Lupus: What do you need to know?

- Lupus
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Lupus?
Lupus is a persistent autoimmune condition that can impact numerous bodily systems. Lupus arises when the immune system, which typically defends the body against infections and illnesses, mistakenly attacks its own tissues. This assault triggers inflammation and, in certain instances, endures damage to tissues, which may extend throughout the body. Individuals with lupus may experience periods of heightened symptoms referred to as flares, as well as periods of reduced symptoms known as remission. The intensity of lupus flares can vary from minor to severe, and their onset is unpredictable. Nevertheless, with appropriate treatment, many individuals living with lupus can effectively manage the condition.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov

Types
Types of Lupus
The four types of Lupus are as follow:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE)
- Drug-induced Lupus
- Neonatal Lupus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- SLE is the prevailing form of lupus.
- It can manifest in varying degrees of severity and impact diverse body areas.
- Common indications consist of weariness, hair thinning, sensitivity to sunlight, achy and inflamed joints, unexplained fever, skin eruptions, and renal complications.2Types| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE)
- This variant of lupus is a dermatological condition that can impact individuals with or without SLE.
- Symptoms can encompass skin rashes, alopecia, inflammation of blood vessels, ulcers, and heightened sensitivity to sunlight.
Drug-induced lupus
- This type is triggered by specific drugs.
- The indications of drug-induced lupus encompass joint discomfort, muscular pain, and elevated body temperature. However, the symptoms are generally less severe.2Types| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
- Furthermore, drug-induced lupus seldom impacts vital organs.
Neonatal lupus
- Neonatal lupus is an uncommon disorder in newborns that stems from specific maternal antibodies.
- These specific antibodies can be detected in mothers diagnosed with lupus.
- However, having lupus does not automatically imply that the condition will be transmitted to the baby.
- The majority of infants born to mothers with lupus are unaffected by the condition.
- It is also feasible for an infant to develop neonatal lupus even if the mother is not currently diagnosed with lupus. However, in cases where an infant is diagnosed with lupus at birth, it is not uncommon for the mother to subsequently develop lupus later in her life.
- Indications of neonatal lupus upon birth can manifest as a cutaneous rash, hepatic issues, or diminished blood cell counts.2Types| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Symptoms
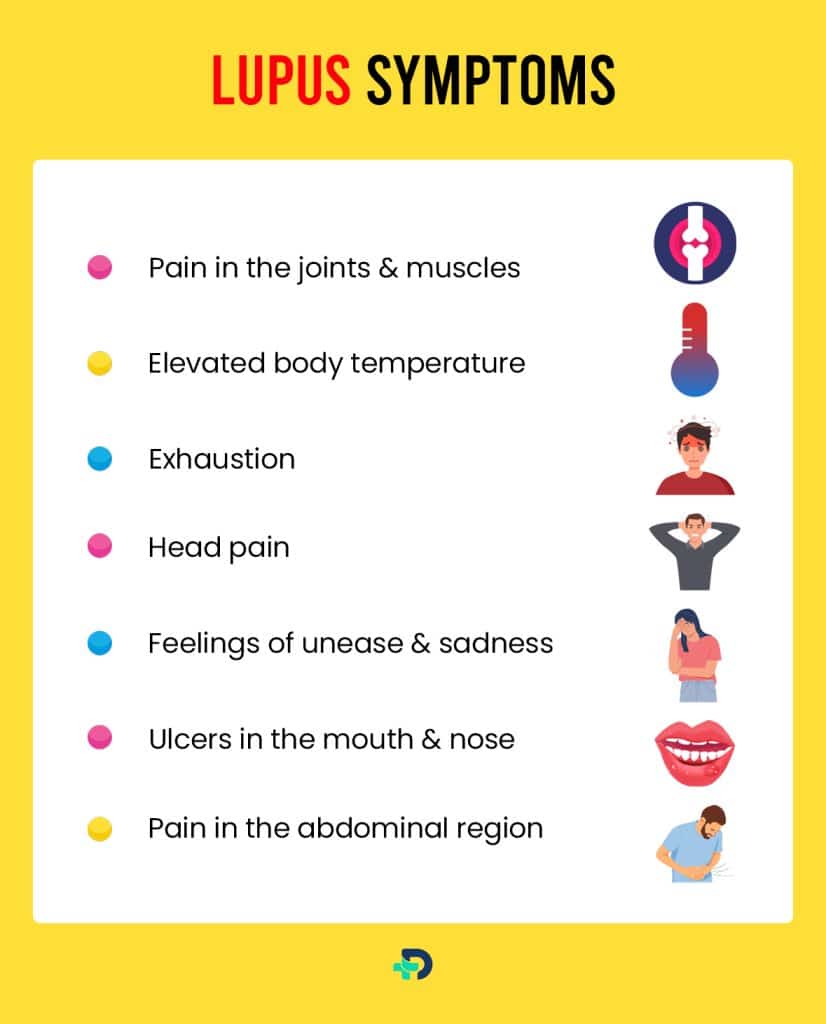
Lupus symptoms
The manifestations of lupus can vary and might encompass:
- Pain in the joints and muscles
- Elevated body temperature
- Hair shedding
- Exhaustion
- Skin eruptions
