Melanoma: Types, Symptoms and Treatment

- Melanoma
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the cells responsible for a person’s skin color known as melanocytes. Melanoma is perhaps the most serious and possibly deadly type of skin cancer, despite being less common. Early diagnosis and management are essential for melanoma to have better outcomes.
This article will cover melanoma in depth, including its symptoms, stages, types, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, therapy, prevention, complications, and prognosis.
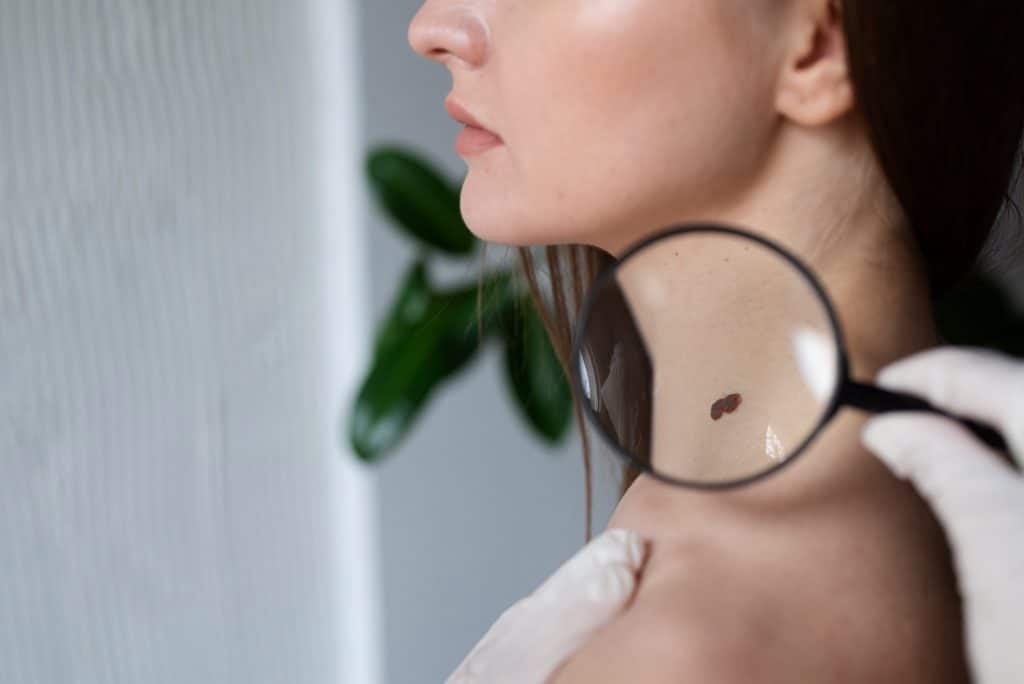

Symptoms
Symptoms of Melanoma
Recognizing melanoma’s signs and symptoms is the first step in detecting it and may include:
- A fresh mole or patch on the skin.
- The mole’s size or appearance might change.
- The spot’s edges may appear uneven rather than smooth.
- The mark could be mottled with various colors, including brown, black, blue, red, white, and light grey.
- The spot may itch or bleed.
- Underneath a fingernail or toenail is a vertical dark-brown or black line1Symptoms| Researched based study from Aad.org
Dermatologists developed the ABCDEs of Melanoma to assist people in identifying melanoma on their skin:
- Asymmetry – one half of the mole may not resemble the other2Symptoms| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Border that is irregular – the mole’s edges are uneven, rough, or poorly defined.
- Color change – the mole might appear in red, black, pink, brown, or blue.
- Diameter – of the mole is more than six millimeters.
- Evolving look – the mole’s size, shape, color, or elevation changes.
It is vital to remember that the ABCDE rule does not apply to all melanomas, and some may develop as a new spot distinct from existing moles.
Types
Types of Melanoma
There are many types of melanomas and four of the main types may be as follow:
- Superficial spreading melanoma.
- Lentigo maligna melanoma.
- Nodular melanoma.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma.
Superficial spreading melanoma
- It begins by spreading along the top layer of the skin and can eventually go deeper into the skin. This is the most frequent type of melanoma3Types| Researched based study from Mskcc.org
Lentigo maligna melanoma
- Appear as colored patches of skin that grow slowly and are also known as Hutchinson’s melanotic freckle4Types| Researched based study from Cancerresearchuk.org
- This type typically develops on the face, head, or neck, mainly affecting elderly adults with severely sunburned skin.
