Anxiety – Understanding and Management

- Anxiety
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is how your brain commonly responds to stress and warns you of any upcoming danger. It can be beneficial to your body as it keeps you alert and pays full attention to your surroundings. Most of the time, physiological and hormonal changes are what allow you to act so fast to protect yourself. Your body uses anxiety to get you ready to either fight, flee, or freeze in the event of danger.
Fighting or running away is a defensive action that you decide to take. Your heartbeat quickens, increasing the amount of oxygen getting to your main muscles. Your ability to feel pain lessens while your hearing gets better. You can now act quickly and appropriately, thanks to these changes. Freezing is by putting your fight or flight response on wait, you can enhance your preparations for self-defense. Also known as reactive immobility. Similar physiological changes occur, but you remain still and prepare for the next action.

Disorder
How is it different from an anxiety disorder?
- Everybody goes through occasional anxiety. For example, you may feel anxious about moving to a new place, before taking a test in your school or university, when you face a new challenge at work, or when making any important life decisions.
- Feeling nervous or anxious occasionally is acceptable. Despite how uncomfortable it could be, it could drive you to work more or to do better. Normal anxiety is an ebb-and-flow emotion that does not disrupt your daily life.
- What differentiates normal anxiety from anxiety disorders is the feeling of unrelenting fear that may be excessive and accompany you all the time. It can be quite painful and even crippling.
- You could stop engaging in activities that you usually love doing like attending school, family gatherings, or other events as you find them increasing your nervousness. If it is extreme, it could even be challenging to get through the day.
- Anxiety disorder will only get worse if it is not managed. Almost 30% of adults experience an anxiety disorder at some point in their lives, making it the most common of all mental disorders.
Nonetheless, there are a variety of therapies for anxiety disorders. Most people who receive treatment can live regular and satisfying lives. 1anxiety and anxiety disorder | Researched based study from psychiatry.org
Symptoms
What are the symptoms?
There are various types of anxiety disorders, each has a unique set of symptoms. The most common symptoms of anxiety disorders are as follows: 2Symptoms of anxiety| Researched based study from nih.org
- Restlessness
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Dizziness
- Nervousness
- Tension
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Sleep difficulties
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling weak or tired
- Increased irritability
- Heart palpitations
- Tense muscles
- Sleep problems
- Inability to remain calm
- Rapid heartbeat
- Breathing faster than normal (shallow breathing)