- Head pain
- Cognitive difficulties and memory issues
- Feelings of unease and sadness
- Impaired kidney function
- Pain in the chest or difficulty breathing due to inflammation of the heart or lung lining.
- Ulcers in the mouth and nose
- Seizures or changes in vision
- Pain in the abdominal region.3Types| Researched based study from betterhealth.vic.gov.au
Causes
Causes of Lupus
A significant number of researchers hold the belief that the development of lupus is influenced by a combination of factors originating from both internal and external sources.
Genetics
- Lupus is considered hereditary, as more than 50 genes have been identified that are associated with the development of the disease.
- The genes are observed more frequently in individuals affected by lupus compared to those who do not have the condition.
- Although the direct causative role of most of these genes in lupus is yet to be established, they are believed to have a contributing influence.
- It is possible for lupus to develop in individuals without a familial history of the disease; however, there is a likelihood of other autoimmune disorders being present in certain family members.
Hormones
- Although the hormone estrogen is produced by both men and women, its production is notably higher in females.
- A significant number of women experience heightened lupus symptoms prior to their menstrual periods and/or during pregnancy when estrogen levels are elevated, which suggests a potential correlation between estrogen and the severity of lupus.
- However, no definitive causal relationship has been established between estrogen, or any other hormone, and lupus.
Environment
- An environmental factor, such as a virus or conceivably a chemical substance, unexpectedly encountered by a genetically vulnerable individual, could potentially serve as a catalyst for the onset of the condition.
Examples of environmental factors include:
- Ultraviolet light
- Sulfa medications, which increase an individual’s sun sensitivity
- Infections, respiratory illnesses, or viral diseases.
- Psychological stress, like marital separation, illness, bereavement, or other life challenges.
- Fatigue and any other elements that impose strain on the body, such as medical interventions, physical damage, harm, maternity, or the process of delivering a baby.
- Antibiotics-Tetracycline medications, which may increase vulnerability to the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation from the sun.4Causes| Researched based study from Lupus.org
Prevalence
Prevalence of Lupus
- Approximately 1.5 million individuals in the United States, and at least five million people globally, are affected by a form of lupus.
- Lupus primarily affects women of childbearing age.
- Out of every ten adults with lupus, nine are women. Nevertheless, lupus can also occur in men, children, and teenagers.
- A study conducted in 2014 revealed that women from racial and ethnic minority groups generally develop lupus at a younger age, experience more severe complications, and have higher mortality rates.
