Gingivitis
- Featured
Featured
Frequently Asked Questions
Gingivitis is an inflammation of gums. It often develops due to plaque accumulation on teeth and is frequently curable, especially with a dentist’s assistance and better dental hygiene. Gingivitis is a common condition that affects majority of adults at some point.
Plaque: It is an invisible, clingy coating that forms on teeth whenever starches and sugars from food interact with oral bacteria. People should remove it every day since it quickly develops again.
Calculus or tartar: It is formed when plaque on teeth’ surfaces solidifies beneath the gum line accumulating bacteria. The longer they are allowed to deposit on the teeth, the more irritated and inflamed the gums get.
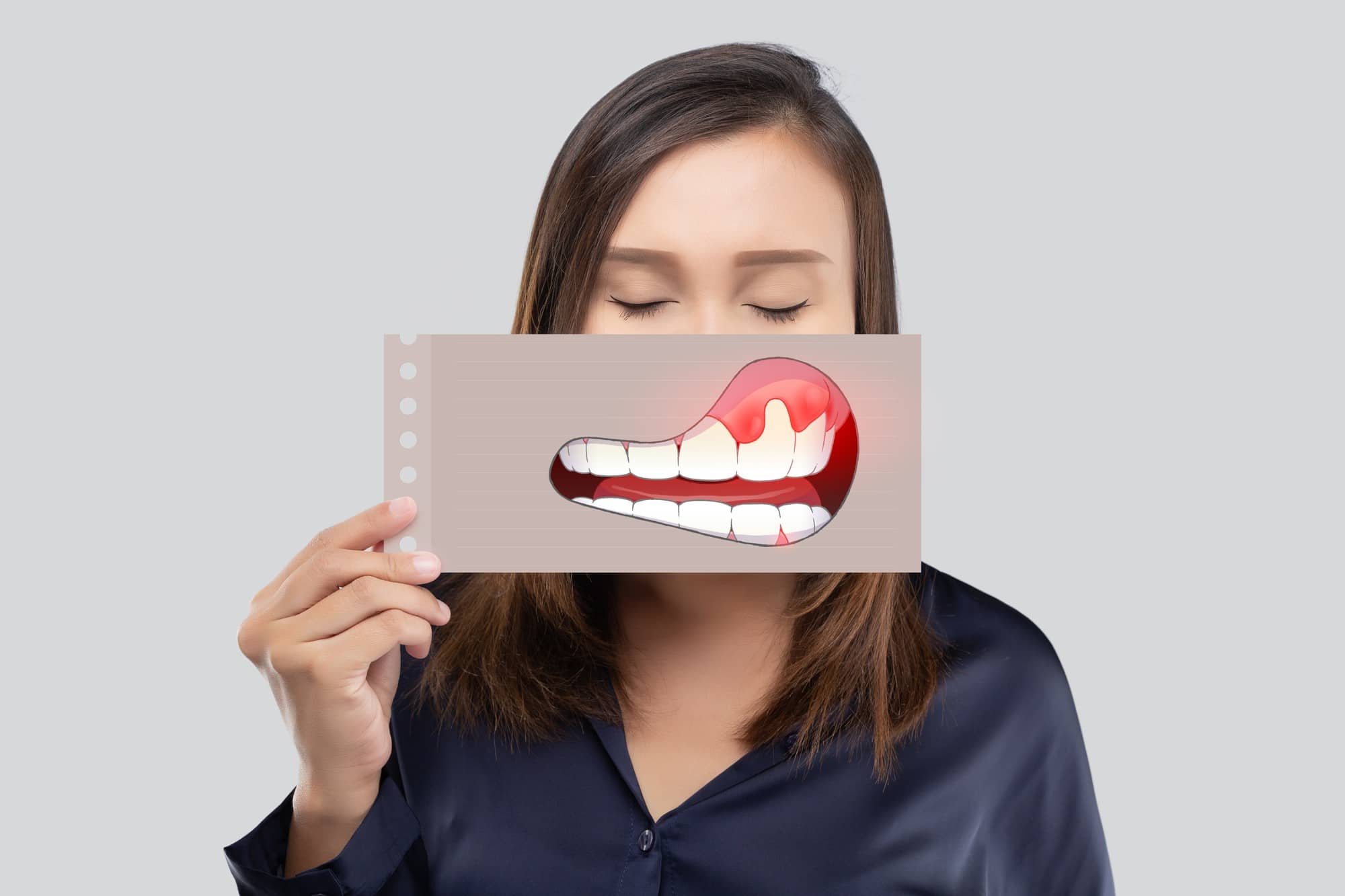
Gingivitis may show the following symptoms
- Enlarged gums.
- Dark red gums.
- Having bad breath.
- Gums that hurt when touched.
- Gums that bleed while brushing.
