Indirect Pulp Cap : A Key Technique For Tooth Preservation

- Pulp Capping
- 20 Sep 2023
Introduction
Pulp Capping
Pulp capping is a method used in dental restorations to prevent the dental pulp (the innermost layer of the tooth) from necrosis (cell death) after it has been exposed during cavity preparation. There are two categories under which pulp capping is classified: direct and indirect pulp capping procedures. Following the removal of dental decay, a dentist chooses the type of pulp capping based on the degree of pulp involvement in the tooth.1 Introduction| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association

Tooth Anatomy
Structure & Functions of the Teeth
- The toughest substances in the human body, the teeth, are not only essential for chewing but also play a crucial role in speech.
- The tooth root is located below the dental crown, while the dental crown is the portion of the tooth that is exposed to the oral cavity.
- Enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp are the teeth’s four main structural layers.
- It is the toughest biological tissue that covers the surface of the dental crown. Inside the enamel and cementum is the dentin layer, which runs from the dental crown to the tooth root.
- The cementum is the tissue that covers the tooth root and is fastened to the alveolar bone via the periodontal ligament.
- The dental pulp is the tooth’s deepest layer which consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. 2Tooth Anatomy| Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Tooth Decay
What is a Tooth Decay?
- Cavities are tiny cracks or openings that permanently harm the strong enamel of the teeth.
- Cavities, also known as tooth decay/caries, are brought on by a number of things, such as oral bacteria, frequent snacking, drinking sugary beverages, and/or improper brushing of your teeth.
- Tooth decay is one of the most common health problems in the world which if unchecked, can lead to toothaches.
- Your best defense against tooth decay is regular dentist appointments, good oral hygiene practices, and flossing. 3Tooth Decay| Researched based study from Mayo Clinic
Indications
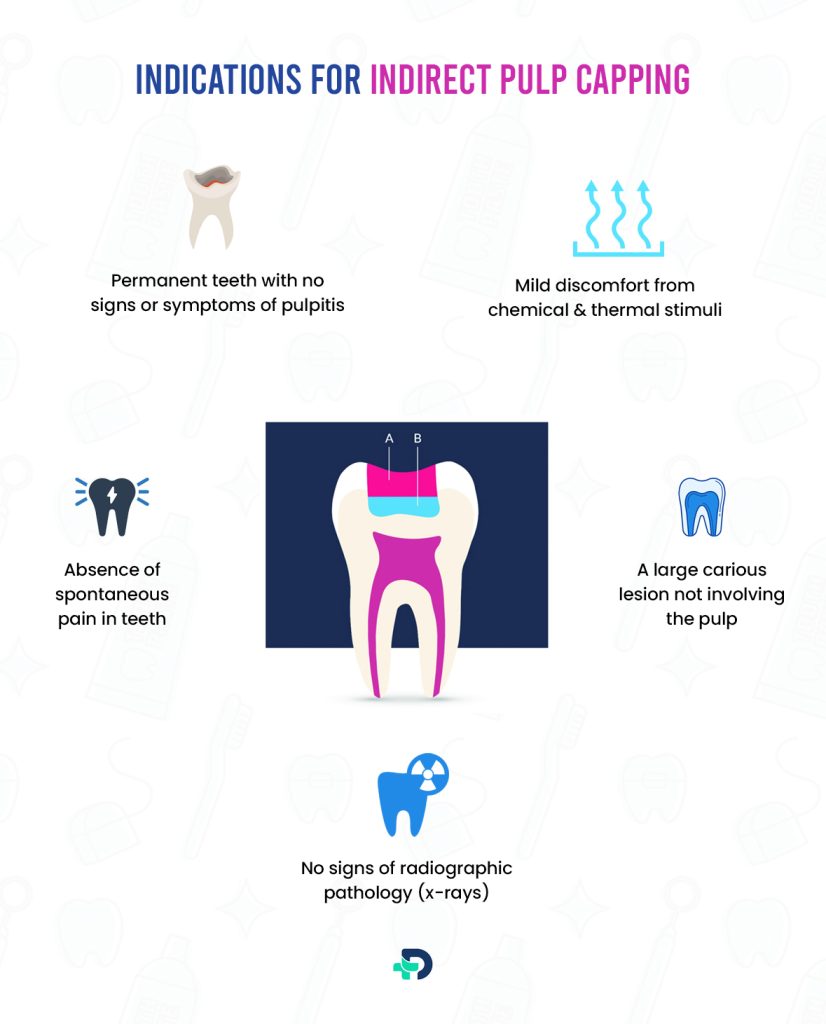
Indications for Indirect Pulp Capping
The following conditions require an indirect pulp capping procedure which includes:
- Permanent teeth with no signs or symptoms of pulpitis (inflammation of pulp)
- Mild discomfort from chemical and thermal stimuli
- Absence of spontaneous pain in teeth
- A large carious lesion not involving the pulp
- No signs of radiographic pathology (x-rays) 1 Indications| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
When is indirect pulp capping used?
