L-tyrosine and its health benefits

- L-Tyrosine
- 16 Aug 2023
Overview
What is L-tyrosine?
L-tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid, which suggests the human body can synthesize it and may also be acquired by food. Numerous neurotransmitters are produced, like dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine, which are crucial for controlling mood, cognition, and stress response. Like some other supplements it can boost productivity and reduce stress.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov

Facts about L-tyrosine
- It is crucial in creating melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, hair, and eyes.
- The Swedish scientist Justus von Liebig isolated it from cheese for the first time in 1846.
- It is one of the 20 amino acids that go into making proteins, and it’s essential for cellular metabolism and protein synthesis.
Benefits
Benefits of L-Tyrosine
Several physiological functions in the human body depend on it.
Synthesis of vital elements
- It serves as a starting point for the production of several neurotransmitters.
- One of the main functions is the production of catecholamine, which is essential for controlling mood, drive, and cognitive function. It is mainly changed into L-dopa, further broken down into dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.1
- Additionally, it acts as a precursor for the creation of thyroid hormones. They are crucial for controlling metabolism, promoting growth, and preserving skin, hair, and nail health.
- It contributes to the creation of proteins vital to the structure and operation of many tissues in the body.1Biological role| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhanced cognitive ability
- Aids with improving mental performance and reducing the effects of stress and fatigue. It could also enhance learning and memory.
Improved concentration and alertness
- It could improve concentration and alertness, particularly under pressure. Additionally, it could enhance mental agility and performance.2Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Improved mood
- When used with other antidepressant drugs, it may help elevate mood and lessen depression’s symptoms.
Improvement of athletic performance
- Lowering tiredness and boosting endurance could also aid in increasing athletic performance.
Reduced ADHD symptoms
- It could also lessen impulsivity and inattention, two signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).2Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Sources
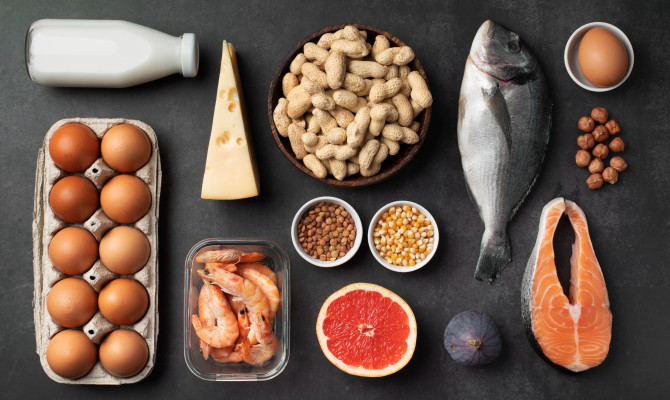
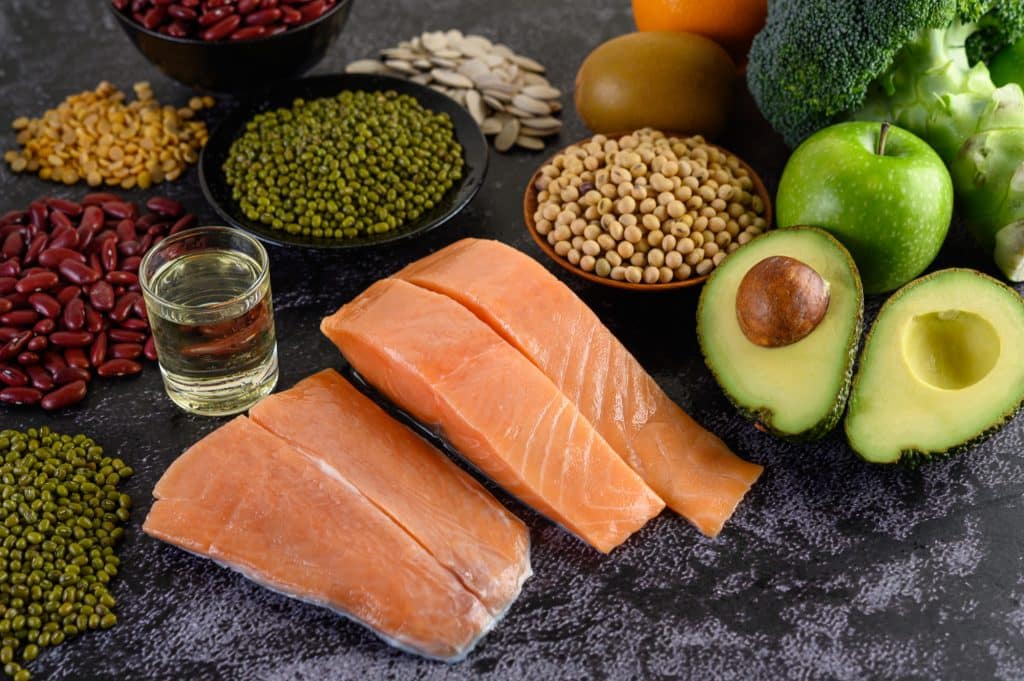
What are the dietary sources?