- It is estimated that approximately 10-15 percent of individuals with lupus will experience premature death due to lupus-related complications.4Prevalence| Researched based study from Lupus.org
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Lupus
Diagnosing lupus can be challenging as it presents a multitude of symptoms that are frequently misinterpreted as symptoms of other illnesses.
Some common ways of diagnosis lupus are discussed below:
Medical history
- Obtaining a detailed medical history is crucial in the diagnosis of lupus, as it helps identify patterns of symptoms, previous diagnoses, and family history of autoimmune diseases.
Physical examination
- During a comprehensive physical examination, rashes and other signs of abnormalities will be looked for by a doctor, in order to identify any indications that something may be wrong.
Blood and urine examination
- During the diagnostic process, blood and urine tests will be conducted by the doctor.
- The presence of lupus-associated autoantibodies in the immune system can be determined through the antinuclear antibody (ANA) test.
- While most individuals with lupus have a positive ANA result, it should be noted that a positive ANA does not always indicate the presence of lupus.
- If the ANA test is positive, further testing for antibodies specific to systemic lupus erythematosus is likely to be ordered by the doctor.
Biopsy of the skin or kidney
- A skin or kidney biopsy, which involves the surgical removal of a tissue sample, allows for microscopic examination of the tissue.
- The passive procedure enables the identification of autoimmune disease indicators in the examined skin or kidney tissue.5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Treatment
Treatment of Lupus
While currently, lupus cannot be cured, various treatments can provide symptom relief and improve overall well-being. The approach to treatment is tailored to individual symptoms and requirements.
The objectives of treatment include preventing flare-ups, addressing symptoms as they arise, and minimizing organ damage and associated complications.
Medications
Medications prescribed by dermatologists can be utilized to address a lupus rash, manage other skin issues, promote hair regrowth, and alleviate discomfort.
A treatment regimen for cutaneous lupus may encompass the administration of one or multiple medications from the following options:
Corticosteroids
- A corticosteroid, whether applied topically to the skin or taken orally, is frequently effective in producing rapid responses in cases of cutaneous (skin) lupus.
Antimalarial medication
- These, known for their use in treating malaria, can also be employed to alleviate skin rashes caused by lupus and prevent flare-ups.
- The effects of antimalarial medication are gradual, and it may take 2 to 3 months before noticeable improvements are observed.
Tacrolimus ointment
- It can be considered an alternative for treating skin areas that are not responsive to corticosteroids.
- Additionally, this ointment may assist in hair regrowth, but its effectiveness depends on whether scarring has occurred.
Medications that possess immunosuppressive properties
- These are employed to help regulate and calm the immune system.
Biologic medications
- These, developed to address inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, are utilized in the treatment of lupus, which is characterized by inflammation and an autoimmune response.
Laser therapy
- This can be an effective option for individuals with persistent thick patches of discoid lupus on the skin that do not improve with treatment.
- This can also be used to address hyperpigmentation, which commonly occurs on darker skin tones after lupus rashes, raised patches, or sores have resolved.
- Additionally, laser therapy can help reduce scarring resulting from acute cutaneous lupus or discoid lupus.6Treatment| Researched based study from Aad.org
Self-care tips
Lupus remedies involve the following:
- Taking precautions to minimize sun exposure
- Using sunscreen
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Receiving annual flu vaccinations
- Attending routine medical check-ups
- Adopting a nutritious and well-balanced diet
- Effectively managing stress levels
- Moderating alcohol consumption.7Treatment| Researched based study from Betterhealth.vic.gov.au
Diet
- Consuming omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as fish oil, canola oil, salmon, and tuna, may have a positive impact on overall health.
- Consuming primrose oil and soybean oil can also be effective.
- Consuming a daily amount of 30 g of flaxseed oil has been shown to reduce serum creatinine levels in individuals with renal dysfunction associated with SLE.
- Maintaining a moderate protein intake of 0.6 g/kg/day, including sources such as meat and eggs, can be beneficial for enhancing renal function in patients with SLE.
