Abscess : Causes and Management

- Abscess
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
About abscess
A localized accumulation of pus, an abscess can develop anywhere on the body. It typically happens due to a bacterial, fungal, or other microbial infection that enters the body by a wound, cut, or scratch. Any organ or tissue of the body can develop an abscess, and they frequently come with pain, swelling, and inflammation.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Types
What are the various types?
Skin abscesses
- They frequently develop due to an infected hair follicle, insect bite, or wound close beneath the skin. Typically, they take the form of a sore, red bump that has the potential to enlarge and fill with pus.
Tooth abscesses
- They typically appear in the teeth or gums due to gum disease or tooth decay. If untreated, they can cause tooth loss and excruciating pain and swelling in the affected area.
Abscesses in the Bartholin’s gland
- The Bartholin’s glands, on either side of the vaginal opening, develop these abscesses. They may result in fever, jaundice, and stomach pain.
A brain abscess
- They typically stem from a bacterial or fungal infection and develop in the brain. They may manifest as headaches, seizures, and confusion, among other symptoms.
Abscesses in the lungs
- They frequently occur from bacterial infection and develop in the lungs. They can result in symptoms like coughing, chest pain, and breathing problems.
Pelvic abscess
- They frequently develop in the pelvis as a surgery or delivery side effect. They may result in discomfort, fever, and issues passing stool or urinating.2Types| Researched based study from Nhs.uk
Causes
What are the causes?
Reasons behind an abscess can be listed as follow :
Bacterial infections
- Common bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus can result in abscesses. These microorganisms can enter the body through an injection site, wound, or surgical incision.
Dental infections
- Dental abscesses, which can cause excruciating pain and swelling in the mouth, can be caused by poor dental care and untreated tooth decay.
Foreign substances
- If not removed immediately, objects like splinters or thorns can penetrate the skin and cause an abscess.
Blocked oil glands
- An abscess on the skin can develop from blocked oil glands.
Inflammatory bowel disease
- Abscesses can form in the digestive tract due to conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Sexually transmissible diseases
- An abscess may develop due to some STDs, mainly if the germs spread to the surgery site, such as gonorrhoea or chlamydia.
Complications following surgery
- An abscess can develop after surgery, especially if bacteria enter the surgical site.
Vulnerability
Who is at risk of getting an abscess?
- Infection risk may increase as a result of poor hygiene.
- Cuts and scratches on the skin can serve as an opening for bacteria to enter the body.
- Higher risk groups include those with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those receiving chemotherapy.
- The immune system may become weakened by diabetes, raising the risk.
- For example, acne and other skin disorders can make it more likely to develop an abscess.
- Due to the use of infected needles or non-sterile injection techniques, people who inject drugs intravenously are at a higher risk.
- The risk may be increased by chronic conditions like Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis.3Vulnerability| Researched based study from Wales.nhs.uk
Symptoms
Common symptoms of an abscess
Warmth and redness
- It turns red, painful, and warm to the touch around the abscess.
Acne and swelling
- Swelling and pain, ranging from mild to severe, are present in the affected area.
Fever
- An abscess may occasionally result in fever and chills.
A discharge or pus
- A pus or fluid discharge from the infected area indicates a spot.
Difficult to move
- Stiffness and trouble moving might result from an abscess in a joint or muscle.
Nausea and vomiting
- It may, in infrequent circumstances, produce nausea and vomiting.
Weakness and fatigue
- Fatigue and weakness may result from a severe infection.1Symptoms| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Diagnosis
How is an abscess diagnosed?
Medical evaluation
- A doctor may examine the affected area to look for any lumps or swellings that might be signs of an abscess. Additionally, the doctor could look for warmth, soreness, and redness.
Review of medical history
- The doctor will question the patient’s medical background, including any prior infections, injuries, or surgeries. They might also inquire about signs and symptoms, including discomfort, chills, and fever.
Imaging tests
- A CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound can be used to confirm the presence of an abscess and identify its size and location.