Nodular melanoma
- It is the second most frequent melanoma. It can be aggressive and is distinguished by a hump or node that rises above the skin’s surface and is stiff to the touch.
Acral lentiginous melanoma
- It can appear on areas that are least exposed to sunlight like the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, and under the toenail and fingernail and are most commonly seen in those with dark skin4Types| Researched based study from Cancerresearchuk.org
Stages
Stages of Melanoma
- Melanoma is staged depending on the depth of invasion, thickness, lymph node involvement, and metastatic presence.
- Stages range from zero to IV, with zero being the first stage and IV being the most complicated.
- Metastasis to the liver, lungs, bone, brain, and intestines is typical in stage IV melanoma.5Stages| Researched based study from Aimatmelanoma.org
- The staging system aids in determining the best treatment method and prognosis.
Causes
Causes and risk factors
The specific cause of melanoma is complicated and multifactorial, and research is continuing. Several risk factors, however, have been found, including:
- Family history – Melanoma risk is higher for people with a history of the disease.
- Age – Melanoma can strike anyone at any age, but the risk rises as a person ages6Causes| Researched based study from Cancerresearchuk.org
- Gender – Men are more prone than women to acquire melanoma.
- Ultraviolet radiation (UV) – Melanoma risk is increased by ultraviolet (UV) light from natural and artificial sources, such as tanning beds.
- Skin type – People with fair complexion, freckles, eyes that are light-colored, and blond hair are at an increased risk.
- Certain moles – Any abnormal or deformed moles raise the risk.
- Previous melanoma – those who have already had melanoma in the past have the likelihood of getting it again.
- Immune suppression – People with compromised immune systems, such as recipients of organ transplants, are more vulnerable7Causes| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Melanoma
For successful therapy, early detection and diagnosis are critical. Melanoma is diagnosed using a variety of approaches, including:
- Visual examination – dermatologists look for abnormal moles or lesions on the skin.
- Dermoscopy – is a non–invasive method that examines skin lesions in detail using a dermoscope.8Diagnosis| Researched based study from Dermnetnz.org
- Biopsy – If a tiny lesion is suspected and identified, the dermatologist will numb the region before removing all or part of it for laboratory testing9Diagnosis| Researched based study from Aad.org
- Imaging tests – like CT scans, PET scans, and MRIs may be used by doctors to assess if the melanoma has progressed beyond the skin.
Treatment
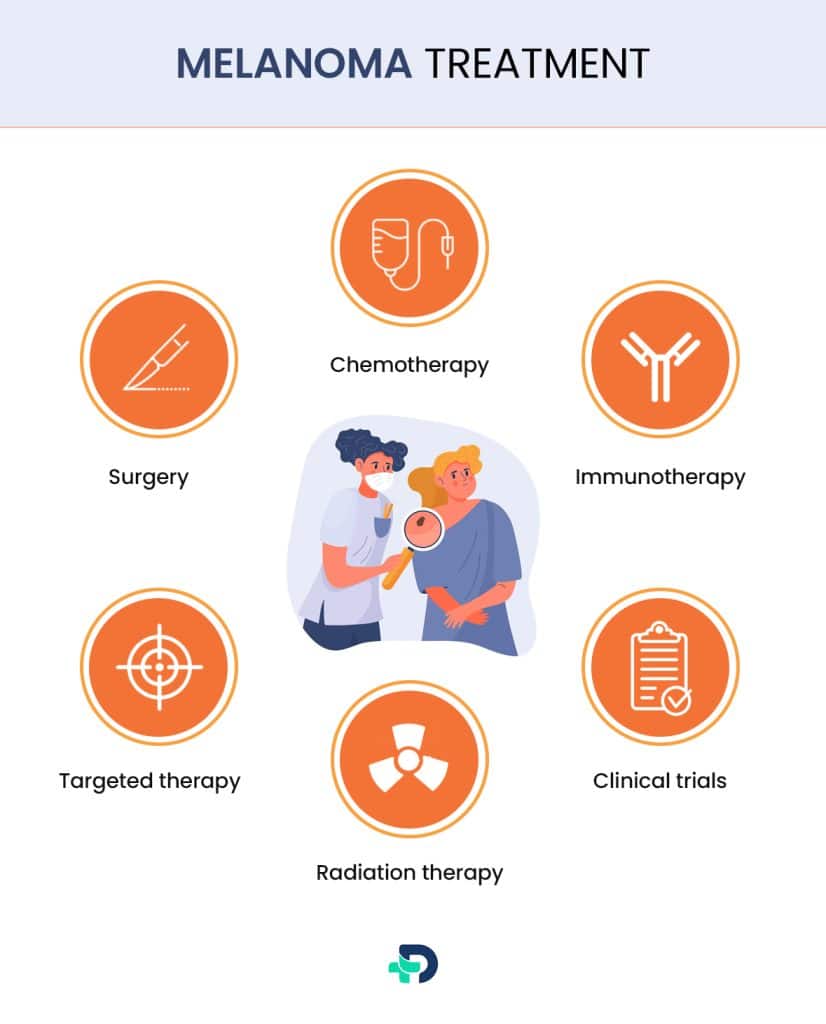
Melanoma Treatment
The stage of cancer determines the treatment strategy for melanoma and may include:
- Surgery – The first-line treatment is usually the surgical removal of the melanoma, and the scope of the surgery depends on the stage and position of the melanoma.10Treatment| Researched based study from Betterhealth.vic.gov.au
- Chemotherapy – Medications are used to destroy or slow cancer cells’ growth and spread. Chemotherapy is typically employed in advanced stages of melanoma or when the cancer has progressed to other organs.
