Understanding Chest pain: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

- Chest Pain
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Chest pain?
Any pain felt in the area between the neck and the upper abdomen is referred to as chest pain. It can vary in intensity and duration, presenting as a sharp, dull, burning, or squeezing sensation. Several internal chest structures, such as the heart, esophagus, lungs, muscles, nerves and ribs, can cause chest pain. It is essential to understand the different aspects of chest pain to identify potential causes and seek appropriate medical attention promptly.
The article aims to provide comprehensive information about chest pain, including its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, potential complications, and prognosis.

Causes
Causes of Chest pain
Chest pain can occur due to any of the following causes:
- Heart-related issues
- Lung problems
- Digestive issues
- Muscle and bone problems
- Other causes
Heart-related causes may include:
- Myocardial Infarction or heart attack – results in heart muscle injury when a coronary artery is completely blocked.1Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Pericarditis – swelling of the heart’s lining.
- Angina – Reduced blood flow to the heart due to narrowed or blocked coronary arteries.
- Aortic aneurism – bulge in the aorta, which is the principal artery carrying blood from the heart’s chambers to other parts of the body.2Causes| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Aortic dissection – a rupture in the aorta lining, a significant blood vessel.3Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Lung problems may include:
- Pneumonia – Infection causing inflammation in the lungs.
- Pleurisy – Chest pain from pleurisy, an enlargement of the lining around the lung, can be intense and frequently worsens when breathing deeply or coughing.4Causes| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Pulmonary Embolism – Blood clot obstructing a lung artery.
- Pneumothorax – Collapse of the lung.5Causes| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
- COVID-19 – caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus is the infectious disease known as coronavirus disease.
- Tuberculosis – is an infectious illness that typically impacts the lungs and is brought on by a specific type of bacteria.
- Asthma – Breathing becomes difficult when you have asthma because your airways narrow, swell, and sometimes create excess mucus.
Gastrointestinal and Digestive issues may include:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – Acid reflux leads to heartburn and chest discomfort.6Causes| Researched based study from Niddk.nih.gov
- Esophageal Spasm – Involuntary contractions of the esophagus causing chest pain.
- Pancreatitis – refers to pancreatic inflammation.
- Esophageal hypersensitivity – feeling pain even with a usually non-painful esophageal stimulus.
- Esophageal rupture – An esophageal rupture means a hole, perforation, or tear in the esophageal wall.7Causes| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Peptic ulcers – An ulcer in the inner layer of your stomach or duodenum, the first segment of your small intestine, is called a peptic ulcer.
Problems with muscles and bones:
- Costochondritis – The cartilage that links the ribs to the breastbone becomes inflamed. 8Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Muscle Strain – Overuse or injury to the chest muscles or surrounding tissues.
- Injured ribs – from road traffic accidents or abuse.
Other causes :
- Hiatal hernia – Weakened muscle tissue allows the stomach to protrude into the chest.9Causes| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Panic attacks – sudden episode of extreme dread accompanied by considerable physical symptoms, even when there is no obvious risk or cause.
Symptoms
Chest pain’s companion symptoms
Depending on the underlying reason, chest discomfort symptoms may include:
Heart-related symptoms
- Tight pain in the middle of the chest.1Symptoms| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Radiating pain to the left arm, jaw, neck, or shoulder
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeat
- Sudden tiredness
Lung problems may cause the following symptoms:
- Chest or shoulder pain. (Worsens while coughing, sneezing)
- Breathlessness during exertion
- Rapid and shallow breathing
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath 4Symptoms| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Fatigue
- Wheezing 10Symptoms| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Coughs
- Fever and chills
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Weight loss
- Appetite loss
- Blue lips or fingertips
- Difficulty staying awake
- Cough with phlegm (green, yellow, or containing blood)
Gastrointestinal issues may include the following symptoms:
- Heartburn 6Symptoms| Researched based study from Niddk.nih.gov
- Fever
- Cough
- Upper abdominal pain
- Trouble swallowing 11Symptoms| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Swollen or tender abdomen
- Hoarseness of throat
- Regurgitation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Rapid breathing
- Pain that radiates to the back
- Touching the chest produces a crackling sound 7Symptoms| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Pain in the upper abdomen after eating
Muscles and bones problems may show the following symptoms:
- Pain on coughing or sneezing.
- Pain while taking a deep breath.
- Pain on exertion or movement.
Severe symptoms: When should you seek medical help?
An individual should get medical help right away if they have:
- Chest tightness or heaviness
- Sense of choking. 12Symptoms| Researched based study from Healthdirect.gov
- Bluish lips or nails
- Confusion
- Severe pain that persists for more than 15 minutes
- Pain that began with dizziness, nausea, and sweating
- Pain spreads to the shoulders, back, neck, or jaw
- Breathing trouble or variations in breathing rate.
Risk factors
Chest pain risk factors
The following can increase the chance of an individual to develop a chest pain:
- Family history of heart disease 13Risk factors| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Older individuals are at higher risk.
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Eating high-fatty food
- Obesity or overweight.14Risk factors| Researched based study from Heart.org
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Anxiety or stress disorders
- Diabetes
- Drinking alcohol
- Drug abuse
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
A heart attack is not usually indicated by chest pain. But emergency department doctors typically check for it first because it may provide the greatest immediate threat to your life.
Proper diagnosis of chest pain involves a thorough medical evaluation. The healthcare provider may perform various tests, including:
Physical examination may include:
- Temperature check
- Weight check
- Checking blood pressure
- Recording the pulse rate
- Breath rate check
- Neck exam
- Heart and lung exam
- Look for any abnormal breath sounds
- Check for any abnormal heart rhythm or sound
- Abdominal examination
Other diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Chest X-ray
- CT (Computerized tomography) scan. 15Diagnosis| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Echocardiogram
- Stress test.16Diagnosis| Researched based study from Betterhealth.vic.gov.au
- Coronary angiography.
Treatment
Treatment of Chest pain
Treatment for chest pain is based on its root cause. Some common approaches include:
- Medications
- Lifestyle changes
- Physical therapy or counseling
- Surgery or a procedure.
Prevention
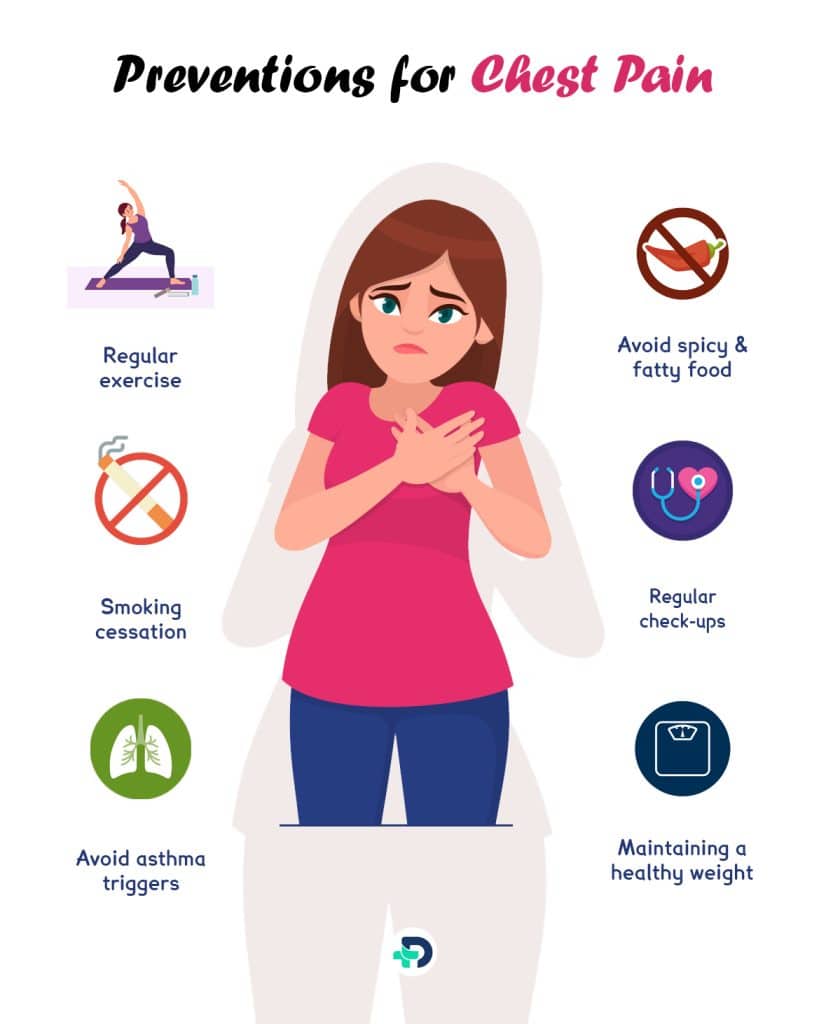

