Gums
- Featured
Featured
Frequently Asked Questions
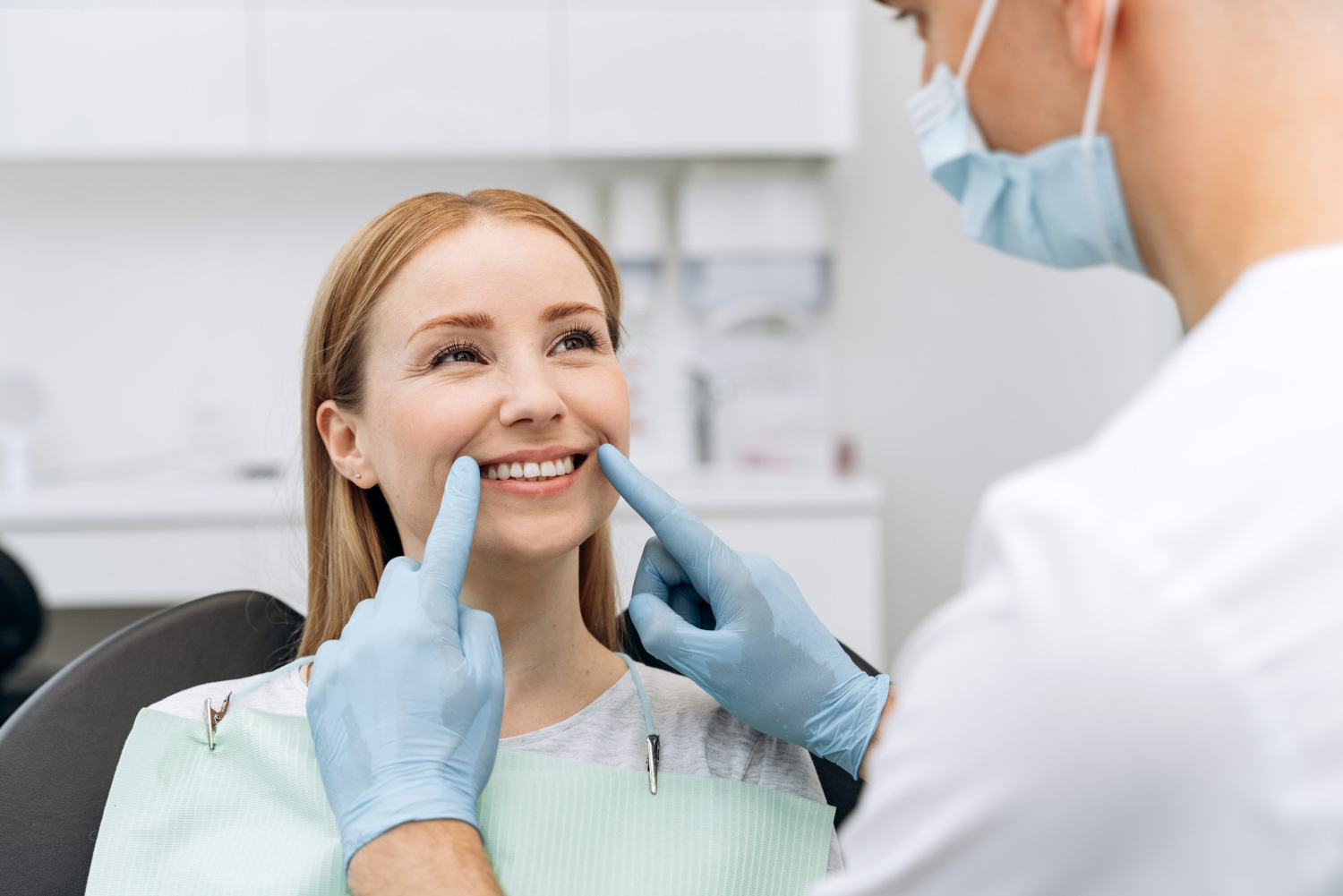
Despite being an important aspect of overall wellness, the condition of our teeth and gums is many times disregarded. While maintaining a clean, bright smile maybe one’s top priority, the condition of our gums can affect much more than just our teeth and without proper oral hygiene, unwanted bacteria can lead to oral infections, such as tooth decay and gum disease.
