Magnesium and its Health benefits

- Magnesium
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a vital plentiful mineral in our body. It is crucial for the brain, bone functioning, and overall body fitness. It is found in a variety of natural foods.1Overview| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Facts of magnesium
- Magnesium stands fourth among the most abundant mineral in our body
- Around half of the body’s magnesium is in our bones.
- Magnesium is required in around 600 enzymatic reactions of our body
- Magnesium is available in fortified products and as health supplements2Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
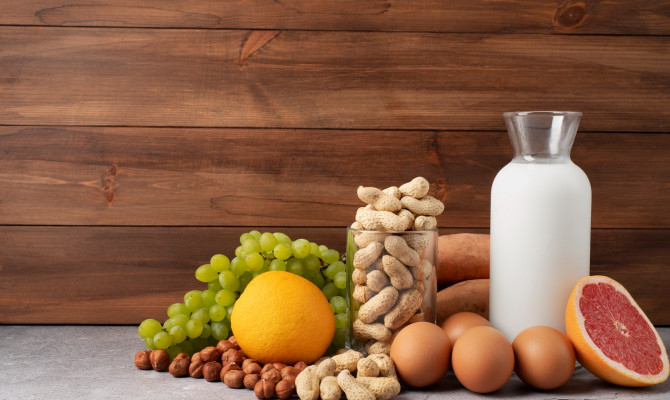
Sources
Sources of magnesium
Plant sources
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Potato
- Pumpkin seeds
- Peanuts
- Black beans
- Kidney beans
- Carrot
- Soymilk
- White rice
- Brown rice
- Papaya
- Avocado
- Almond
- Cashew
- Apple
- Banana
- Blackberries
- Dried figs
- Fortified cereals
- Whole wheat bread
- Oatmeal
- Raisins
- Dark chocolate
Animal sources
- Salmon
- Milk
- Chicken breast
- Beef
- Dairy products
- Yogurt
Natural sources
- Normal tap water
- Packaged mineral water1Sources| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Dosage
Dosage of magnesium
The recommended daily intake of magnesium in different age groups is as follows
Children
- Age 1-3 years-80 mg
- Age 4-8 years-130 mg
- Age 9-13 years-240 mg
Adolescent
Age 14-18 years
- Male- 410mg
- Female-360 mg
Adults
Age 19-30 years
- Male – 400 mg
- Female- 310 mg
Age 31-50 years
- Male- 420 mg
- Female- 320 mg
Age 51 years and above
- Male-420 mg
- Female-320 mg
Pregnant woman
- Age below 19 years-400 mg
- Age 19 -30 years-350 mg
- Age 31 years and above- 360 mg
Nursing mothers
- Age below 19 years- 360 mg
- Age 19-30 years- 310 mg
- Age 31 years and above- 320 mg3Dosage| Researched based study from Nih.gov
Benefits

Benefits of magnesium in our body
In regulating body functions
- Magnesium is involved in DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA(ribonucleic acid)synthesis and bone development.
- It participates in the creation of energy.
- It plays a vital role in the transport of potassium and calcium across cell membranes.
- It maintains a regular heartbeat, muscle contraction, and nerve impulses, i.e., sending sensation to the brain following external stimulation.
- It nullifies the stomach acid and helps in passing stool through the intestine.
Regulates blood sugar
- It decreases the risk of type 2 diabetes
- It increases insulin sensitivity (the body can utilize the blood glucose effectively)4Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Help fight depression
- Magnesium reduces the symptoms of depression5Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- It enhances the mood
Prevent migraine attacks
- It prevents migraine attacks
- It relieves the severe migraine headache quickly6Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhances exercise performance
- It increases muscle mass and energy
- It improves the body’s movement7Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Increases the anti-inflammatory effect
- It reduces oxidative stress in the body
- It decreases the markers of inflammation (Markers of inflammation viz; C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 increase during any body injury)8Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhances bone health
- It increases the bone mineral density
- It decreases the risk of bone fractures9Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhances heart health
- Magnesium lowers the blood pressure
- It lowers the risk of stroke (bleeding in the brain’s blood vessels)10Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Improves premenstrual symptoms
- Magnesium reduces abdominal pain
- It decreases migraine attacks
- It decreases anxiety and depression
However, more research is warranted to prove the effect of magnesium on premenstrual symptoms.11Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Decreases anxiety
- It decreases the symptoms of anxiety
- It decreases stress and nervousness 12Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Promotes good sleep
- It improves the sleep quality
- It decreases the time to fall asleep13Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Side effects
Side effects of magnesium
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Electrolyte(body minerals) imbalance14Side effects | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Overdose
Overdose toxicity of magnesium
- Extreme tiredness
- Depression
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stomach pain
- Low blood pressure
- Kidney problem
- Breathing difficulty
- Loss of central nervous system control
- Confusion
- Cardiac arrest (heart suddenly stops pumping blood around the body)
- Coma( prolonged loss of body consciousness)
- Death15Overdose | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency
Deficiency symptoms
- Extreme tiredness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Appetite loss
- Sleep difficulty
Severe deficiency causes
- Itchiness
- Muscle pain
- Irregular heartbeat
- Seizures (uncontrolled body shaking)
- Loss of sensation in body parts
- Personality changes16Deficiency| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
People prone to magnesium deficiency
People with the following health condition are prone to magnesium deficiency.