- Bleeding while eating apples or guavas.
If untreated, it can worsen and lead to several issues, such as
- Gum infection returning.
- Periodontitis is inflammation of the jaw bones, the periodontal ligament, and other supporting structures.
- Abscess or infection of the jawbones or gums.
- Declining gum line.
- Loss of bone surrounding teeth.
- Tooth loss.
The following actions are the best ones to take to prevent gingivitis
- Brush teeth twice daily with a toothbrush with soft bristles and light pressure.
- Every three months, change the soft-bristle toothbrush.
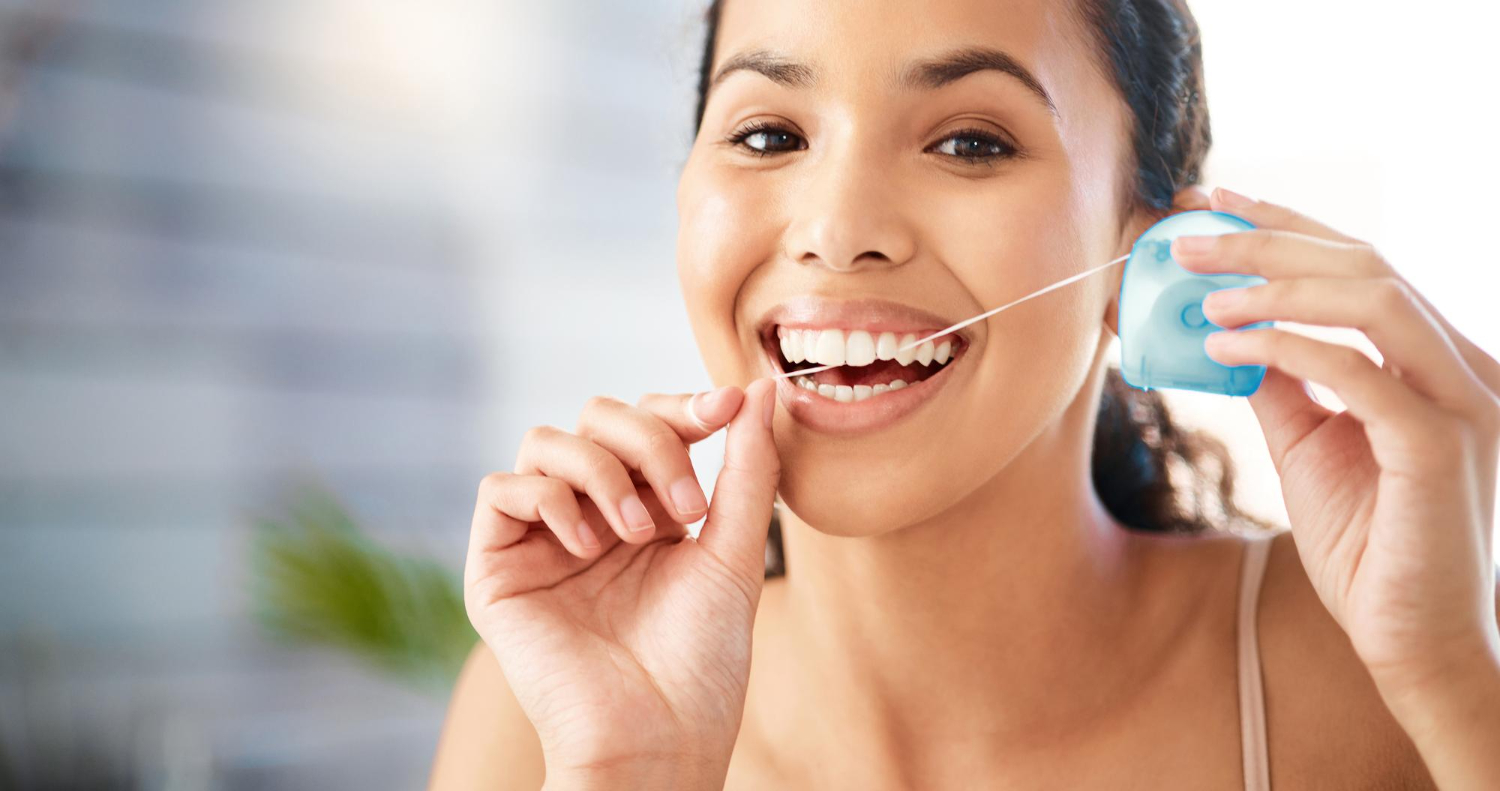
- Floss at least once every day to avoid plaque accumulation between the teeth.
- The dentist could recommend that patients more susceptible to gingivitis wash their teeth after each meal.
- People with diabetes should maintain their blood sugar levels.
- Give up smoking and other tobacco use.
