Culture and aspiration
In rare instances, the doctor may use a needle to draw a sample of the abscess fluid for laboratory analysis to pinpoint the bacterium causing the infection and choose the best course of treatment.3Diagnosis | Researched based study from Wales.nhs.uk
Treatment
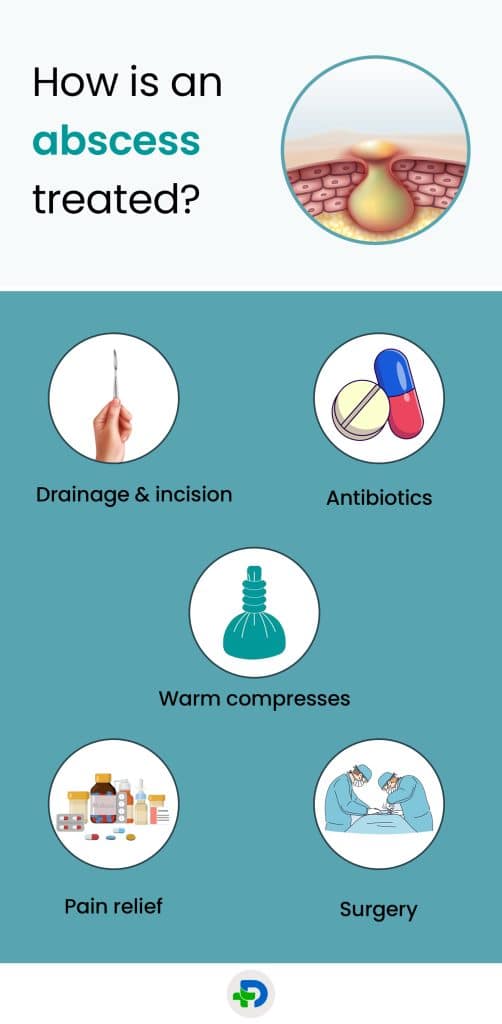
How is an abscess treated?
Drainage and incision
- The abscess is punctured, and the pus is removed with the help of a sterilized scalpel or needle.4Treatment | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- More than one incision may be necessary for larger bumps during this surgery, often carried out under local anesthesia.
Antibiotics
- They are frequently recommended to treat the underlying infection that gave rise to the abscess. A particular antibiotic may be administered depending on the microorganisms causing the infection and the treatment period.4Treatment | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Pain relief
- Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are over-the-counter medications that can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Warm compresses
- Warm compresses can ease pain and swelling in the injured area.
Surgery
- In some instances, if the abscess is deep, large, or challenging to drain, surgery may be required to remove it. A prolonged recovery period and general anesthesia may be necessary. 4Treatment | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Complications
What are the associated Complications ?
Sepsis
- A potentially fatal condition that can result in organ failure and death can be brought on by an infection that has spread to the bloodstream.5Complications | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cellulitis
- Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and soft tissues that can develop from an untreated abscess and cause fever, chills, and swelling.
Fistula
- An improper connection between two organs or tissues is called a fistula; an abscess can occasionally bring it on. Chronic drainage and infection may result from this.5Complications | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Scarring
- The affected area can develop scarring, which could be permanent and compromise the skin’s appearance and functionality.
Systemic Infection
- Untreated abscesses can develop into systemic infections affecting the heart, lungs, brain, and other organs.5Complications | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Recurrence
- An abscess partially drained or treated may return or spread to other body parts. 5Complications | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cyst & Boil
What differentiates an abscess from a cyst and a boil?
These are the criteria on which a cyst or boil can be distinguished from an abscess.
Causes
- A boil is brought on by a bacterial infection of an oil gland or hair follicle, but a bacterial infection often brings on an abscess.
- Typically, a cyst is brought on by a blockage in a gland or duct that results in fluid buildup.
Location
- Anywhere on the body can develop an abscess.
- In most cases, boils appear on the face, neck, armpit, buttocks, or thighs.
- A cyst can develop anywhere there are glands, but it typically appears on the skin.
Prevention
Prevention of an abscess
In order to avoid an abscess, the following steps can be taken:
- Maintain proper hygiene. wash your hands frequently and maintain a clean environment.2Prevention | Researched based study from nhs.uk
- Don’t share personal belongings, never exchange personal items like towels, razors, or clothing with other people.
- Cuts, scratches, and wounds should be promptly cleaned and treated to avoid developing infections.
- To stop the spread of STIs that might result in abscesses during sexual activity, use barrier protection, such as condoms.2Prevention | Researched based study from nhs.uk
- Work with your doctor to successfully manage any chronic problems you have, such as diabetes or other conditions that raise your risk.
- Your immune system can be strengthened by leading a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and enough sleep. 2Prevention | Researched based study from nhs.uk
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Abscesses | Overview | Symptoms
-
National Health Service
Abscess-Overview | Types | Prevention
-
National Health Service
Abscess | Diagnosis | Risk
-
National Library of Medicine
Evidence-based approach to abscess management | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Abdominal Abscess | Complications