Alopecia: Types, Diagnosis, and Management

- Alopecia
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
Overview
Alopecia is nothing but the sudden loss of hair, either all over or in patches from areas where you normally grow hair. Hair grows all over the human body except on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet. The loss of hair gets worse over time. You lose about 100 hairs from your head each day.
It is very common to see hair loss or balding in individuals with age when baldness runs in their family. There are so many treatment options available to prevent or decrease further hair loss, but it is always better to talk to a dermatologist to understand the cause of your hair loss before starting any treatment.
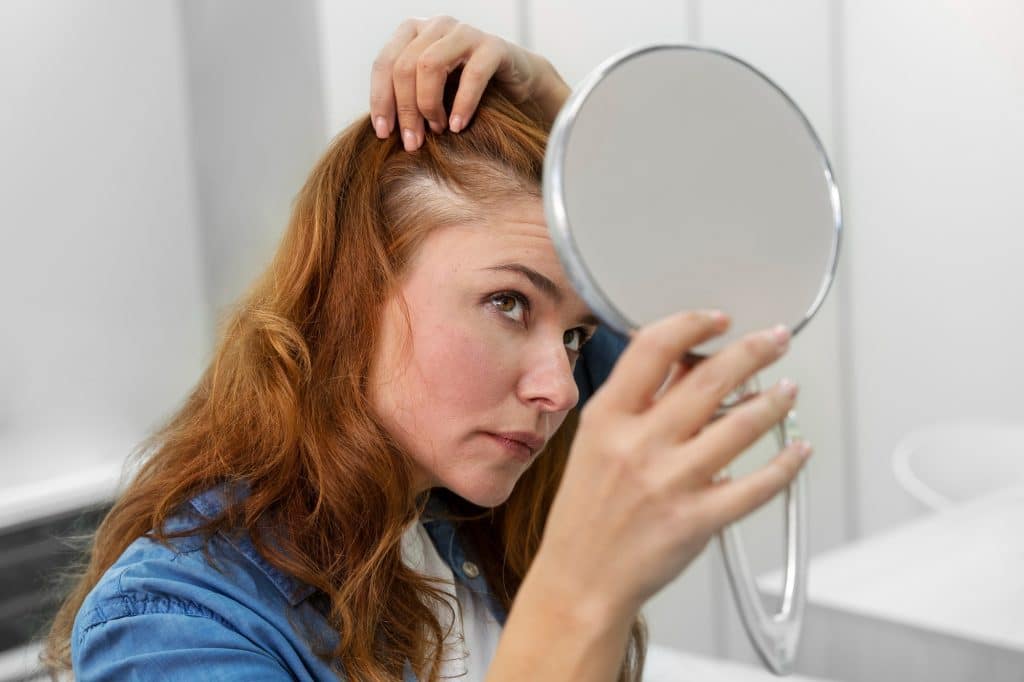

Prevalence
Prevalence
Alopecia areta is an autoimmune disorder in which there is temporary hair loss that does not leave a scar behind. 1there is an unpredictable course and it can manifest in different forms. 1prevalence | Researched based study from nih.gov Both women and men are mostly affected equally by alopecia areta and it can affect 2% of the global population at some point in their lifetime.2prevalence | Researched based study from nih.gov It can affect individuals of any age. If there is an onset at a very early age, there could be an increased risk of an extended lifetime disease. The disease affects both children and adults, and it is distinguished by oval patches of hair loss, loss of all the hair on your scalp, loss of all the body hair, or hair loss in the back or sides of the head like a band. 3prevalence | Researched based study from nih.gov
Vulnerability
Who is at risk?
- You have a slightly larger risk of developing alopecia if you have a family member suffering from this condition.
- If the autoimmune disease runs in your family, it could increase your risk.
- Males have an increased risk of developing alopecia areta in childhood
- Females are likely to develop it in their adolescence and show nail involvement or other autoimmune diseases. 4who is at risk?| Researched based study from nih.gov
- If you have conditions like diabetes, lupus or thyroid problems.
Symptoms
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of hair loss in patterns mentioned as follows could be observed:
- Exclamatory point hairs (at the periphery of hair loss patches)
- Smooth patches of hair loss
- Hair loss with sharply defined borders
- Round patches of hair loss
- Total loss of hair on the scalp
- Total loss of hair on the body and the scalp 5signs and symptoms| Researched based study from nih.gov
- A band-like hair loss on the sides and back of your head
- Hair loss that is spread out causes thinning of hair
- Repeated hair loss in one particular area
Some abnormalities in the nails 6signs and symptoms | Researched based study from nih.gov could be observed as follows:
- Nail pitting
- White nails (transverse whitening or patches)
- Spoon shaped nails
- Thinning or thickening of nails
- Shedding of nails
- Red spots in the nails
Causes
Causes of alopecia
- Hereditary cause- mostly pattern baldness could be inherited. Men are more harmed than women. By the age of 70, over 80% of males exhibit male pattern baldness symptoms.
