Fibromyalgia Back Pain: Causes, Symptoms & Management

- Fibromyalgia
- 02 Oct 2023
Overview
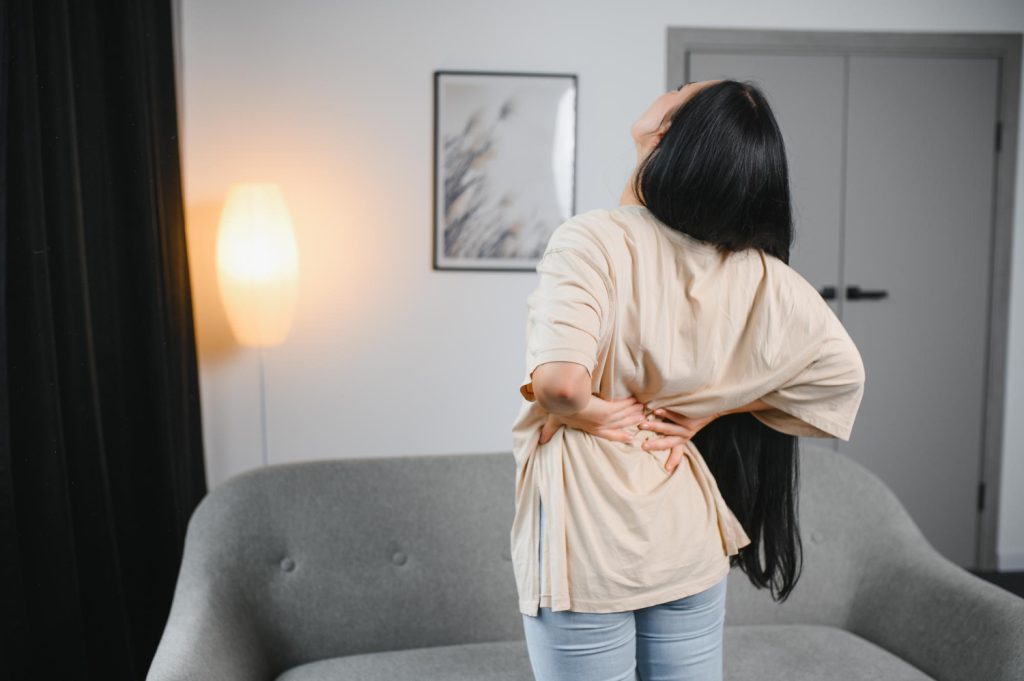
Fibromyalgia Back Pain
Fibromyalgia is a health issue that mainly targets muscles and soft tissues, resulting in long-lasting pain and fatigue that affects the entire musculoskeletal system. Fibromyalgia is believed to impact approximately 2-4% of the general population, and it is more commonly diagnosed in women. 1 Overview | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine ,2 Overview | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine Fibromyalgia back pain is often described as a deep, constant ache that can vary in intensity. It results in discomfort, rigidity, and sensitivity in muscles, tendons, and joints. 2 Overview | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine Fibromyalgia is not classified as a neuropathic pain condition, although it can involve neuropathic pain as one of its components. This neuropathic pain can manifest as burning or tingling sensations and may be associated with areas of muscle tightness and tenderness. 3 Overview | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine

Causes

What is the Root Cause of Fibromyalgia?
The precise root cause of fibromyalgia remains elusive, and it is regarded as a complex condition. There are several factors that contributed to the onset of fibromyalgia:
- Genetics
- Neurological abnormalities
- Abnormal Pain Processing
- Physical or Emotional Trauma
- Neurochemical Imbalances
- Infections
- Vaccinations
- Hormonal Factors
Genetics:
- Fibromyalgia seems to have a genetic element, as it can be seen in families.
- Specific genetic differences may raise the likelihood of developing the condition.
Neurological Abnormalities:
- In some studies, it has been suggested that abnormalities in the brain’s processing of pain signals may play a role.1 Causes| Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- Research suggests that fibromyalgia also involves abnormalities in the central nervous system, leading to an increased perception of pain. This is why it is known to as a condition involving both muscles and nerves.6 Causes | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- People with fibromyalgia often experience heightened pain sensitivity, which can amplify the perception of pain throughout the body.
Abnormal Pain Processing:
- Studies indicate that fibromyalgia is linked to irregularities in how the central nervous system interprets pain signals, resulting in an increased sensitivity to pain.
Physical or Emotional Trauma:
- Physical trauma, such as motor car accidents, or emotional trauma may spark the onset of fibromyalgia back pain in some individuals.
Neurochemical Imbalances:
- Alterations in neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine have been noted in people with fibromyalgia.
- These neurotransmitters are involved in both pain control and mood regulation.
