus (HPV) is a frequent source of aberrant cervical cells.
Even if HPV tests come back clear, epithelial cells can still be messed up. Here are some of the reasons why:
- Other diseases: Other types of viruses besides HPV can also cause changes in the way epithelial cells work. Changes in the way cells look can also be caused by diseases with bacteria or fungi.
- Non-infectious causes: Inflammation, changes in hormones, and other non-infectious things can lead to abnormalities in epithelium cells.
- Collection of samples: The results of a Pap smear or other tests can be affected by the quality of the cell sample taken. Sometimes, there might not be enough odd cells in the sample to find.
- Different kinds of HPV: HPV testing 6 HPV Testing | Researched based study from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and usually focuses on the types of the virus that are most strongly linked to cervical cancer and have a high risk of causing it. It might not be found if you have a low-risk strain or one that isn’t checked for.
- False Negative: False-negative results can happen with any medical test. This is when the test doesn’t pick up something that is there. This can happen for a number of reasons, like when the test was done in relation to the problem.
- Other risks: Epithelial cell problems can also be caused by things like smoking, a weakened immune system, and other health problems.
Can epithelial cells repair themselves?
- Yes, epithelial cells can fix and replace themselves, especially when they are hurt or damaged in small ways.
- Epithelial tissues, which cover many body areas and spaces, are always open to the environment, physical stress, and the possibility of damage. In order to keep doing their job as safe shields, these cells have found ways to fix themselves and grow back.
Duration it takes to repair epithelial cell abnormality depends on:
- Movement of cells: When an injury kills epithelial cells, healthy cells from nearby start to move in and cover the area. This helps the cut or damaged area heal faster.
- The division of cells: At the edges of the damaged area, healthy epithelial cells divide more quickly to replace the lost or damaged cells. This split helps bring the thickness and shape of the tissue back to normal.
- Differentiation: As the new cells multiply, they go through a process called “differentiation,” which helps them take on the properties of the tissue they are replacing. This makes sure that the mended tissue works the way it should.
- Tight Junction: Tight junctions hold epithelial cells together, which helps keep the structure of the tissue. During healing, these connections are put back together to recover the protective function of the tissue.
- The making of extracellular matrix: In some cases, damaged epithelial tissue may need help from the extracellular matrix, which is a structure that looks like a framework and helps guide cell movement and tissue healing.
Overall, the ability of epithelial cells to fix themselves is important for keeping different organs in the body healthy and working. But it’s important to get the right care, stay away from things in the surroundings that could be dangerous, and get medical help right away if you need it.
Treatment
Treatment of Epithelial Cell Abnormalities
Epithelial cell abnormalities can be treated in different ways, depending on where the abnormal cells are, how bad they are, what’s causing them, and how healthy the patient is generally. There are many ways to treat someone, from just watching and waiting to doing more. Here are some popular ways to fix problems with epithelial cells:
- Observation and Tracking: For weak or low-grade problems that don’t seem to be a big deal right away, doctors might suggest regular monitoring and follow-up to see if anything changes.
- Medical Treatment: If the changes are caused by illnesses or conditions that cause inflammation, you might be given antibiotics or antifungals to treat the underlying cause.
- Surgical Procedures: In some cases, abnormal cells may need to be removed or fixed with surgery. Procedures like ablation, freezing, laser treatment, and electrocautery can be used for this.
- Catheterization: It is the process of destroying or removing abnormal tissue by using heat or electricity. It can be used to treat certain growths and sores.
- Cryotherapy: In cryotherapy, abnormal tissue is killed by freezing it, often with liquid nitrogen. It is often used for tumors that could turn into cancer. When it is very cold, the cells freeze and finally fall off, making room for new, healthy cells to grow in their place.
- Laser Treatment: In laser treatment, directed rays of light are used to find and kill abnormal cells. It may be used to treat a variety of gastrointestinal and skin issues. The laser’s extreme heat kills the cells, which makes it easier for the tissue to heal and grow back. Laser surgery can be especially helpful for treating epithelial cell problems in places that are sensitive or hard to get to.
- Medication: In some cases, abnormal growths or changes can be treated by putting a topical medicine directly on the area.
- Hormone treatment: Certain tissue problems that are caused by changes in hormones, especially in the reproductive system, can be treated with hormone treatment.
- Chemotherapy: If there are signs of cancer, chemotherapy drugs may be used to find and kill abnormal cells, either by themselves or in combination with other treatments.
- Radiation treatment: High-energy beams are used in radiation treatment to find and kill diseased or precancerous cells. It is often used for problems that go deeper.
- Targeted Therapies: Therapies that directly target certain chemicals or processes involved in abnormal cell growth may be used for some cancerous abnormalities.
- Surgical Excision: In cases where there is a high chance of cancer, the affected area might be removed by cutting out the abnormal tissue.
- Electrocautery: An electric current is used to heat and kill the abnormal cells in electrocautery. This method is often used to treat epithelium cell problems on the skin, like warts or small tumors. The abnormal cells are burned and killed by the electric current, which helps the body heal.
Prevention
Prevention of Epithelial Cell Abnormality
Epithelial cells protect our interior and exterior surfaces against infection and dehydration. Their importance to our health cannot be emphasized.
However, aberrant epithelial cells may cause several health issues.
Daily preventative measures protect our epithelial cells and reduce the danger of problems.
Promoting epithelial health with these practical tips:
- Hygiene: Prevent epithelial cell abnormalities by practicing adequate hygiene. Washing your hands regularly removes hazardous bacteria that might damage cells. Awareness of your surroundings and avoidance of contaminated surfaces and items further minimizes infection risk.
- Stay safe: Do not expose yourself to dangerous substances: Avoid hazardous compounds that may injure epithelial cells. Tobacco, air pollution, and harmful chemicals must be avoided. To avoid exposure, utilize protective gear while working with dangerous products.
- Enjoy a healthy diet: Healthy eating is vital for epithelial cell health. Nutrient-rich diets, especially fruits and vegetables, contain vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote epithelial cell function.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise improves epithelial cell health and general well-being. Exercise strengthens the body, particularly epithelial tissue, and promotes cell health. Physical exercise reduces stress, which may cause epithelial cell abnormalities.
These precautions may help epithelial cells stay healthy and limit the possibility of abnormalities. Practicing excellent hygiene, limiting exposure to dangerous chemicals, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly helps epithelial cells stay healthy.
Conclusion
Epithelial Cell Abnormality – Prognosis
The prognosis for abnormalities of epithelial cells relies on the particular abnormality and its stage of development. Some anomalies, particularly malignant ones, could need continuing care and therapy to keep the condition under control. The prognosis is much better in non-cancerous situations, and with the right therapies, the anomaly may frequently be successfully treated or controlled.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Epithelial Cell
-
National Institutes of Health
Epithelial Cell Abnormality
-
National Institutes of Health
Types
-
American Cancer Society
Pap Smear
-
National Institutes of Health
Pap Smear Results
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
HPV Testing