- Hands or feet that are cold, sweaty, or numb.
- Uncontrollable worries
- Beads of sweat on your forehead
- A sense of impending danger, panic, or doom
- Gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances
- Having a strong desire to avoid situations that cause anxiety
- Feelings of panic, fear, and uneasiness
- Avoiding feared objects or places obsessively.
Types
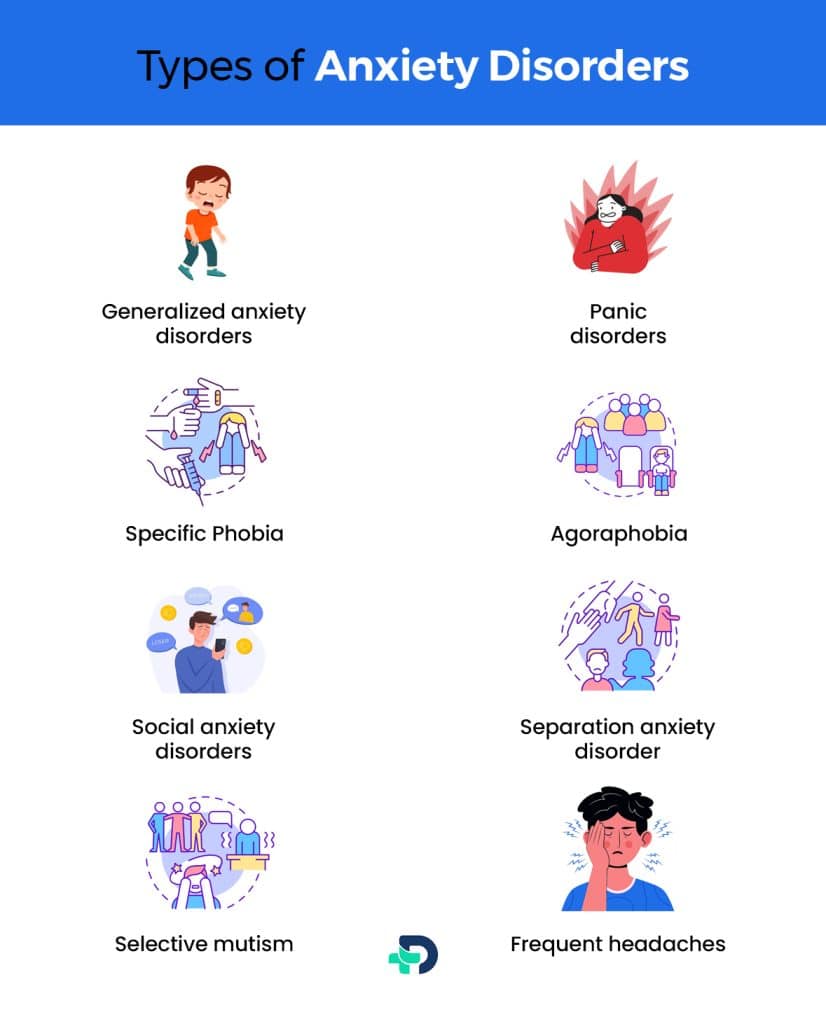
Types of Anxiety disorders
There are several types of anxiety disorders generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and phobia-related disorders.
Generalized anxiety disorders (GAD)
This type of anxiety disorder is chronic and is explained by a persistent sense of anxiety or dread that interferes with daily life. This is the most common type of anxiety disorder and people who suffer from it are unable to identify the reason for their anxiety. People suffering from GAD, experience frequent anxiety for months or even years. There are some symptoms specific to GAD, as follows:3Types of anxiety | Researched based study from nih.gov
- Restlessness
- Feel easily tired
- Edgy and highly defensive
- Difficult to fall asleep
- Angry or very worried
- Unable to concentrate
- Being grumpy
- Stomachaches
- Frequent headaches
- Muscle aches
Panic disorders
People with panic disorders often have feelings of stress, anxiety, and panic at any time and mostly without any reason. It can be associated with scary experiences or long-standing stress, but it can also occur without any reason. People with panic disorders have
- Panic attacks that are very frequent and usually unexpected.
- Repetitive panic attacks are the major symptom of panic disorders.
- People with panic disorder often worry about the occurrence of their next panic attack.
- Actively trying to avoid future attacks by avoiding the triggers like some places, situations, or people.
What is a panic attack?
Panic attacks are sudden and intense episodes of anxiety that can trigger physical symptoms like a faster heartbeat, faster and shallower breaths, cold hands, and feet, etc. You could also feel like losing control over your body and all of this happens when there is no clear trigger. Panic attacks can be as frequent as several times a day or sometimes rarely as a few times a year. You may be shaking, dizzy, confused, or nauseous when you experience a panic attack. These attacks happen suddenly without any triggers and can escalate quickly. 5types of anxiety | Researched based study from who.int
A person under a panic attack may experience the following symptoms:
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating
- Palpitations
- Racing heart
- Chest pain
- Feeling suffocated
- Not able to breathe deeply
- Faster breath rate
- Sweating
- Shivers
- Lightheadedness
- Feeling dizzy
- Legs shaking
- Feeling of choking
- Chills
- Hot flashes
- Fear of losing control
- Numbness of hands and feet
- Fear of death
- Abdominal disturbances
- Fear of something tragic is about to happen.