Infections:
- Fibromyalgia has been proven to contribute to the progression of certain infections, such as hepatitis C, HIV, and Lyme disease.4 Causes | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Vaccinations:
- Research indicates that vaccinations might be involved in initiating the onset of fibromyalgia. 5 Causes | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Hormonal Factors:
- Hormonal imbalances, especially in relation to the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, have been studied in connection with fibromyalgia.
Is fibromyalgia a nerve or muscle pain?
- Fibromyalgia is a complex condition that involves both muscle and nerve-related symptoms.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia Back Pain
What does Fibromyalgia Back Pain feel like?
Fibromyalgia-related back pain can vary from person to person, but it’s often described as:
- Widespread: The most prominent symptom is chronic, widespread pain. Pain occurs in a bilateral manner, affecting both sides, and is frequently present in upper and lower part of the waist.
- Deep Aching: Many people with fibromyalgia report a deep, dull ache in their back. This pain can give the impression that it originates from the muscles, ligaments, or even the bones.
- Burning or Stabbing Sensations: Some individuals describe their back pain as a burning or stabbing sensation that can be intense at times. 7 Symptoms | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- Tenderness: The back and surrounding areas may feel especially sensitive to touch. Even gentle pressure or massage can trigger discomfort.
- Radiating Pain: Back pain experienced in fibromyalgia can extend to different regions like the neck, shoulders, and lower back. Additionally, it might be linked to the occurrence of headaches.
- Fatigue: Back pain in fibromyalgia is often accompanied by overall fatigue, which can make the pain feel more debilitating.
- Tender Points: Fibromyalgia patients frequently experience tender spots on their bodies. The tender spots are identified as localized areas where even slight pressure can bring pain.
Other Symptoms may include:
- Cognitive Symptoms: Often referred to as “fibro fog,” cognitive difficulties may occur. Memory worries, difficulty concentrating, and changes in mental clarity are some of the problems that may emerge.
- Depression and Anxiety: Emotional symptoms often coexist with fibromyalgia. The chronic pain and limitations linked with the situation can contribute to the mood disorders.
Rare Fibromyalgia Symptoms:
While fibromyalgia commonly presents with symptoms like widespread pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, some individuals may experience less common or rare symptoms. These symptoms can include:
- Sensitivity to Touch: Heightened sensitivity to touch or tactile sensations, even clothing or light pressure, can be a less common symptom.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Some people with fibromyalgia may have unusual sensitivity to temperature changes, experiencing discomfort in response to both cold and heat.
- Vision Problems: On rare occasions, fibromyalgia can be connected to visual issues like blurry vision or heightened sensitivity to light.
- Dizziness and Balance Issues: A subset of individuals with fibromyalgia may experience dizziness, vertigo, or problems with balance.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): While not exclusive to fibromyalgia, RLS is a condition described by crawling, tingling, or itching sensations in the legs.8 Symptoms | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- Raynaud ’s phenomenon: Here, the blood vessels in the fingers and toes are prone to narrowing. The response to cold temperatures or emotional stress can cause it to constrict.
- Skin Issues: Skin problems like rashes or itching are infrequent but have been reported in some cases.
- Digestive Symptoms: Although not exclusive to fibromyalgia, digestive issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) may co-occur with the condition.
- Chest Pain: Some individuals may experience chest pain, which should be evaluated to rule out other cardiac or pulmonary conditions.
- Migraines and Headaches: While headaches are common in fibromyalgia, some individuals may experience more severe migraines.
- Sensory Overload: Overstimulation from sensory inputs, such as noise, light, or crowded environments, can be overwhelming for a subset of people with fibromyalgia.
- Tactile Allodynia: Allodynia is a condition where sensations that aren’t typically painful, like gentle pressure or touch, are interpreted as painful. People with fibromyalgia may experience this heightened sensitivity to tactile stimuli in various areas of their body.8 Symptoms | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing: Can be a rare symptom of fibromyalgia. It may be linked to muscle stiffness and pain in the throat and neck area.
- Hypersomnia: While insomnia and disrupted sleep are more common in fibromyalgia, some individuals may experience the opposite—hypersomnia. Fibromyalgia can disrupt sleep patterns, causing problems like trouble falling asleep, frequent nighttime awakenings, and inadequate rest during sleep. It’s common to wake up not feeling refreshed.
- Tinnitus: Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, is an auditory symptom that can occur alongside fibromyalgia. It can be bothersome and contribute to sleep disturbances.
Fibromyalgia Back Pain Spots
- In fibromyalgia, back pain typically isn’t localized to specific “spots” like in some other conditions.
- Fibromyalgia tender points are not specific to the back but are distributed across various areas of the body, including the neck, shoulders, chest, elbows, buttocks, and knees.
- During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will apply gentle pressure to these points to assess tenderness and pain response.
- However, there are specific tender points used in the diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, and some of these points are located in the back and neck area.