- Autoimmune conditions- lupus, alopecia areta, etc.
- Nutritional deficiencies- protein-calorie malnutrition, iron, zinc, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption syndrome.
- Habits– some people have the habit of pulling their hair or rubbing the scalp vigorously, also tying their hair too tight causing the constant pulling effect.
- Emotional stress- is often temporary and stops once the stress is managed.
- Physical stress- severe infections, childbirth, major surgeries, sudden blood loss, and crash diets can cause hair loss.
- Improper hair care – excessive shampooing, hair dying with harsh chemicals, or blow drying with hot air can damage the hair follicle.
- Scalp infections- ringworm infection of the scalp (tinea capitis), bacterial infections of the scalp, fungal infection of the scalp, or dandruff causing inflammation of the scalp leading to temporary hair loss and patches of red, scaly skin.
- Hormonal imbalances- start, stop, or change of combined oral contraceptive pills (COCP), Polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD)
- Acute illness – blood loss or trauma, burns
- Chronic illness – thyroid dysfunction, hepatic or renal failure, HIV, sarcoidosis, Syphilis infection, tumor of the adrenal gland or the ovaries.
- Medications- beta blockers, anti-coagulants, retinoids, anti-depressants, anti-arrhythmic, anti-thyroid drugs.
- Cancer treatment- hair loss due to radiation therapy and chemotherapy is generally reversible. 7Causes of alopecia | Researched based study from nih.gov
- Excessive exposure to arsenic, and thallium.
- Aging- hair follicles in both men and women, cease to grow as we age. This is not associated with any disease.
Types
Types of alopecia
- Alopecia Areta- It is an autoimmune disorder where your body’s immune system starts attacking your healthy hair follicles which results in hair fall. It can be inherited. There are few types of alopecia areca like patchy alopecia areca, alopecia totalis, alopecia universalis, alopecia incognita, Ophiasis and sisaipho type.
- Androgenic alopecia- when the androgen in the body gets increased beyond normal values, it causes hair loss. In males, you observe male pattern hair loss where there is recession of your hairline and thinning of hair at the crown. In females, the hair loss pattern is similar to male pattern baldness but starts usually with thinning hair along the parting line. Complete balding is very rare in females.
- Cicatricial type – the cause of this type is not known. But this inflammatory condition is developed after the skin undergoes severe infections or burns.
- Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia- this occurs in a group of conditions where the hair follicles are destroyed and replaced by scar tissues resulting in permanent hair loss.
- Lichen planopilaris- the hair follicles are irreversibly damaged by the chronic inflammatory disease lichen planopilaris. This affects young women more than men. Patches of hair loss happen and the patches of the scalp appear smooth.
- Frontal fibrosing type- this is a type of lichen planopilaris, but the hair loss occurs from the hairline and eyebrows. It usually causes slow and progressive hair loss. This mostly affects women after menopause.
- Chemotherapy-induced alopecia – is usually the side effect of the medications used. And it is the most distressing type of alopecia. Mostly temporary.
- Traction alopecia- constant pulling of hair is seen when the hair is styled too tight in a ponytail or a braid, leading to hair loss. If stopped early, it is completely reversible but could become could end up damaging the follicles irreversibly over a long period.
- Trichotillomania- it is a psychological condition where you cannot stop pulling your hair even if it pains. People usually pull hair from their scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
- Telogen effluvium – excessive hair loss occurs. It could be a self-limiting type in case of childbirth, major surgery, etc., or persistent, as is the case with female pattern baldness.
- Alopecia barbae- is an autoimmune disorder where beard hair starts falling out in small circular patches. It can be progressive sometimes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, your doctor may ask you questions related to your family history, medical history, your diet, your hair care routine, etc. following which you may be asked to undergo a few tests:
- Blood tests- might be done to understand if you have any deficiencies or any other underlying medical conditions that are contributing to your hair fall.
- Pull test- this is done to find the stage of your shedding process and the doctor gently pulls your hair in a bunch. Depending on the number of hair that comes out, your doctor evaluates your condition. Less than 3 hairs per area normally come out with every pull. If the hairs that come out are more than 10. The pull test is considered positive.
- Pluck test- this test is done by pulling your hair by the roots and the root of the hair is viewed under a microscope to find out the phase of your hair growth and also can be done to diagnose any defect in the telogen, or anagen.