Phobia-related disorders:
A phobia is a persistent and uncontrollable fear of a specific object, situation, or activity. This fear can be so intense that a person will make any effort to escape the source of anxiety. Some of these fears can make sense for example fear of falling, fear of snakes, etc. There are a few types of phobias and phobia-related disorders like,
Specific Phobia
- Specific phobia is also called simple phobias.
- People who experience specific phobia, or fear of a particular object or a situation.
- Phobias are so different from other anxiety disorders, as they can be related to a specific cause.
- People with phobias may constantly worry about encountering the feared object or situation. They take steps to avoid their triggers. They may even end up having a panic attack when they encounter the feared object of a situation.
- A person suffering from a phobia can recognize their fear as extreme and unreasonable, but they cannot control their anxiety in the presence of the trigger.
Some phobias are specific to the triggers and are as follows:
- Fear of animals
- Fear of insects
- Reptiles
- Blood
- Injections
- Doctors
- Hospitals
- Heights
- Speed
Agoraphobia
- Agoraphobia is the fear of being in spaces or situations from which one cannot find ways to escape or it could be embarrassing to escape, or required help might not be available when they experience panic symptoms.
- The fear is generally out of proportion to the situation and could last six months or more and could disturb a person’s proper functioning.
- A person with agoraphobia could fear leaving home, using public transport, or using an elevator (enclosed space). In untreated and severe cases of agoraphobia, a person could be homebound and never come out. 4Agarophobia | Researched based study from nhs.uk
Social anxiety disorders
- Also known as social phobia is an extreme and repeated fear of being watched and judged by others. It could be the fear or judgment from others or of public embarrassment.
- It includes a range of feelings, such as the fear of being on stage, a fear of intimacy, and a fear of rejection or humiliation in social interactions. person usually try to avoid such situations or go through them with great anxiety.
- Some social anxiety disorders are very common like the fear of public speaking, meeting new people, being on a first date, etc.
- For people with social anxiety disorder, the fear may feel so extreme that it seems not under their control. In extreme cases, this fear may get in the way of everyday activities like going to school or to work, etc.
People suffering from social anxiety disorder may show symptoms like:
- Sweating
- Shaking/ trembling.
- Racing heart
- Blushing
- Avoiding eye contact
- Stomach aches
- Rigid posture
- Being self-conscious
- Fear of being judged
- Overly sweet voice than normal
- Avoid being around unfamiliar people
Separation anxiety disorder
- It is the anxiety that one feels after separation from a person or place that usually provides them with a secure feel.
- This is most common in kids, but this can also affect people of all ages.
- People who suffer from separation anxiety, fear that something bad or dangerous could happen to their person while they are separated.
- They may have nightmares about their separation. This feeling of being anxious about separation persists and causes problems in normal functioning.
- A person with separation anxiety will constantly worry about losing that closest person. They may not be ready to go out or, sleep without that person.
Selective mutism
- It is when a person cannot speak in certain places or about certain things, even if they may have excellent verbal communication skills around the people, they are comfortable with.
- This is a rare type of anxiety disorder. It is often seen with extreme shyness, fear of social situations like embarrassment, and clinging behavior.
- People who show symptoms of selective mutism, also often show symptoms of other anxiety disorders.
- It usually begins before 5 years of age. Kids who experience selective mutism may not be able to speak in front of some people like they usually speak around their family members.
- This could lead to problems in school like social isolation. They may also experience high social anxiety. Many kids may surpass selective mutism.
- Selective mutism may disappear in kids who also are diagnosed with social anxiety disorder, but symptoms of social anxiety disorder may persist.
Vulnerability
Who is at risk?
People who have a history of, Trauma, stress build-up, other mental health disorders, a family history of anxiety disorders, or other illnesses like heart problems, etc. are at risk of developing anxiety disorders.
- Genetics, people who have a family history of anxiety are more prone to developing anxiety disorders. Especially if parents have a history of anxiety or other mental disorders.