These tender points include:
- Suboccipital muscle insertions (at the base of the skull)
- Trapezius muscle (near the shoulder blades)
- Supraspinatus muscle (top of the shoulders)
- Gluteal muscles (buttocks)
- Greater trochanter (hip area)
- Inner knee (at the inside of the knee) 9 Symptoms | Researched based study from Oman Medical Journal
These tender points can be sensitive or painful in individuals with fibromyalgia. The pain tends to be widespread and may migrate or shift over time.
Management
Management of Fibromyalgia Back Pain
How do you stop back pain from fibromyalgia?
Here are common strategies used in the management of fibromyalgia back pain:
- Medications
- Physical therapy
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Pain Management techniques
- Support Groups and Counseling
- Alternative Therapies
- Medications for Sleep
- Mind-Body Practices
Medications:
- Pain killers: can be used to achieve pain relief and to reduce inflammation.
- Antidepressant Medications: To address pain and sleep issues in fibromyalgia, your doctor may recommend medications. Additionally, some medications may be prescribed to aid in pain management and mood enhancement. 10 Management | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- Muscle Relaxants: These can help alleviate muscle spasms and tension contributing to back pain.
Physical Therapy:
- A physical therapist has the ability to create a workout plan that is customized to enhance energy, stamina, and posture.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
- Psychosomatic aspects of fibromyalgia can be effectively addressed through CBT.
- It helps individuals to cope with strategies, manage stress, and improve their mental well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Exercise: Engaging in regular, low-impact exercise such as swimming, walking, or gentle yoga can help improve muscle tone, and reduce pain. 10 Management | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing good sleep habits and maintaining a regular sleep schedule can help relieve fatigue and improve sleep quality.
- Stress reduction techniques: Relaxation therapy, meditation, and deep breathing can have positive effects.
Pain Management Techniques:
- Thermotherapy, cryotherapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) are all methods that can help manage pain and reduce muscle stiffness. 10 Management | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Diet and Nutrition:
- Some individuals with fibromyalgia find relief by reducing caffeine and avoiding certain trigger foods.
Support Groups and Counseling:
- Participating in a support group or seeking individual counseling can offer emotional assistance.
Alternative Therapies:
- A number of people with fibromyalgia experience ease from complementary therapies like acupressure techniques, therapeutic massage, and supplements derived from plants.
Is a back massage good for fibromyalgia?
- Back massage can help reduce muscle tension and alleviate localized pain in the back and other areas affected by fibromyalgia. 10 Management | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Medications for Sleep:
- Sleep disturbances are common in fibromyalgia. To improve sleep, medications like muscle relaxants or low-dose tricyclic antidepressants may be prescribed in certain cases.
Mind-Body Practices:
- Techniques like mindfulness meditation and tai chi can help improve relaxation, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being. 10 Management | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Prognosis
Prognosis of Fibromyalgia Back Pain
- Prognostic factors are linked to the intensity of symptoms, whether it’s fatigue, pain, accompanying signs, or the overall assessment like the FIQ (Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire). 8 Prognosis | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- It’s important to recognize that fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, and complete recovery in the traditional sense is rare.
- For some individuals, the pain may be chronic and ongoing, lasting for months or even years.
- Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, and while there may be periods of relatively lower pain or symptom intensity, it often involves long-term management.
- Effective management, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, can help reduce the duration and severity of back pain.
- Stress, changes in weather, overexertion, or other triggers can lead to flare-ups of pain, which may be temporary.
- The presence of other health conditions, such as arthritis or mood disorders, can influence the course and duration of back pain.
- Lifestyle choices, including physical activity levels, sleep quality, and stress management, can impact the persistence of symptoms.
- The long-term outlook for fibromyalgia can vary. Some individuals may experience periods of stable symptom management, while others may have fluctuations in symptom severity.
How long does fibromyalgia back pain last?
- Fibromyalgia is a condition that lasts for a long time and is described by fatigue, sleep disturbances, and psychological difficulties.
Take Away
Fibromyalgia Back Pain – Combination of Treatments to Relieve Symptoms
- Back pain is a common symptom of fibromyalgia, and it can affect various areas of the back, including the upper, middle, and lower back.9 Take Away | Researched based study from Oman Medical Journal
- Fibromyalgia is a complex syndrome with varying symptoms, and the interplay of these factors likely contributes to its development.
- Furthermore, fibromyalgia can co-occur with other medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), further complicating the understanding of its root cause.
- Fibromyalgia treatment centers on symptom management and enhancing quality of life, typically involving medications, physical therapy, exercise, and lifestyle changes since a permanent cure for the condition does not exist. 9 Take Away | Researched based study from Oman Medical Journal
- Stress, weather changes, overexertion, and certain triggers can lead to flare-ups of fibromyalgia symptoms.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Overview | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Symptoms | Prognosis
-
Oman Medical Journal
Symptoms | Takeaway
-
National Library of Medicine
Management