Knee pain: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment

- Knee Pain
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Knee pain?
Knee pain is the soreness, sensitivity, and discomfort in and around one or both knees.
The knee is the connection between the upper and lower leg, which provides the stability to support the entire body. It also allows our legs to bend and keep walking, jumping, and running. Bones, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and muscles are the several parts that help the knee to perform the work efficiently. Injury or disease in any of the parts can lead to knee pain.
There can be several causes for the knee pain. Identifying the root cause of knee pain enables one to get the correct treatment, relieve the pain and regain movability.
One can treat minor knee pain with self-care and medications. However, severe knee pain might require surgery to relieve the symptoms.
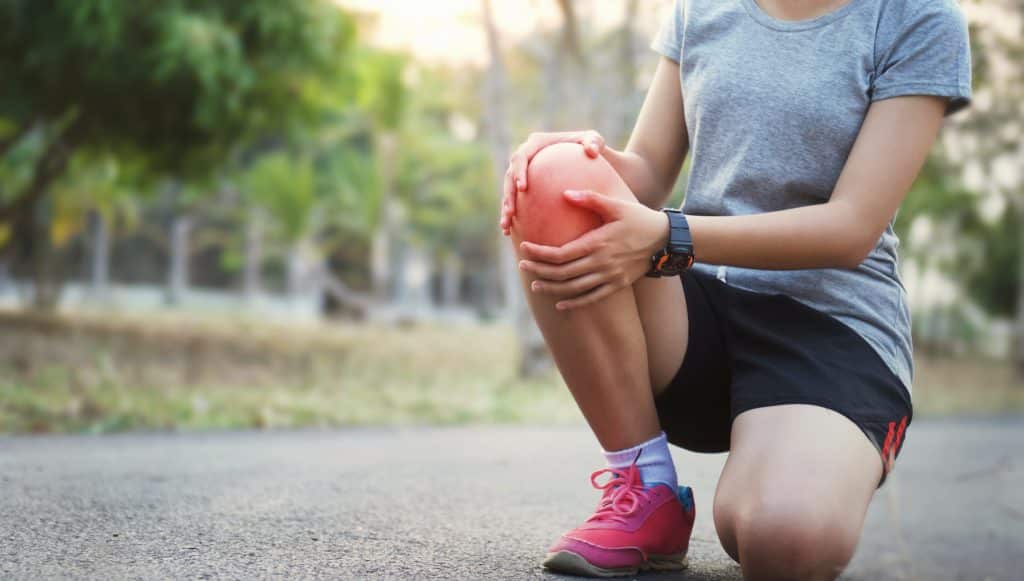

Prevalence of Knee pain
- Knee pain can occur to people of all ages, but older people are more prone to knee pain due to degeneration of the joints.
- Around 25% of people over the age of 50 experience knee pain due to degenerative knee diseases
- The global prevalence of knee osteoarthritis (joint disease) is 22.9% in individuals over 40 years and 16% in individuals 15 years and older.
- In the United States, more than 3 billion dollars are spent yearly on knee surgeries1Overview| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com ,2Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov .
Symptoms
Symptoms of Knee pain
Common symptoms accompanying Knee pain
- Weakness and instability to stand
- Redness and warmth in the knee area
- Swelling and stiffness of the knees
- Difficulty in complete stretching of the knees
- Popping sounds on moving or stretching the knees
- Constant soreness and tenderness
- Dull burning sensation
- Sharp pain when in use 3Symptoms| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Causes
Causes of Knee pain
There can be numerous causes for knee pain. Some of the common causes of knee pain are mentioned below:
- Overusing the knee joint
- Knee injuries
- Chronic or acute medical conditions
- Obesity
Overuse
Some examples of knee overuse that could lead to pain are as follows:
- Repetitive jumping sports such as basketball and volleyball cause tendon injury (tendonitis), leading to knee pain. Tendon is a connective tissue that connects bone to muscles
- In runners, pain in and around the knee cap occurs due to excess stress on the knees for good performance
Injuries
A knee injury can be due to the following reasons:
- Accidental fall from a height
- Repetitive movement in sports or frequent changes in direction
- Receiving a direct blow to the knees
- Participating in sports without protective equipment
- Performing strenuous physical activity that impacts the knees
Injury can lead to the following condition in the knees:
- Fracture of the kneecap
- Dislocation of the kneecap
- Tearing of the ligament (connective tissue connecting bone to bone)
- Tearing of the cartilage in the knee
- Swelling of the fluid-filled sac that cushions the knee joint
Medical conditions
Some medical conditions that can lead to knee pain are as follows:
- Osteoarthritis-Osteoarthritis is when the cartilage that cushions the end of the joints deteriorates with time. It causes pain and swelling
- Rheumatic arthritis -Rheumatic arthritis is an inflammatory condition that affects one or more joints.