- Immunotherapy – activates the immune system, causing it to spot and kill cancer cells and has shown promising results in treating melanoma11Treatment| Researched based study from Skincancer.org
- Targeted therapy – is intended to fight cancer cells with specific genetic abnormalities and are helpful in the treatment of advanced melanoma with particular mutations.
- Radiation therapy – entails using high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to destroy cancerous cells or shrink tumors. Radiation therapy is often utilized as a symptomatic or supportive treatment.
- Clinical trials – Participating in research studies gives you access to experimental therapies and novel medicines for melanoma.
Prevention
Melanoma Prevention
While it is not feasible to prevent melanoma, the following measures can decrease the risk:
- Limit UV exposure by avoiding direct sunlight, especially during peak hours, to limit UV exposure. All outdoor activities should be scheduled for later in the day.
- Wear protective clothing and use a broad-spectrum sunblock with a high SPF all year to protect the skin from sunlight.
- Avoid artificial tanning beds as they emit hazardous UV radiation12Prevention| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Check your skin for changes regularly and report any abnormal moles or lesions to a healthcare expert.
- Be aware of risk factors – Recognizing your risk factors and taking proper actions may help in prevention.
- Seek professional skin tests regularly as full-body skin checks can help discover early symptoms of melanoma.
Complications
Complications
Melanoma, if left untreated or found late, can result in significant problems such as the following:
- Spread to distant organs.
- Secondary infections.13Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Scarring and hyperpigmentation.
- Anxiety and depression.
- Lymphedema.
- Local recurrence13Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Prognosis
Prognosis
Melanoma in its early stages is curable and has a high survival rate. However, advanced-stage melanoma has a reduced survival rate. Prognosis is considerably improved by early discovery, intervention, and effective therapy. Getting medical care for any worrisome moles or skin abnormalities is critical. Melanoma prognosis has improved dramatically because of advances in diagnosis and treatment. We can reduce the effect of melanoma and save lives by raising awareness and emphasizing skin health.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
American Academy of Dermatology Association
SKIN CANCER TYPES: MELANOMA SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS | Symptoms
-
Medline Plus
Melanoma | Symptoms
-
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Melanoma | Types
-
Cancer Research UK
Melanoma |Types
-
AIM at Melanoma
Stages of Melanoma | Stages
-
Cancer Research UK
Risks and causes of melanoma | Causes
-
Cleveland Clinic
Melanoma | Causes
-
DermNet New Zealand Trust
Dermoscopy of melanoma | Diagnosis
-
American Academy of Dermatology Association
SKIN CANCER TYPES: MELANOMA DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT | Diagnosis
-
Better Health Channel
Melanoma | Treatment
-
Skin Cancer Foundation
Melanoma Treatment | Treatment
-
Mayo Clinic
Melanoma | Prevention
-
National Library of Medicine
Malignant Melanoma | Complications