Know your Sleep: Stages, Benefits and Tips

- Sleep
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Sleep?
Sleep is an important and often disregarded element of our lives. It is an intricate biological process that helps both our bodies and minds recover and regenerate. It is a regularly occurring state of physical and mental rest marked by less consciousness and diminished receptivity to outside stimuli. Our bodies carry out a number of essential functions while we sleep that aid in physical and mental recovery.
This article delves into the fascinating world of sleep, exploring its mechanism, stages, health benefits, the difference between rest and sleep, the amount of sleep we all need, and tips for improving sleep quality.

The Process
Mechanism of Sleep
The exact mechanism of sleep remains a subject of ongoing research, but it involves a complex interplay of neurotransmitters and brain regions.
Sleep is possible because of mainly two internal biological cycles:
- Circadian rhythm
- Sleep-wake cycle
Circadian rhythm
- The biological clock in your body, which relies on a roughly 24-hour day, regulates the majority of circadian rhythms.
- Environmental cues (such as light and temperature) concerning the actual time of day synchronize with circadian rhythms, although they can also exist without them.
Sleep-wake cycle
The key players in regulating sleep-wake cycles are two hormones, namely:
- Melatonin
- Adenosine
Melatonin
- Our circadian cycle is regulated by melatonin, which the pineal gland produces in reaction to darkness.1The process| Researched based study from Nccih.nih.gov
- It makes people drowsy and tells their bodies to go to sleep.
Adenosine
- A neurotransmitter is produced as a result of energy expenditure that progressively builds up in the brain during the day.2The process| Researched based study from Yale.edu
- As adenosine levels rise, it binds to specific receptors in the brain, promoting drowsiness and sleep initiation.
Stages
Stages of Sleep
Sleep stages can be broadly divided into two, namely:
- Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
- Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep.
Each of these categories consists of multiple stages, serving unique functions:
Non-REM stages
- Non-REM Stage 1 – This is the stage between being awake and asleep. It is a light sleep stage, and people may experience slow heartbeat, breathing, eye movements, and sudden muscle contractions, known as hypnic jerks.
- Non-REM Stage 2 – Eye movement stops, and brainwave activity becomes slower in this stage. It consumes a sizable portion of the total amount of sleep time.
- Non-REM Stage 3 – Also referred to as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep, is an essential stage for immune system support, hormone regulation, and physical recovery.
REM stages
- REM Sleep – REM sleep is distinguished by rapid eye movements, greater activity in the brain, and vivid dreams. It is essential for processing emotions and consolidating memories. 3Stages| Researched based study from Ninds.nih.gov
The sleep cycle normally comprises of several cycles through these stages. The percentage of REM sleep rises during the night while the percentage of deep sleep (NREM Stage 3) tends to decline.
Health benefits
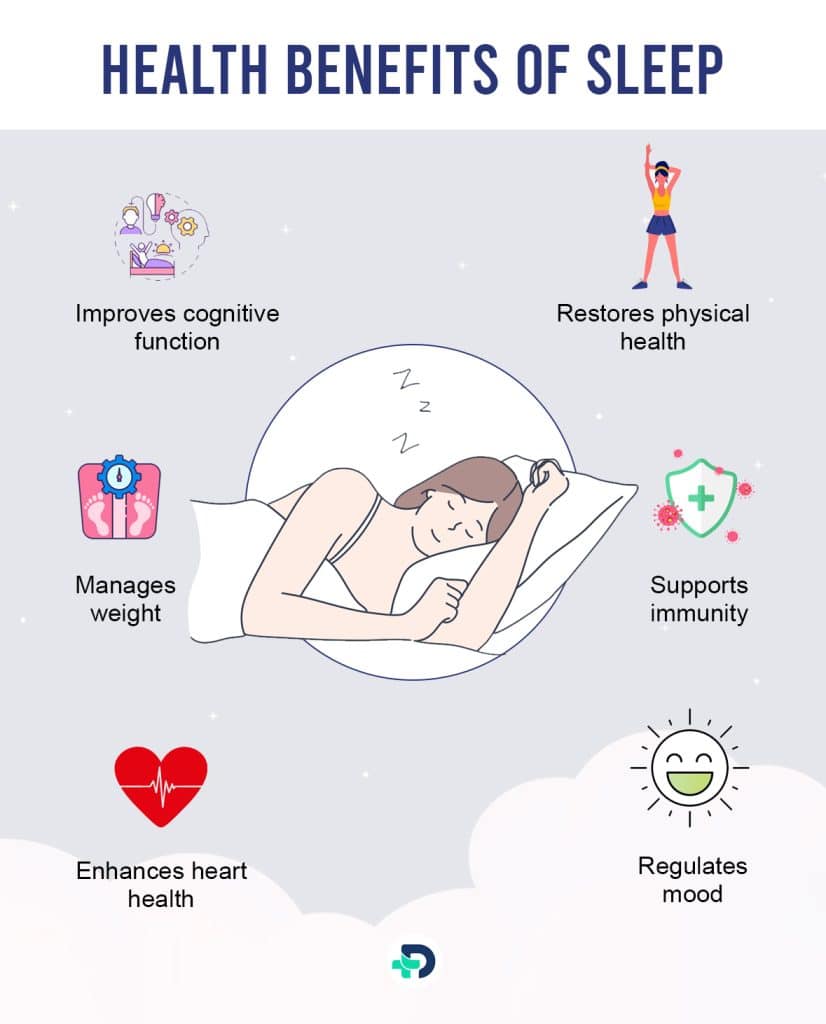
What are the health benefits offered by a good night Sleep?
