Vitamin B12 and its benefits

- Vitamin B12
- 16 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Vitamin B12 ?
Cobalamin, or vitamin B12, is a vitamin that dissolves in water and is essential for metabolism. It’s one of eight different B vitamins. It is offered as a dietary supplement and a prescription drug and is naturally found in some foods and added to others.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov

Facts of vitamin B12
- The largest and most physically intricate vitamin is vitamin B12.
- Vitamin B12’s active form is methyl cobalamin.
- Cyanocobalamin is the most prevalent supplement type, which the human body must transform into its active version.
- Animals need it for various biological processes, while plants do not.
- B12 can be kept in the body’s reserves for up to four years.
- Any extra or undesired amounts are excreted in the urine.
Functions
Functions of vitamin B12
The body needs vitamin B12 for several biological functions to occur, as follows:1Biological role| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- The functioning of the brain and nerves.
- In the bone marrow, for the red blood cell formation and maturation.
- Creation of DNA molecules, which carry genetic information inside cells.
- Amino acid and fatty acid metabolism.
Sources
Major sources of vitamin B12
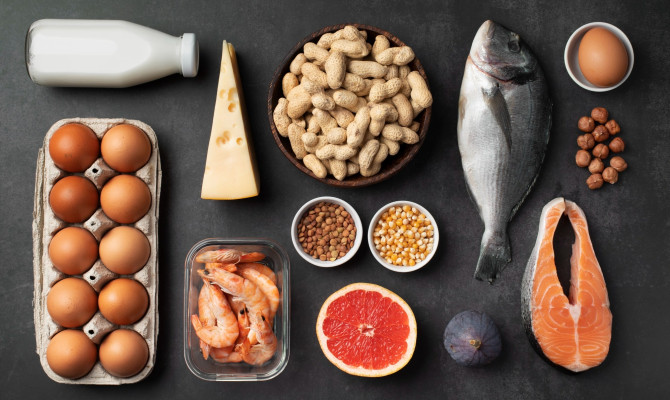
Vitamin B12 can be gotten from food sources or dietary supplements as follows:
Food sources
- Animal sources – organ meat from lambs and beef, eggs, and dairy products.2Sources| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Sea food – fishes like sardines, salmon, rainbow trout, and tuna, shellfish like clams,
- Breakfast cereals, nutritional yeasts, and other food fortified with Vitamin B12.
Supplementation
- A supplement may be necessary for those who have trouble receiving vitamin B12 from food.
- Vitamin B12 supplements come in tablet, injectable, and nasal spray forms. 2Sources| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- For some patients with pernicious anemia, problems with vitamin B12 malabsorption, or severe deficiency, doctors may provide vitamin B12 injections.
- The vitamin B12 in these injections comes in cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin.
- Older persons over 50 have been given 25–100 mcg of vitamin B12 orally daily to keep their levels stable.2Sources| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Whether or not the person has to continue taking supplements depends on the cause of the deficiency. To find the proper dosage for a specific condition, speak with a medical expert.
Dosage
Dietary requirement
The RDA, or recommended dietary allowance, is the amount that should be ingested by an individual each day.3Dosage| Researched based study from Nih.gov The daily requirement for vitamin B12 varies depends on a person’s age.
Infants
- Birth to 6 months – 0.4 mcg/day
- 7 – 12 months – 0.5 mcg/day
Kids
- 1 – 3 years – 0.9 mcg/day
- 4 – 8 years – 1.2 mcg/day
- 9 – 13 years – 1.8 mcg/day
Adolescents
- 14 – 18 years – 2.4 mcg/day
Adults
- 19 – 50 years – 2.4 mcg/day
- Pregnant women – 2.6 mcg/day
- Breastfeeding mothers – 2.8 mcg/day
Benefits
What are the benefits of Vitamin B12?
Doctors prescribe vitamin b12 for the following health conditions
Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Individuals who are deficient in vitamin B12 can be cured and avoided by taking supplements.4Health benefits| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
Imerslund-Grasbeck disease
- An uncommon hereditary disorder characterized by a B12 deficiency. Effective treatments for this illness include monthly vitamin B12 administered by doctors after a 10-day shot course.4Health benefits| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
Cyanide poisoning
- Doctors may successfully treat cyanide poisoning by injecting hydroxocobalamin, an organic form of vitamin B12.
Canker sores
- Canker sores’ symptoms appear lessened by applying vitamin B12-containing ointment or ingesting vitamin B12 under the tongue.