- Aged people
- Kidney disease
- Heart disease
- Parathyroid disorder (abnormal calcium level in blood)
- Crohn’s disease (a disease causing swelling and pain in the digestive tract)
- Migraine (headache)
- Alcoholism(addicted to alcohol)
- Diabetes(high blood sugar)
- Alzheimer’s disease(a brain disease causing memory loss)
- Gastrointestinal disorders(diseases involving the digestive tract)
- Cancer (abnormal cell growth in the body)17Deficiency | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Interactions
Drug interaction with magnesium
Levodopa
- Levodopa is used for treating Parkinson’s disease
- Taking magnesium oxide with levodopa decreases the efficiency of the drug
Tetracycline antibiotic
- Taking magnesium and tetracycline togetherdecreases the body’s absorption capacity and reduces the effectiveness of the drug
- So, one must take tetracycline antibiotics 2 hours before or 6 hours after magnesium consumption.
Quinolone antibiotic
- Taking magnesium and quinolone together decreases the body’s absorption capacity and reduces the efficiency of the quinolone
- So quinolone must be consumed 2 hours before or 5-6 hours after magnesium consumption.
Aminoglycoside antibiotic
- Taking magnesium and aminoglycoside together causes muscle problem
Bisphosphonates
- Taking magnesium and bisphosphonates together reduces the blood levels of biphosphonates and minimizes the bisphosphonate’s effectiveness
- So, bisphosphonates should be consumed 2hours before magnesium consumption
Muscle relaxant
- Magnesium relaxes the muscles
- So consuming magnesium and muscle relaxant together increases the side effect of the drug
Anticoagulant (blood thinning medicine)
- Magnesium delays the blood clotting
- Taking magnesium and anticoagulant together increases the risk of profuse bleeding
Water pills
- Water pills increase the magnesium in the body
- Taking magnesium and water pills together can lead to excess magnesium in the body
Calcium channel blockers
- Calcium channel blockers are used to treat high blood pressures. they obstruct calcium from entering the cells
- Magnesium also blocks calcium from entering the cells
- Taking magnesium and Calcium channel blockers together might cause an excessive decrease in blood pressure
Lanoxin
- Lanoxin is used to treat irregular heartbeat
- Taking magnesium and linoxin together decreases the lanoxin levels in the blood and reduces the effect of the drug
Diabetes medication
- Taking magnesium and diabetes medication together increases the blood levels of diabetic medicine hence increases the risk of low blood sugar
Antacids
- Taking magnesium and antacid together decreases the laxative effect of magnesium
Gabapentin
- Taking magnesium and gabapentin together decreases the body’s absorption capacity and reduces the drug’s effectiveness
- So, gabapentin must be consumed 2 hours before or 6 hours after magnesium consumption.
Ketamine
- Taking high doses of magnesium and ketamine together increases the side effects of the drug
Sevelamer
- Taking magnesium and sevelamer together increases the risk of very high magnesium levels in the body18Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Interaction with other supplements
Calcium tablet
- Taking magnesium and calcium together reduces the body’s capacity to absorb calcium
Multivitamin supplement containing iron and zinc
- Taking magnesium and multivitamin with iron and zinc decreases the absorption of iron and zinc in the body19Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- It reduces the efficiency of the multivitamin supplement
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium is an essential macronutrient in many bodily processes such as nerve, muscle, and bone.
- Magnesium deficiencies can lead to several health problems
- Magnesium supplements are available in health stores for magnesium-deficient individuals
- One should always consult a physician before including magnesium supplements in their diet to get the correct dose and to avoid the risk of overdose
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Magnesium in Disease Prevention and Overall Health | Overview | Sources
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium in man: implications for health and disease | Overview
-
National Institutes of Health
Magnesium-Fact Sheet for Health Professionals | Dosage
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium Intake, Quality of Carbohydrates, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Results From Three U.S. Cohorts | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effect of magnesium supplementation on depression status in depressed patients with magnesium deficiency: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Comparison of therapeutic effects of magnesium sulfate vs. dexamethasone/metoclopramide on alleviating acute migraine headache | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Dietary Magnesium Is Positively Associated With Skeletal Muscle Power and Indices of Muscle Mass and May Attenuate the Association Between Circulating C-Reactive Protein and Muscle Mass in Women | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Plasma C-reactive Protein Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Impact of magnesium on bone health in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of Magnesium and Vitamin B6 on the Severity of Premenstrual Syndrome Symptoms' | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Role of magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression: A randomized clinical trial | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Association of magnesium intake with sleep duration and sleep quality: findings from the CARDIA study | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions - PMC | Side effects
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium Toxicity | Overdose toxicity
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium deficiency: Does it have a role to play in cataractogenesis? | Deficiency
-
National Institutes of Health
Magnesium-Fact Sheet for Health Professionals | Deficiency
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium and Drugs | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Magnesium Sulfate | Interactions