- When dental decay affects/involves only enamel & dentin and not the pulp, an indirect pulp capping procedure will be recommended which helps to protect the pulp from dental decay.
- A pulp cap prevents bacteria and other harmful elements from getting inside the tooth’s pulp which additionally can stop cavities from getting worse.
- If a patient has a history of dental pain or tooth pulp is damaged, the dentist may advise an alternative method to manage the carious lesion.1 Indications| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Procedure
Indirect Pulp Capping Procedure
Indirect pulp capping is a method that preserves a damaged tooth (without an exposed pulp) to avoid more invasive procedures such as tooth extraction/root canal which helps to retain the tooth by allowing its roots to grow further. 1 Procedure| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Types of indirect pulp cap procedures
Depending on the severity of the tooth decay, your dentist may advise one of two indirect pulp cap procedures which include:
- One-step indirect pulp cap procedure
- Two-step indirect pulp cap procedure
One-step indirect pulp cap procedure
- In this type of indirect pulp capping procedure, the dentist fills the dentin layer of the tooth after treating cavities (without exposing the pulp) and then places a filling to protect the pulp.
Two-step indirect pulp cap procedure
- In this kind of indirect pulp capping, the dentist removes damaged dentin from the tooth’s outermost portions before sealing the exposed tooth structure and temporarily filling it.
In order to determine whether the pulp cap was successful, your dentist may physically examine the teeth and may take X-rays. 1 Procedure| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Indirect pulp capping in permanent teeth
- Indirect pulp capping can be done on permanent teeth when complete removal of the carious lesion would expose the pulp.
- Following a step-by-step approach at predefined intervals, the cavity is first closed with calcium hydroxide and after 8 to 12 weeks, the second step is scheduled which involves the complete removal of the last remaining carious lesion followed by a routine restoration of the tooth. 4Procedure| Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Materials
Materials used in Indirect Pulp Capping
A dentist can do an indirect pulp capping procedure by utilizing a variety of filling materials. Few of those materials have sedative properties that slow the regeneration of dentin and soothe nerves that are degenerating.
An expert dentist can make recommendations for the best material based on the requirement since each filling material will have its own distinctive properties which include the following:
Glass ionomer cement (GIC)
- In addition to having a natural appearance, it adheres well to teeth and releases fluoride to stop caries from developing.
Resin-modified glass ionomer cement
- When compared to glass ionomer cement, resin-modified glass ionomer cement is a form of filler material that contributes higher adhesion since it is stronger and more wear-resistant.
Calcium hydroxide
- Is an antibacterial filling material that promotes healing and production of reparative dentin in the teeth
Dentin-bonding agent
- Is a type of filler substance that guards the pulp during impression-taking and restoring processes. 1Materials Used| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Sedative fillings
- During indirect pulp capping procedures, sedative/temporary fillings are frequently employed.
- The role of sedative fillings is to calm a dental nerve that has been irritated by tooth decay.
- Sedative filling materials, in contrast to conventional filling materials, have inherent qualities that facilitate dentin healing.
- Calcium hydroxide and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) are the two sedative substances that are employed the most frequently.
- Calcium hydroxide and mineral trioxide aggregate are antibacterial agents that aid in the formation of reparative dentin and provide protection from bacterial invasion in a tooth. 1Materials Used| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Advantages
Advantages of Indirect Pulp Capping
Compared to alternative methods of treating a decaying tooth, indirect pulp capping has a number of advantages which are as follows:
- Your tooth may be saved.
- You can stay away from more intrusive and difficult procedures like a root canal.
- The price of a pulp cap is typically cheaper than that of a root canal.1Advantages| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
What dentin is formed in indirect pulp capping?
- In general, reparative/tertiary dentin is created after an indirect pulp capping technique, which helps to maintain the pulp complex’s health and vitality.