- Children who have a history of trauma or abuse in any form may have a higher risk of developing an anxiety disorder in their lives.
- Children or adults who experienced a traumatic event recently also can develop anxiety disorders. E.g., losing a parent or a loved one, experiencing physical trauma in an accident, etc.
- Physical health can affect a person’s mental health. Having a long-standing health condition or any serious illness like thyroid problems, or heart problems can make you more prone to have an anxiety disorder.
- People who are naturally shy or nervous are more prone to anxiety disorders.6who is at risk? | Researched based study from nih.gov
- People with other mental disorders like depression may develop anxiety disorders.
- People who use excessive alcohol or drugs can develop anxiety disorders on withdrawal.
- Those who consume excess caffeine, or any other medications can worsen the symptoms of anxiety.
Causes
Causes of anxiety
Some experience anxiety with particular triggers and in most cases, the trigger or the cause is unknown.
Psychological causes:
- Genetic reasons: Can be inherited from parents or blood relatives if there is a family history of anxiety disorders or other mental disorders.
- Traumatic events in the past could be one of the reasons to develop anxiety. Example: abuse, trauma, sudden loss of a loved one or a parent, etc.
- History of insult or humiliation in public or being constantly misjudged for your actions.
Medical causes:
Anxiety could be a symptom that could indicate some medical illness in some individuals. If your doctor suspects your anxiety might have a medical cause, he may suggest tests to confirm it.
Some medical conditions that may be related to your anxiety include:
- Heart diseases like arrhythmias.
- Hyperthyroidism
- Respiratory problems like asthma.
- Alcohol withdrawal
- Withdrawal from certain medications like anti-anxiety medications or anti depressives
- Rare tumors that produce adrenaline.
- Diabetes
- Chronic pain
Unknown cause:
It is possible for you to develop anxiety disorder with no cause, for example: If you have a sudden occurrence of anxiety that is not related to any of your life events, if you do not have a family history of anxiety disorder, or if you do not have any other medical illness, or if you do not have excessive fear towards any particular object or situation.
Diagnosis
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor may ask you a few questions related to your experiences to understand the signs and symptoms and whether it is related to any medical illness if at all needs to be treated.
The doctor may refer you to a mental health specialist if he or she suspects your problem to be anxiety.
A single test can never conclusively diagnose an anxiety disorder. It needs an extensive process which could be time-consuming, which will include,
- Physical routine examinations (blood, and urine tests to rule out medical illnesses that could contribute to your anxiety),
- Mental evaluation, which may need you to fill up psychological questionnaires, etc.
- Anxiety tests and scales that could help doctors assess your level of anxiety.
- A psychological evaluation may include discussions about your feelings, thoughts, fears, and behavioral patterns to arrive at a diagnosis.
Anxiety disorders mostly occur along with other mental health disorders like depression or substance abuse. 7Diagnosis of anxiety | Researched based study from DSM-5
Prevention
Prevention of anxiety
We cannot entirely prevent anxiety as mostly the cause is unclear. But we can take a few steps to reduce the severity of symptoms, as follows:
- As parents, you may maintain honest and open communication with your child to ensure the child is making healthy decisions.
- You can engage yourself in activities that make you feel good about yourself.
- You can try to avoid people or situations to decrease your anxiety as a short-term solution but in the long run, you need therapy.
- Anxiety needs to be diagnosed and managed as early as possible to avoid making it hard to treat.
- You can practice mindfulness and stress management through yoga, meditation, breathing exercises, etc.
- Restrict caffeine which can worsen your symptoms of anxiety.
Treatment
Treatment for an anxiety disorder
There are two main treatments for anxiety disorders and you may benefit most from a combination of the two:
- Psychotherapy.
- Medications.
Psychotherapy:
- This is psychological counseling, where you may be working with a therapist to reduce your symptoms of anxiety.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBC) is a therapy that teaches you particular skills to improve your symptoms and may help you return to the activities that were avoiding because of your anxiety.