Chest pain prevention
The following are some necessary preventive measures:
- Regular exercise
- A balanced diet is low in saturated fats and sodium
- Avoid spicy and fatty food
- Smoking cessation
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing stress levels
- Limit or quit alcohol consumption.
- Avoid asthma triggers 17Prevention| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Treat respiratory infections promptly
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional.
Complications
Complications
Failure to seek timely medical attention for chest pain can lead to potentially severe complications, including:
- Heart attack
- Chronic pain or disability
- Heart failure
- Multiple organ failure 3Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Death.
Prognosis
Prognosis
Life-threatening causes of chest pain include heart attacks and other lung-related conditions. The best action is to visit a medical professional who recognizes and treats your chest pain. Based on the root cause and the quickness of medical response, the outlook for chest pain varies. Early detection and appropriate treatment significantly improve outcomes. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if chest pain occurs to determine the cause and receive the necessary care.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Myocardial Infarction | Causes
-
Cleveland Clinic
Aortic Aneurysm | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Aortic Dissection | Causes
-
Mayo Clinic
Pleurisy | Causes
-
Mount Sinai
Collapsed lung (pneumothorax) | Causes
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Symptoms & Causes of GER & GERD |
-
Cleveland Clinic
Esophageal Rupture | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Costochondritis | Causes
-
Cleveland Clinic
Hiatal Hernia | Causes
-
Mayo Clinic
Asthma | Symptoms
-
Mayo Clinic
Chest pain | Symptoms
-
Health Direct
Chest pain | Symptoms
-
Medline Plus
Chest pain | Risk factors
-
American Heart Association
Angina (Chest Pain) | Risk factors
-
Mayo Clinic
Chest pain | Diagnosis
-
Better Health Channel
Chest pain | Diagnosis
-
Cleveland Clinic
Chest pain | Treatment