- Gout-A condition that causes uric acid build-up in the joints causing severe pain and swelling. It affects the knee moves
- Bursitis-A painful swelling of the fluid-filled sac near the joint
- Tendinitis-Tendinitis is the inflammation of the thick cord that connects bone to muscles.
- Chondromalacia patella-It is the cartilage breakdown in the underside of the patella (knee cap)
- Baker’s cyst-It is the fluid-filled swelling at the back of the knee
- Cellulitis around the knee-It is a bacterial skin infection that affects the knee joint area
- Tumor-It is the abnormal cell growth in the knee area
Increased weight (obesity)
- Increased weight puts extra stress on the knees to bear the weight and leads to chronic knee pain 4Causes| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Knee pain
Physical Examination
- The doctor conducts a thorough physical examination to identify the cause of the pain. He will look for any knee locking, swelling, noises, and range of motion. Following this, he might order subsequent tests to confirm the diagnosis.
X-ray
- X-ray is a type of radiation to create pictures inside of our body
- It shows the bones and their alignment, along with any soft tissue injury
CT (Computed Tomography) – scan
- It uses computers and X-rays to get a detailed three-dimensional image of the body.
- It evaluates any injury in the bones and soft tissues
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- MRI is a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to get a detailed picture of the inside of the body
- It evaluates any soft tissue injuries 5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Risk factors
Risk factors for Knee pain
- Bad posture during physical activity
- Incorrect stretching of the muscles
- Strenuous occupation
- Certain sports, such as skiing and basketball
- Lack of muscle flexibility that increases the risk of knee injuries
- Bacterial Infection
Who are at risk of getting Knee pain?
- Who are over the age of 60 years
- One with increased weight
- People with previous injuries
- One involved in athletic and other strenuous activity 6Risk factors| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Complications
Complications of Knee pain
Some medical conditions, such as osteoarthritis, if left untreated, can lead to the following complications:
- Joint damage
- Severe unbearable pain affecting regular activities
- Immobility 7Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment
Treatment of Knee pain
Self-care
- Taking adequate rest might help inflammation to subside
- Applying an ice compress on the affected knee area for 15 to 20 minutes at a time can relieve the pain
- Using supports viz; braces, taping, and wraps might help relieve symptoms depending on the diagnosis
Physical therapy
- Physical therapy is a range of exercises that strengthen the muscles and improve movement.
- The exercises are prescribed by a trained professional (physical therapist) based on the diagnosis.
Medications
NSAID (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication)
- It is given for treating arthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis
Cortisone Injections
- It is prescribed for knee osteoarthritis
Antibiotic
- It is prescribed for any infection
Steroids
- It is given for gout disease
Surgery
Surgery is recommended for the following conditions:
- Knee fractures
- Knee dislocation
- Infected knee joints requiring surgical drainage
- Knee osteoarthritis advanced stages(Knee replacement surgery)
- Rheumatic arthritis (Joint replacement surgery)
Knee replacement surgery
- It is a surgical procedure that replaces parts of the worn-out knee joints
- The surgery helps the knee work better and eases pain.
Joint replacement surgery (Arthroplasty)
- It is a surgical operation that replaces the damaged joint with an artificial metallic, plastic, or ceramic joint.
- Knees, hips, and shoulders are the common joints surgeons replace with surgery 8Treatment| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Symptoms needing emergency medical attention
Not all knee pain needs urgent medical attention. Delaying treatment can increase discomfort and mobility. Some symptoms that require acute treatment are as follows:
- Pain and swelling lasting more than two days
- Reduced motion
- Fever accompanied by redness and warmth
- Joints look deformed
- Noticeable knee swelling
- Inability to bear the weight on the knees
- Sudden swelling and intense pain after injury
Home remedies
Home remedies for Knee pain
RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation)
- Add ice packs to the knee and wrap them with a compression bandage to prevent swelling. Then keep the foot elevated while resting.
Heat and cold therapy
- Heat therapy might reduce pain while resting. On the other hand, cold therapy might help reduce the swelling.
- One can alternate between the ice pack and heat pad to reduce pain and swelling.
Tai chi
- It is an ancient Chinese mind-body exercise to enhance flexibility and balance.