- Daily hair count- when the pull test comes out negative, daily hair count is usually done. In this method, every day the hair that is fallen out during morning combing or washing is collected in a clear bag. Usually, 100 hairs fall out every day, but during washing, an expected hair fall of 250 hairs can happen. If anything, more than that is said to be abnormal.
- Trichoscopy- it is a non-invasive method of evaluation of hair and scalp. Hand-held dermo scope or a video dermo scope is used in this method. 8Diagnosis | Researched based study from Infona.pl
- Scalp biopsy- biopsy of the scalp is usually taken when alopecia is present in an individual but the type has to be found. Your doctor may scrape the skin from your affected scalp or the hair itself from the affected areas. This can assist in determining whether an underlying infection is the root cause of hair loss.
Prevention
Prevention
Hair fall can be prevented in general conditions by taking a few measures, as follows:
- Avoid hairstyles that pull your hair back or on the sides like tight braids, tight ponytails, etc.
- Avoid using overheating hair styling tools like hair iron, high-heat blow dryers, hair curling iron, etc.
- Do not put your hair through chemical bleaching or any extensive chemical treatment.
- Use hair products that are suitable to your hair, you cannot use every product that comes in the market.
- Applying rosemary essential oil to your scalp may be equally effective as minoxidil for the stimulation of hair growth. 9Prevention| Researched based study from nih.gov
- Using a natural brush or comb instead of plastic brushes and combs can decrease hair fall induced by the materials due to friction.
- Applying shampoo or scalp treatments that have antioxidants in them, may help you decrease hair loss and improve the health of your scalp. 10Prevention| Researched based study from nih.gov
- Eat a healthy and nutritious diet that includes enough protein, calories, and minerals.
- Avoid crash diets to lose weight.
- Find strategies to control your stress.
- Manage your medical conditions if any.
- Washing your hair and scalp on a regular basis will help you maintain good hygiene.
- Try using a cooling cap during chemotherapy to decrease hair fall.
- Start taking multivitamin supplements if required (always consult a doctor before this)
- Massaging your scalp regularly is shown to improve your scalp’s blood circulation.
- Protect your hair while sleeping by sleeping on a satin or silk pillowcase instead of cotton cases to decrease hair fall due to friction.
- Applying coconut oil to your hair is proven to protect your hair from damage from Ultraviolet radiation
When should you worry?
Talk to your doctor if you notice any of the following to avoid progression to a permanent irreversible problem,
- Rapid hair loss at an early age.
- Pain or constant itching of your scalp.
- Hair loss in any unusual pattern.
- There is a noticeable recession in your hairline.
- Bald spots or hair loss are seen on your eyebrows or beard.
- You are also experiencing acne, excessive facial hair, and irregular periods along with hair loss.
- You are a woman experiencing male pattern hair fall.
- Infected scalp with redness, itchiness, or foul-smelling discharge.
- The skin of your affected scalp gets red or scaly.
- If your hair falls are more in number than usual and are visible to you.
Reversal
Can you reverse hair loss?
Whether or not hair loss can be reversed purely depends on the cause. It could be reversible in certain conditions like,
- Post-partum hair loss- usually occurs due to a sudden drop in estrogen levels and is usually temporary. It could last up to 3 months after childbirth. If it exceeds that, please consult your dermatologist.
- Hair falls due to ringworm infection of the scalp can be fully reversed when patients are treated early. If left untreated, it could lead to an abscess which could permanently damage the hair follicles, causing permanent baldness in the affected area.
- People experiencing hair fall due to stress can get back their hair if they start managing their stress effectively.
- Hair falls due to any major illness or infection like typhoid or any major surgery can be reversed once the patient recovers from it.
- If medicines for any illness are causing hair loss, hair will start to grow back once the medication is stopped.
- Hair fall can be recovered even in mild cases of autoimmune disorders.
- Chemotherapy-induced hair falls are usually temporary and are reversible once the treatment is completed.
Complications
Complications related to alopecia
- Psychosocial complications: people who experience sudden hair loss could be at an increased risk to develop psychosocial complications like anxiety and depression.
- Ringworm infection of the scalp in children may lead to irreversible hair loss if untreated at an early stage. This could make them get bullied in school resulting in social anxiety disorder.
- Patients with alopecia should be tested for other autoimmune diseases like vitiligo, thyroid conditions, etc.11Complications | Researched based study from nih.gov
- Patients with alopecia areata may have an increased risk of developing insulin resistance. 12Complications | Researched based study from nih.gov
Treatment

Treatment options
Alopecia can be managed effectively in its early stage by detecting and treating the cause. The majority of the time (80%), hair regrows naturally within a year. There are several treatment options available based on the stage of hair loss, its severity, and the cause.