Hyperhomocysteinemia
- Homocysteine levels can be lowered by taking vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and folic acid together as supplements.4Health benefits| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
Post-herpetic neuralgia
- This Condition also known as shingles-related nerve pain People with nerve damage from shingles can have vitamin B12 injections in the form of methyl cobalamin six times a week for up to four weeks.4Health benefits| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
Deficiency
What are the deficiency symptoms?
A deficiency of vitamin B12 may cause the following symptoms:5Symptoms | Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
In adults
- Depression.
- Confusion.
- Fatigue.
- Headaches.
- Mood changes.
- Memory problems.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Weight loss.
- Diarrhea.
- Weak muscles.
- Trouble walking.
- Nausea.
- Decreased appetite.
- A fast heart rate.
- Difficulty balancing.
- Shortness of breath.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- A sore mouth or tongue.
- Menstrual problems.
- A pale or yellowing skin.
- Numb or tingling feeling in hands and feet
In infants
- Difficulty feeding.
- Reflex problems.
- Facial tremors.
- Problems with growth.
Deficiency reasons
A deficiency of vitamin B12 may result from the following conditions:
- Hydrochloric acid deficiency in the stomach causes problems with absorption.5Reasons | Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Reduced dietary consumption, especially among vegetarians and vegans.
- A deficiency in the intrinsic factor required for its absorption.
- Surgery to remove or bypass the small intestine’s end, where the vitamin B12 absorption occurs, is a severe medical condition.
Who are vulnerable for Vitamin B12 deficiency?
The following individuals are more vulnerable:
- People over 50.
- Women who are expecting or nursing.
- An inheritance of vitamin B12 insufficiency.
- Individuals with type I diabetes, pernicious anemia, and atrophic gastritis, among other autoimmune illnesses.
- People whose stomachs or intestines have been partially or entirely removed. (gastrectomy).
- IBS, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, chronic gastritis, and other problems in the stomach or small intestine.
- Those who are HIV-positive.
- Vegans and strict vegetarians.7Vulnerability| Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
- Long-term alcoholism.
Side effects
Side effects of vitamin B12
It may occasionally have a few side effects, such as:
- Headache.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Weakness.
- Fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Hot flashes.
- Tingling sensation in hands and feet.
- If given through shots, swelling, irritation, or pain, at the injection site.6Side effects| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Precautions
Precautions to take while consuming vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is typically regarded as safe, even at greater doses. However, the following individuals should exercise caution and consult a doctor before taking supplements:
- People sensitive or allergic to cobalt or cobalamin should avoid taking supplements.
- After getting a coronary stent, avoid taking B12, folate, and B6 together. Blood vessel narrowing may become more likely as a result of this combination.
- Because the FDA does not regulate most supplements, consumers should use caution while taking them and ensure they are bought from a reputable retailer.
- Because cyanocobalamin has an aluminum component, it is also advised to use caution when treating renal insufficiency.
- Supplements containing vitamin B-12 are considered safe when used in the recommended dosages. The safety of higher doses has also been established because the body only absorbs what is necessary and excretes the rest in urine.
Interactions
Interaction of vitamin B12 with medicine
Vitamin B12 supplementation may interact with the following drugs
Amino salicylic acid
- Taking this medication for digestive issues may make it harder for your body to absorb the B-12 vitamin.
Colchicine for Gout
- This anti-inflammatory drug could make absorbing vitamin B-12 into the body more challenging.
Metformin
- This diabetes medication may make it harder for the body to take vitamin B-128Interactions | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Proton pump inhibitors
- Omeprazole, lansoprazole, and other stomach acid-lowering medications may make it harder for the body to absorb the vitamin B-12.1Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Vitamin C supplements
- The quantity of vitamin B-12 accessible in the body may be decreased if vitamin C is taken along with vitamin B-12.
- People should take vitamin C supplements at least two hours after a vitamin B-12 dose.
Takeaway
Takeaway
Those who eat a balanced diet typically have enough B12 in their system. However, oral supplements may be advantageous for elderly people, vegetarians, vegans, and those with medical disorders that limit their capacity to absorb vitamin B-12 from food. Especially crucial when breastfeeding and throughout pregnancy. The best strategies to ensure that anyone obtains the right balance are to avoid taking excessive amounts of supplements and to eat foods high in vitamin B12 as part of a regular diet.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin B12 in Health and Disease | Biological role | Interactions
-
Medline Plus
Vitamin B12 | Sources
-
National Institutes of Health
Vitamin B12-Fact Sheet for Consumers | Dosage
-
Mount Sinai
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia | Health Benefits
-
Cleveland Clinic
Vitamin B12 Deficiency | Reasons | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | Vulnerability
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia | Vulnerability
-
Mayoclinic
Vitamin B-12 | Interactions