- Consumption of alfalfa sprouts or supplements containing alfalfa should be avoided, as a chemical compound found in alfalfa has the potential to induce symptoms of lupus.
- Certain individuals with lupus may require supplements, such as vitamin D, if prescribed by a doctor.
- Incorporating fruits, leafy greens such as spinach and kale, dairy products like milk, yogurt, and soy milk, as well as whole-grain cereals fortified with calcium, can be beneficial additions to the diet.8Diet| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Risk
Who are at risk?
- Gender-Lupus is more prevalent among women, with symptoms and diagnosis typically occurring between the ages of 15 and 44.
- Age-Only a small proportion, around 15 percent, of individuals diagnosed with lupus experience symptoms before the age of 18.
- Race-In the United States, lupus is more commonly found in people belonging to ethnic groups, as compared to the Caucasian population. Furthermore, it has been observed that lupus tends to develop at an earlier age and can be more severe in these ethnic groups.
- Family history-There is a 5-13 percent chance for relatives of individuals with lupus to develop the condition. The likelihood is around 5 percent for children of mothers with lupus to develop the disease4Risk| Researched based study from Lupus.org
Prevention
Prevention of Lupus
- Consistent adherence to prescribed lupus medications, even during periods of remission, is crucial for preventing flares and reducing the potential for side effects in individuals with lupus.
- To prevent lupus flares triggered by UV rays, it is important for individuals with lupus to avoid sunlight during peak hours, apply sunscreen regularly, and utilize sun-protective clothing.
- To prevent flares triggered by emotional stress and exhaustion, individuals with lupus should prioritize sufficient sleep, maintain restfulness, proactively plan activities to minimize stress, and seek assistance when necessary.
- Maintaining a well-rounded diet that includes a diverse range of nutritious foods like fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and moderate portions of lean protein sources such as meat, legumes, etc. is crucial9Prevention| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Prognosis
Prognosis of Lupus
- Presently, the outlook for individuals with lupus is more favorable than ever before.
- Advancements in medical science and improved treatment options have resulted in approximately 80-90% of people with lupus being able to lead a normal lifespan.
- Although a cure for the disease has not yet been discovered, and although fatalities can still occur, the majority of individuals with lupus today do not succumb to the disease.
- Severe flare-ups of lupus carry an increased risk of being life-threatening for individuals experiencing them.
- While it is true that some individuals with lupus may experience severe recurrent attacks that necessitate hospitalization, the majority of people with lupus, particularly those who maintain a healthy lifestyle, typically have infrequent hospitalization requirements.
- Individuals with non-organ threatening forms of lupus can anticipate a normal lifespan by adhering to their doctor’s instructions, taking prescribed medications as directed, and promptly seeking medical assistance for unexpected medication side effects or new lupus symptoms4Prognosis| Researched based study from Lupus.org
Takeaway
Key takeaways
- Lupus is a lifelong disease that primarily affects women, with symptoms often emerging between the ages of 15 and 44.
- Lupus can be a serious condition and can have varying degrees of severity, but with proper management and treatment, the majority of individuals can expect to live a normal lifespan.
- Each individual’s experience with lupus is unique, and treatment plans may vary depending on the specific manifestations and severity of the disease.
- It is important for individuals with lupus to work closely with their healthcare team to tailor a comprehensive treatment approach that addresses their specific symptoms and needs.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus) | Overview
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Lupus in Women | Types
-
Better Health Channel
Immune system -Lupus | Symptoms
-
Lupus Foundation of America
Lupus | Prevalence | Risk | Causes | Prognosis
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Diagnosing and Treating Lupus | Diagnosis
-
American Academy of Dermatology Association
LUPUS AND YOUR SKIN: DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT | Treatment
-
Better Health Channel
Lupus and medication | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Significance and impact of dietary factors on systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis | Diet
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Lupus | Prevention