- It includes relaxation techniques and deep breathing
- It reduces stress and persistent pain and improves mobility 9Home remedies| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Ginger extract
- Ginger can be used as a supplement, ginger tea, or ginger spice
- It helps reduce arthritis pain when used alongside other prescription medication 10Home remedies| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Prevention
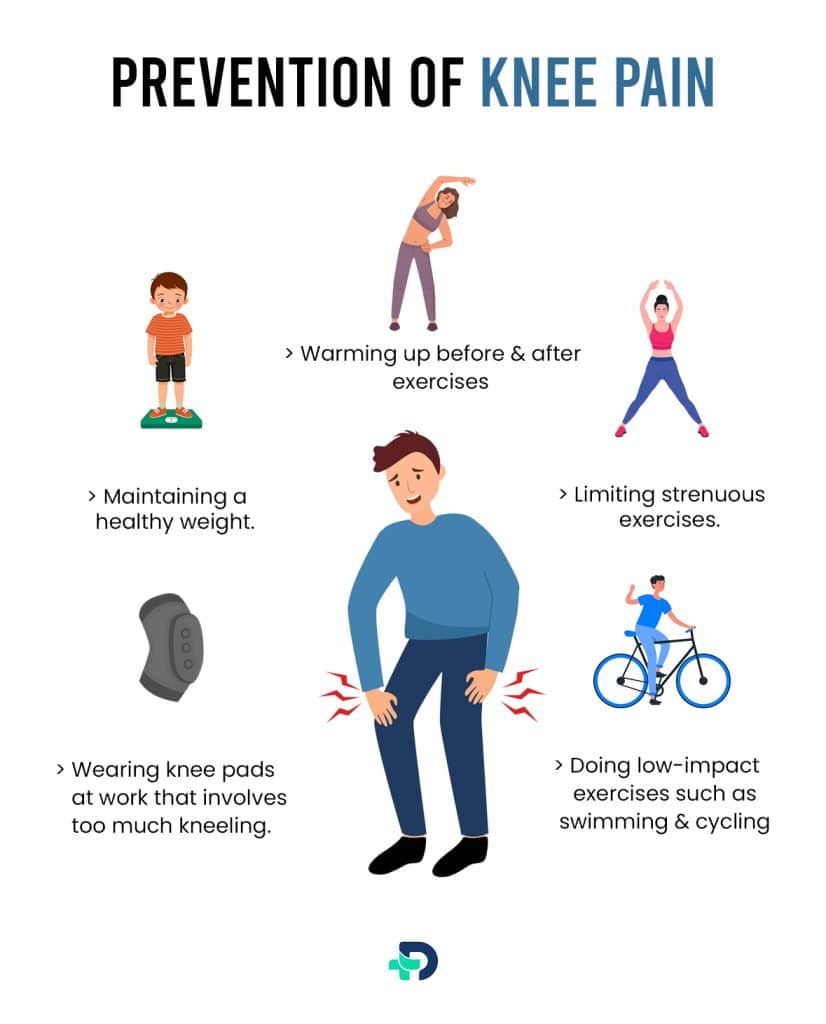
Prevention of Knee pain
It is not always possible to prevent knee pain. However, the following tips help prevent joint injuries and joint deterioration:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting strenuous exercises
- Doing low-impact exercises such as swimming and cycling
- Practicing regularly and ideally the movement patterns in sports
- Building the muscles in the front and back of the thighs to prevent injuries during sports
- Wearing knee pads at work that involves too much kneeling
- Warming up before and after exercises
- Replacing running shoes frequently for proper support and cushioning 11Prevention| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Knee pain is the discomfort in the knees that affect people of all ages
- Certain medical conditions and injuries can lead to knee pain
- Treatment relies on the cause and may include self-care, medication, and surgery
- Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding joint overuse can prevent knee pain
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Knee pain | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies | Prevalence
-
Science Direct
Knee Osteoarthritis | Symptoms
-
Science Direct
Factors associated with pain resolution in those with knee pain: the MOST study | Causes
-
Science Direct
Diagnosis and treatment of anterior knee pain'. Journal of ISAKOS | Diagnosis
-
National Library of Medicine
A prospective study on knee pain and its risk factors | Risk
-
National Library of Medicine
Knee pain, knee osteoarthritis, and the risk of fracture'. Arthritis Rheum | Complications
-
National Library of Medicine
Symptomatic Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and a Network Meta-Analysis with a 6-Month Time Horizon | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Tai Chi is Effective in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial | Home remedies
-
Science Direct
Efficacy and safety of ginger in osteoarthritis patients: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials | Home remedies
-
National Library of Medicine
Strategies for the prevention of knee osteoarthritis'. Nat Rev Rheumatol | Prevention