- It is the most effective therapy. This will also include exposure therapy where you will be gradually made to encounter the objects or situations that trigger your anxiety.
- So, with time, you can outgrow your fear and build your confidence that you can manage the situation and your symptoms. 7Treatment of Anxiety| Researched based study from who.int
Medication:
Depending on the type of anxiety disorder you have, there are several types of medications used, to help you relieve symptoms.
For example:
- Anti-depressants like buspirone, escitalopram
- Sedatives like benzodiazepines like diazepam, clonazepam, or beta blockers.
- Selective serotonin uptake inhibitors like fluoxetine, and paroxetine.
- Selective non-epinephrine reuptake inhibitors like duloxetine
- Antipsychotics like ariprazole.
- Anxiolytics like buspirone.
Emergency
When to seek medical help?
- If person suddenly find himself worrying too much and if it is disturbing his work, peace or relationship, or any other parts of life, he may need to seek medical help.
- If person is unable to control himself and often find depressed or worried.
- If one have any dependencies on alcohol or drug.
- If one have any other mental disorders along with anxiety
- If person have a long-standing medical illness.
- If one feel lonely or isolated and have suicidal or self-harming thoughts, he/she need to get help immediately.
Complications
Complications
- Anxiety can be one of the symptoms of depression. Anxiety disorder can worsen the symptoms of depression.
- To decrease the anxiousness and to calm oneself, some people look comfort in alcohol or drugs, creating dependencies and addiction. In such case, alcohol problem or drug addiction has to be treated before treating anxiety.
Management
How can anxiety be managed at home?

Few things can help you cope with your symptoms like,
- Stress management techniques: Practicing Mindfulness, meditation, yoga, etc.
- Taking help from support groups can be found online. This helps you share your experiences and coping strategies with each other.
- Avoid or decrease the intake of caffeine as it can worsen your symptoms.
- Getting enough sleep
- Staying active
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a balanced diet (flax seeds, chia seeds, turmeric, fatty fish, vitamin D, tryptophan, and magnesium in your diet might help)
- Avoiding alcohol consumption
- Quit smoking if you are a smoker.
Reports
Reports of WHO
Anxiety disorders are the sixth leading cause of non-fatal health loss worldwide and are among the top ten causes of YLD (years of healthy life lost due to disability) in all WHO regions. The duration of symptoms that people with anxiety disorders typically experience makes it a chronic rather than an episodic disorder. There are an estimated 264 million people worldwide who suffer from anxiety disorders. As a result of population growth and aging, this total for 2015 represents a 14.9% increase since 2005. 5who reports| Researched based study from who.int
Takeaway
The bottom line
It is acceptable to occasionally worry about specific things, like money, health or family troubles. Usually, anxiety disorders are more serious than passing worries. It could be challenging to go through a typical day. You could have symptoms like restlessness, palpitations, increased sweating, shivering, etc. Adults with anxiety disorders are very common and if left untreated, they could get worse over time. More people can enjoy regular lives, thanks to the treatments available. See a doctor if you experience any symptoms and discuss how your anxiety disorder could be managed. 8the bottom line | Researched based study from thelancet.com
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Psychiatry.org
What are Anxiety Disorders? | Overview
-
National Institutes of Health
Anxiety Disorders | Symptoms
-
National Institutes of Health
Specific Phobia | Details
-
National Health Service
Overview - Agoraphobia
-
World Health Organization
Depression and Other Common Mental Disorder
-
National Institutes of Health
Social Anxiety Disorder: More Than Just Shyness
-
DIAGNOSTIC AND STATISTICAL MANUAL OF MENTAL DISORDERS-5
DIAGNOSTIC AND STATISTICAL MANUAL OF MENTAL DISORDERS | Treatment
-
The Lancet
A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 - The Lancet




