Meat
- Turkey, beef, pig, and chicken are all excellent sources.3Sources| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Fish
- These include salmon, tuna, and other fatty fish.3Sources| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dairy items
- Include yogurt, milk, and cheese.3Sources| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Legumes
- Good sources include kidney beans, lentils, and soybeans.
Seeds and nuts
- Almonds, sesame, sunflower, and pumpkin seeds.
Whole grains
- Rice, wheat, and oats are all excellent sources.3Sources| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Deficiency
Deficiency of L-tyrosine
- Decreased synthesis of melanin
- Anxiety-The neurotransmitter norepinephrine, which is involved in the body’s stress response, is also a dopamine precursor. Low amounts of L-tyrosine may reduce dopamine production. Insufficient amounts might lead to anxiety symptoms and more stress.
- Fatigue-It may make you feel tired and have less energy.4Deficiency| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Decreased synthesis of thyroid hormones
- Parkinson’s condition-Dopamine production decline may cause Parkinson’s symptoms to worsen.4Deficiency| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.g
Symptoms of deficiency
- Depression
- Lack of desire
- Poor cognitive performance
- Gaining weight
- Tiredness
- Slower metabolism
- Pale skin
- Having light-colored eyes and hair
- Decreased concentration, focus, and recall.
- Increased stress4Symptoms| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Causes of having insufficient L-tyrosine?
Inadequate nutrition
- A diet low in these items, which are present in foods high in protein, may result in a deficit.
High levels of stress
- Financial and emotional stress can raise the need for L-tyrosine and cause a deficit.
Injury or illness
- Deficiency happens when the body cannot meet the extra demand brought on by a disease or injury.
Certain medications
- Some medications, such as those that affect thyroid function or dopamine synthesis, can prevent the body from producing L-tyrosine.8Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage
The recommended dose
- For teens (14 to 18) is 150-500 mg/day
- 9–13-year-olds: 100–350 mg/day.
- 4–8 year-olds: 50–200 mg daily
- 150–500 mg per day for adults.9Dosage| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
L-tyrosine supplementation should be done under a doctor’s supervision, especially for children and babies. It’s crucial to adhere to the manufacturer’s advised dose guidelines.9Dosage| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Form
What are the various forms?
- Tablets and capsules
- Powders, for easier intake, combined with water or other liquids.
- Adding liquids to beverages or ingesting them directly
- The modified version of L-tyrosine, known as N-Acetyl L-Tyrosine (NALT), is more bioavailable than conventional supplements.
- A different form of the amino acid used in certain supplements is l-tyrosine hydrochloride.1Form| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Toxicity
Overdose toxicity of L-tyrosine
- Nausea and diarrhea
- Headache
- Heart palpitations
- Restlessness
- Weakness and exhaustion
- Higher blood pressure
- Insomnia or issues with sleeping
- Anxiety and agitation.
If you think you have taken too much, get help immediately. Supportive care may be part of the treatment, such as monitoring vital signs and alleviation of symptoms. Hospitalization may be required in difficult situations.1Toxicity| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Interactions
Interaction with medicines
MAOIs
- Antidepressants known as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) can raise the brain’s concentration of certain neurotransmitters. L-tyrosine combined with MAOIs can result in a risky rise in blood pressure and a heart attack or stroke.7Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Levodopa
- Parkinson’s disease is treated using this medication. Levodopa should not be used with it since it may interfere with its absorption and efficacy. Instead, a doctor should be consulted before taking both together.6Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Hormone replacement for the thyroid
- Tyrosine supplementation may raise the risk of overstimulating the thyroid glands when receiving this medication.5Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
The use of antipsychotic drugs
- It could reduce the efficiency of antipsychotic medications.6Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Precautions
What must I consider before taking L-tyrosine?
Medical history
- Your health issues, such as thyroid, melanoma, or phenylketonuria, should be reported to your doctor.
Medications
- It could interfere with medications, as was previously noted. Let your doctor know if you take any medications, including over-the-counter, herbal, or vitamin supplements.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Since the safety of tyrosine during pregnancy has not yet been identified, women should refrain from using the supplements until after visiting a doctor.
Allergic responses
- Some people may be allergic and display signs including a rash, itching, and breathing problems.1Precautions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- L-tyrosine is a beneficial vitamin that can promote general health and well-being.
- It is a crucial amino acid with many activities in the body.
- Natural sources of it include meals and supplements.
- Although it is usually considered safe, it is crucial to adhere to dose recommendations and get medical advice before using it, especially if you have any previous medical conditions.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Regulation of Dopamine Synthesis | Overview | Biological role | Precautions
-
National Library of Medicine
Behavioral and cognitive effects of tyrosine intake in healthy human adults | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
COMPOUND SUMMARY-Tyrosine | Sources
-
National Library of Medicine
Tyrosine Hydroxylase Deficiency | Deficiency | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Drug-drug interactions in patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of Tyrosine on Parkinson's Disease: A Randomized, Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled Trial | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI) | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Tyrosine supplementation for phenylketonuria | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Protein and Amino Acids | Dosage