Types of Gum Diseases
Gum diseases primarily come in two forms:
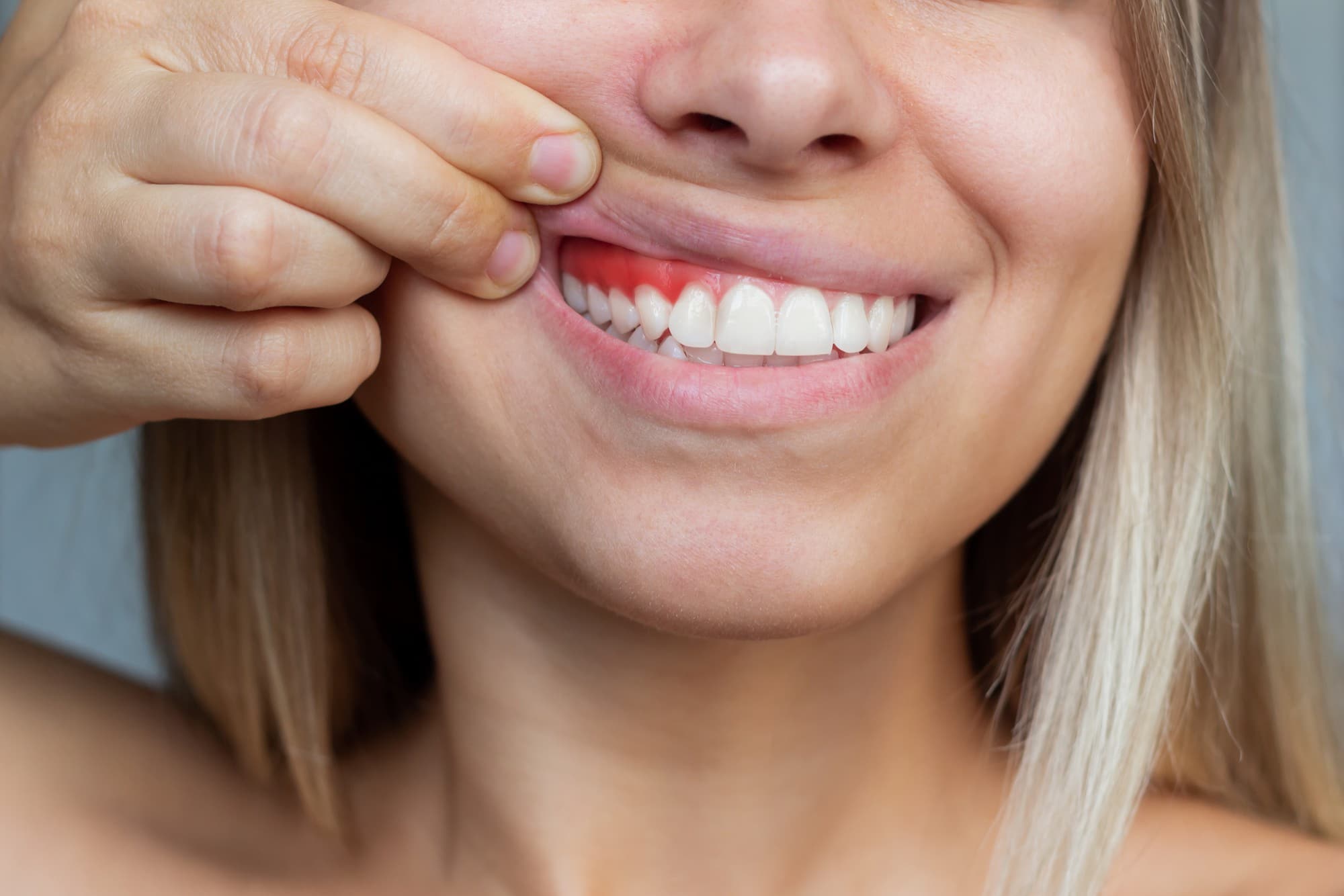
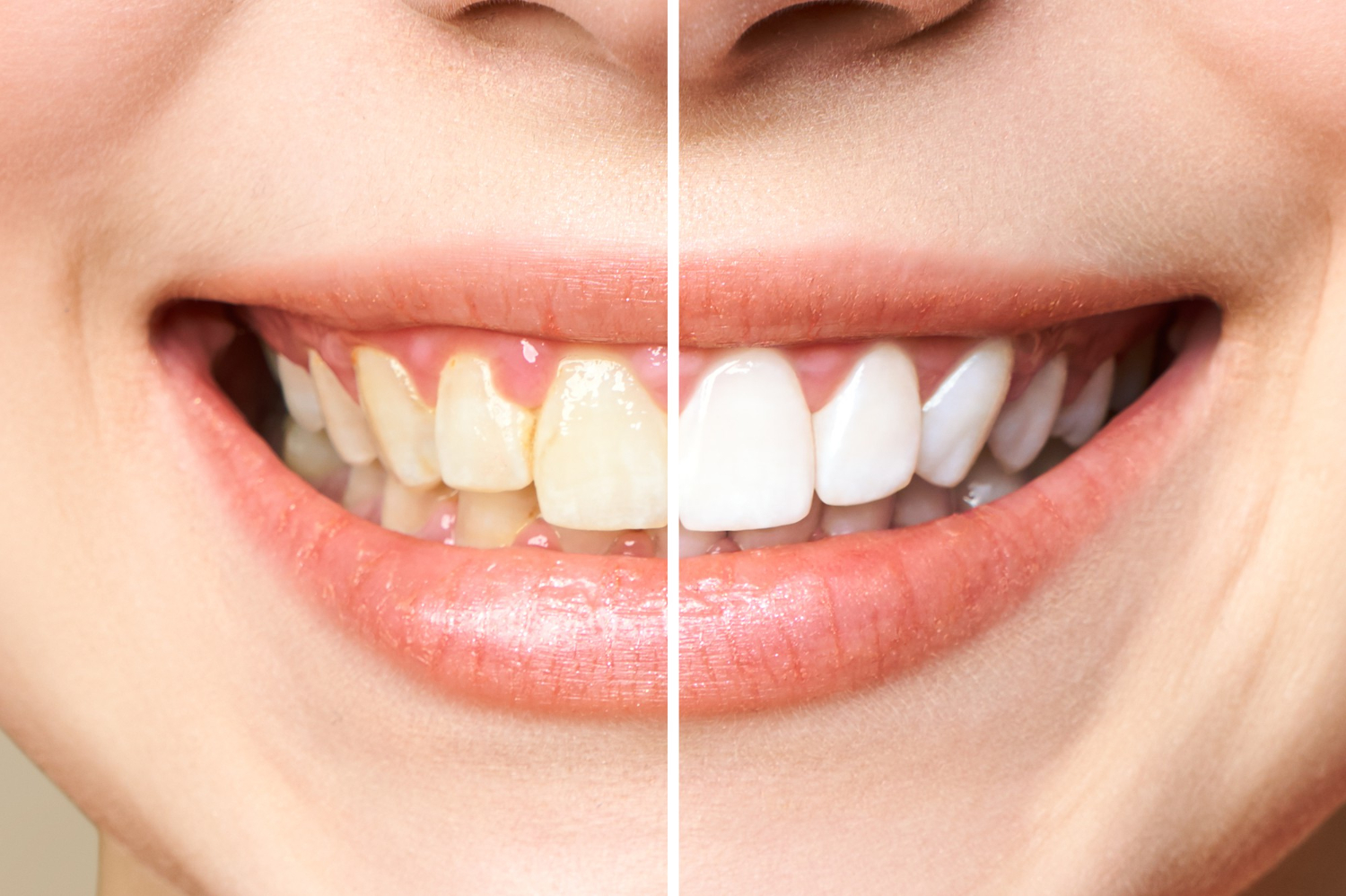
Gingivitis: Plaque accumulation on the gums and teeth causes gingivitis, the less severe type of gum disease. Gums that are red, swollen, and tender as well as bleeding when brushing or flossing are signs of gingivitis.
Periodontitis: Periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease, emerges from untreated gingivitis. Periodontitis is characterized by the gums pulling away from the teeth, resulting in bacterially contaminated pockets. Gum recession, ongoing bad breath, loose teeth, and changes in the bite are all signs of periodontitis.
- Improper Oral Health
- Medications and Drugs
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Hormonal changes
- Genetics
Some common symptoms of gum disease are:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums: The early signs of gum disease include redness and tenderness in the gum regions. This is painful to touch and may appear inflamed and swollen.
- Bleeding gums: After eating or drinking, one may observe bleeding of gums, or sometimes during brushing or flossing, which is one such of gum disease.
- Receding gums: The layers that protect the gum and tooth region may start to recede which makes the teeth look longer than usual, and exposes the roots of the teeth, which can also cause tooth sensitivity.
- Persistent bad breath: When the mouth is not cleaned properly, the bacteria present in the mouth start to grow rapidly, and this excessive build-up of bacteria produces bad breath also known as halitosis, which is a symptom of gum disease.