The following medicines can help treat generally hereditary pattern baldness.
- Minoxidil is the most common medication available. It is most effective if used directly on your scalp once every day for women and twice a day for men. This works well to stop additional hair loss and to stimulate hair growth. Results typically don’t appear for at least six months.
- There is another drug called finasteride which is usually prescribed for men. This could slow the process of hair loss and also may help with regrowth.
- Corticosteroids- when taken, can suppress your immune system and reduce the damage caused to the healthy hair follicles. These drugs are available as injectables, topical solutions, or oral tablets.
Other treatment options include:
- Micro-needling – is a recently found treatment method to boost hair growth. The scalp is punctured with microneedles promoting the production of collagen. This in turn can regrow your hair.
- Immunotherapy- Immunotherapy has been discovered to be a very successful treatment for hair loss. You need to apply diphencyprone (DPCP) to the affected areas, once in seven days, slowly increasing the doses. Hai may start to appear after about 3 months of treatment. Once you stop your treatment abruptly, hair may start to fall out again.
- Platelet-rich plasma therapy (PRP): in this treatment, your blood plasma is isolated from the remaining components of your blood. This is then injected into your scalp, where it may assist to improve the health of your scalp and the conditions under which your hair can grow. Hair loss is decreased by doing PRP and this also may increase your hair growth after a few sessions.
- Laser therapy- Laser therapy may help your hair fall by improving your hair density.
- Hair transplant surgery- this is preferred in cases where only the top of your head is affected. This is done by a dermatologist or a cosmetic surgeon. The damaged area normally receives hair transplantation from a different location on your head. You do not have to stay in a hospital for this procedure. To achieve the desired outcome, you might need to repeat the process a few times. If your hair loss is hereditary, it can progress even after this surgery.
Care
How to take care of alopecia symptoms?
- Manage your stress – practice mindfulness, meditation, yoga, exercise, or involve yourself in some sports activities that you may like.
- Eat a balanced diet – helps with your hair growth.
- Talk to your hair stylist for ideas to cover the affected part of your scalp with your remaining hair.
- You can use extensions or wigs to cover the affected area in case of temporary or permanent baldness.
- You may need to wash your scalp and hair regularly and maintain its hygiene to improve the health of your hair and scalp.
- If your eyelashes are lost due to alopecia, you may want to wear sunglasses to protect your eyes while you are out.
- You can use a hat or a cap or a scarf to cover your head if it bothers you.
Myths
Myths related to alopecia
- Alopecia/baldness can affect only your scalp: this is not true, as alopecia may even lead to the loss of a patch of hair or total loss of hair of your beard, body hair, eyebrows, and even eyelashes in some cases.
- Some people like to believe that alopecia can occur only in people who are unhealthy. However, the fact is that many people who develop alopecia are in good health. It happens when your immune system is working well but mistakenly starts attacking your healthy hair follicles, thus contributing to your hair loss.
- Some fear alopecia is contagious- This is 100% wrong. Autoimmune disorders are passed through genes and do not show symptoms until they get triggered by factors like hormonal imbalance, severe infections, physical stress, etc.
- If you think vitamins can stop your hair loss, you may be wrong. As Vitamin supplements will only work for your hair loss if your hair loss is due to any particular vitamin deficiency. In rare circumstances, consuming too many vitamins might have a detrimental impact and speed up hair loss.
Outlook
Outlook
Alopecia or baldness is treatable in some cases where you can regrow your hair once the reason for your hair fall is found and treated. In some cases, where permanent damage to your hair follicles occurs, you may not be able to get back your lost hair. In such situations people may develop anxiety or depression. There are online support groups in which you can share your challenges and concerns. If that does not help, you may need to seek help from a psychological counsellor.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Alopecia areata | Prevalence
-
National Institutes of Health
Alopecia areata: a review of disease | pathogenesis
-
National Institutes of Health
Overview of alopecia areata | Prevalence
-
National Institutes of Health
Gender differences in alopecia areata
-
National Institutes of Health
Alopecia areata update | Symptoms
-
National Institutes of Health
Alopecia Areata: Review of Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Pathogenesis, and New Treatment Options
-
National Institutes of Health
Analysis of quantitative changes in hair growth during treatment with chemotherapy or tamoxifen in patients with breast cancer: a cohort study
-
Infona.pl
Alopecia areata: A review | Diagnosis
-
National Institutes of Health
Rosemary oil vs minoxidil 2% for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia: a randomized comparative trial
-
National Institutes of Health
Scalp application of the antioxidant piroctone olamine reduces hair shedding in an 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study
-
National Institutes of Health
Alopecia | Complications
-
National Institutes of Health
Adiponectin as a novel biomarker of disease severity in alopecia areata