- It aids in the formation of reparative dentin by inducing pulp cells which additionally arrests any residual caries progression in the teeth of an affected person. 1Advantages| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Contraindications
Contraindications for Indirect Pulp Capping
The tooth is not recommended for indirect pulp capping if any of the following conditions exist:
- Non-vital tooth
- Discolored/ shaky tooth
- Any signs of radiographic pathology (x-rays) 1Contraindications| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Failure
Indirect Pulp Cap Failure Symptoms
Symptoms of indirect pulp cap failure are as follows:
- Spontaneous pain
- Hypersensitivity to stimuli such as cool, heat, or sweets
- Pain in response to palpation/percussion
- Swelling
- Mobility of treated teeth 5Failure Symptoms| Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Direct vs Indirect Pulp Cap
Difference between Direct & Indirect Pulp Capping
Direct and indirect pulp capping, utilizing various materials and clinical techniques, is used to maintain the health and vitality of the pulp complex and promote pulp cells to produce hard tissue (reparative/tertiary dentin).
- Direct pulp capping is performed when the pulp is visibly exposed as a result of caries, trauma, or an iatrogenic event such as unintended exposure during tooth preparation.
- With no obvious exposure to the pulp, indirect pulp capping is typically employed in deep cavity preparations.
- Any pulp capping method should ultimately aim to control bacteria, stop the advancement of any remaining caries, encourage pulp cells to produce new dentin and build a biocompatible and long-lasting seal that shields the pulp complex from noxious substances and germs.
- The success of both direct and indirect pulp capping approaches depends on the pulp complex’s initial health and vitality.
- If a tooth has a history of unprovoked spontaneous pain, necrotic or partially necrotic pulps, radiographic pathology, and/or severe hyperemia brought on by irreversible pulpitis, the prognosis for that tooth becomes poor.
- These teeth frequently need endodontic treatment or extraction at some point whereas pulps that are strong and healthy make good candidates for pulp capping techniques.1Direct vs Indirect Pulp Cap| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association
Prognosis
Success rate for Indirect Pulp Capping
- According to studies, indirect pulp cap techniques surpass direct pulp cap methods, which may be responsible for 90% of success rates. 6Prognosis| Researched based study from American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry , 7Prognosis| Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
- In a small percentage of cases, the procedure may not be successful when cavities enter the pulp chamber following the procedure resulting in inflammation of the pulp also known as pulpitis.
- This is usually rare in occurrence since indirect pulp capping is typically carried out when the pulp is healthy and free of decay in affected individuals.
Facts for successful pulp capping include:
- Even if it means leaving behind a thin layer of carious dentin, avoid exposing the pulp.
- Use saline or water to stop bleeding during the procedure.
- To ensure the success of the procedure, a properly sealed final restoration should be placed immediately following the cavity excavation. 6Prognosis| Researched based study from American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry
Takeaway
Takeaway Points for Indirect Pulp Capping
- Your dentist could suggest pulp cap therapy if the pulp of the tooth has not yet been affected by decay.
- Depending on the tooth type and degree of decay, there are two types of pulp cap treatments: direct and indirect pulp capping procedures.
- When there is no pain present but the dentin has been so profoundly affected by decay that removing it will expose the pulp, a dental practitioner may advise indirect pulp capping.
- In patients with afflicted teeth, indirect pulp capping enables them to keep their natural teeth and helps them avoid invasive procedures like root canal therapy.
- The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry examined various research and discovered that indirect pulp cap treatments, particularly in children and adolescents, have a greater success rate when compared to direct pulp cap and pulpotomy procedures.
- If the functional tooth is seen without any clinical signs or symptoms of pulp or peri radicular disease, such as the absence of spontaneous pain, non-hypersensitivity to stimuli, soft tissue oedema, or movement, the indirect pulp capping procedure is considered successful.1Takeaway| Researched based study from Michigan Dental Association ,4Takeaway| Researched based study from National Library of Medicine , 5Takeaway| Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Michigan Dental Association
Introduction | Indications | Procedure | Materials Used | Advantages | Contraindications | Direct vs. Indirect pulp cap | Takeaway
-
Cleveland Clinic
Tooth Anatomy
-
Mayo Clinic
Tooth Decay
-
National Library of Medicine
Procedure | Takeaway
-
National Library of Medicine
Failure Symptoms | Takeaway
-
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry
Prognosis
-
National Library of Medicine
Prognosis