The following are some of the important health benefits linked to regular, peaceful sleep:
- Improves cognitive function
- Restores physical health
- Supports immunity
- Regulates mood
- Enhances heart health
- Manages weight
- Regulates hormones
Improves cognitive function
- Cognitive functions including learning, problem-solving, and memory consolidation all greatly benefit from sleep.
- Focus, attentiveness, and decision-making skills are improved.4Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Restores physical health
- The body heals and regenerates its organs, muscles, and tissues as people sleep.
- It promotes growth in children and aids in muscle recovery in adults.
Supports immunity
- The immune system is strengthened by getting enough sleep, which makes the body more capable of battling diseases and infections.5Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Regulates mood
- The processing of emotions and the control of mood are directly related to sleep. It can lessen stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms.6Health benefits| Researched based study from Health.gov
Enhances heart health
- Sleep deprivation is linked to an elevated likelihood of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
Manages weight
- Hormones that control hunger are influenced by sleep, and getting little sleep can throw off the hormone balance and cause an increase in weight and obesity.7Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Regulates Hormone
- During sleep, the body releases essential hormones that regulate various functions, such as growth hormone, cortisol, and melatonin. These hormones are essential for keeping up general health8Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Vs Rest
Sleep Vs Rest
- Although they are two separate ideas, rest and sleep are frequently used interchangeably.
- Rest typically refers to a state of relaxation or reduced physical activity without complete disengagement from the environment.
- On the other hand, sleep involves a temporary suspension of consciousness, accompanied by specific brainwave patterns and physiological changes.
- While resting can be refreshing, it cannot fully substitute the benefits of sleep regarding cognitive restoration and physical healing.
Amount
How much Sleep do we need?
The amount of sleep needed differs from individual to individual based on their age.
The National Sleep Foundation provides the following guidelines for the recommended amount of sleep:
- Newborns – 0 to 3 months of age – 14-17 hours per day
- Infants – 4 to 11 months of age – 12-15 hours per day
- Toddlers – 1 to 2 years of age – 11-14 hours per day 9Amount| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Preschoolers – 3 to 5 years of age – 10-13 hours per day
- School-age children – 6 to 13 years of age – 9-11 hours per day
- Teenagers – 14 to 17 years of age – 8-10 hours per day
- Adults – 18 to 64 years of age – 7-9 hours per day 10Amount| Researched based study from thensf.org
- Older adults of 65 years and above – 7-8 hours per day
Tips
Tips to improve Sleep quality
If you find it challenging to get restful sleep at night, try incorporating these sleep-enhancing habits into your routine:
- Maintain a Sleep Schedule – every day including weekends, make sure you go to bed and get up at the same time as this can help you sleep better and adjust your body clock effectively. 11Tips| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
- Establish a Calming Routine – Before going to bed, relax by reading, enjoying a warm bath, or doing breathing exercises like breathing deeply or meditation.
- Create a cozy sleeping environment – To encourage sound sleep, maintain a cold, clean, dark, and quiet bedroom. To drown out sounds, use white noise machines, earplugs, or blackout drapes.12Tips| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Keep Moving Throughout the Day – Regular exercise might enhance the quality of sleep. An intense workout should be avoided shortly before bed, though, as it can make it more difficult to nod off.
- Reduce Stress – Sleep can be substantially impacted by anxiety and stress. Try stress-reduction techniques like meditation, mindfulness, yoga, or journaling to unwind the mind before bed.
- Reduce screen time before bed – Your sleep-wake cycle may be thrown off by the blue light that electronics like laptops and cell phones emit. To encourage healthier sleep, avoid screens for a minimum of one hour before bedtime.13Tips| Researched based study from Healthdirect.gov.au
- Limit naps – Short naps are sometimes beneficial, but taking too many during the day can interfere with your ability to sleep at night. If you must nap, limit the duration of your nap and take it early in the day.
- Watch What You Eat – Large meals and spicy foods should be avoided shortly before bedtime as they might cause discomfort and disrupt your sleep.
- Limit Liquid Intake Before Bed – Reducing your water intake a few hours before bedtime can minimize nighttime awakenings due to the need to use the bathroom. Also avoid alcohol and caffeine as they have the potential to disrupt sleep.14Tips| Researched based study from Sleepeductaion.org
- Do not take sleeping pills – without a prescription from a reputable physician, as they can become addictive and not treat the underlying reason for your sleeplessness, and won’t be of long-term use to you.
- If necessary, seek professional assistance – Even after using these suggestions, if you still have trouble sleeping, think about getting help from a doctor or sleep expert. They can offer individualized treatments and assist in identifying any underlying sleep issues.
Takeaway
Takeaway
Human life is dependent on sleep, as it is also crucial to our overall health and happiness. By adopting healthy sleep practices and making our sleep environment more conducive to restful sleep, we can reap the rewards of a well-rested mind and body, enhancing our quality of life and productivity during waking hours. Let’s respect sleep for what it is and recognize the potential benefits it may have on our well-being.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Melatonin: What You Need To Know | The Process
-
Yale School of Medicine
Good Sleep Recipe | The Process
-
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Brain Basics: Understanding Sleep | Stages
-
National Library of Medicine
Sleep for cognitive enhancement | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Sleep and immune function | Benefits
-
Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
Get Enough Sleep | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Sleep Deprivation: Effects on Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
The Impact of Sleep and Circadian Disturbance on Hormones and Metabolism | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
National Sleep Foundation's updated sleep duration recommendations: final report | Duration
-
National Sleep Foundation
Interesting Sleep Facts and Statistics (2021) that We Can Learn From | Duration
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Tips for Better Sleep | Tips
-
Mayo Clinic
Sleep tips: 6 steps to better sleep | Tips
-
Health Direct
Sleep | Tips
-
Sleep Education
Healthy Sleep Habits | Tips