Anger issues: Classification, Symptoms and Management

- Anger Management
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
What are anger issues?
Anger issues are habituated, uninhibited anger due to a strong dislike against persons or things and can give rise to a verbal outburst or physical assault.
Anger overview
- Anger is one of the strong sentiments in a person’s life, such as pleasure, sorrow, anxiety and depression.
- Anger is a negative emotion that can sometimes be good as it urges one to find a solution for many hurdles in our life.
- Anger activates the sympathetic part of the autonomous nervous system and energizes the body to fight or run the situation.
A small amount of anger is necessary for survival, but too much anger can lead to hypertension (high blood pressure) and destroy the brain’s neurons through the excess release of stress hormones. Additionally, it can deteriorate the immune system and weaken our memory.

Classification
Classification of anger issues
Assertive anger
- Assertive anger is the anger situation which is shown
- To bring favourable impacts in a person’s life
- To improve the lifestyle
- Resolves quarrels and
- Improves relationship
- Assertive anger is the only one that brings positive effects without affecting the sentiments of the other individual.
Passive aggressive anger
- Passive aggressive anger is an anger type that
- avoids confrontation
- Anger showed in the form of
- Silence
- Deliberate being unresponsive
- Acting as if everything is all right
- Offensive comments
Open aggressive anger
- Open-aggressive anger is an anger type that
- Aggressively outbursts the anger both physically and verbally
- Fights and hurt oneself as well as others
- Shouts and yells at others
- Criticize in a wrong way
Chronic anger
Chronic anger is the prolonged low-level anger which can lead to
- Frustration
- Anger towards oneself
- Irritation about certain earlier circumstances
- Hatred for some people due to specific previous incidents
- Verbal abuse
- Violent behavior
- Criminal tendency
Behavioral anger
Behavioral anger is the spontaneous, aggressive anger type that
- Crosses the limit of being emotional and becoming physical by
- Hitting another person
- Punching
- Throwing objects
- Hurting with sharp instruments
- This type of anger completely deteriorates the healthy relationship between individuals and results in legal consequences, which have the worst impact on the person’s later life.
Verbal anger
Verbal anger is the anger type that involves verbal abuse via ;
- Intense yelling
- Extreme blaming
- Scolding
- Threatening
- Insulting
- Criticizing
- Using inappropriate words to humiliate the other person
- It significantly impacts the other person psychologically and emotionally.
Volatile anger
Volatile anger is the type that comes all of a sudden at small or big resentment and can lead
- To destructive behavior, throwing things around
- This type of anger subsides quickly after aggressive behaviour
- But this anger highly impacts the person’s interpersonal relationships as the other person starts losing trust and stability in the relationship
- If untreated, volatile anger can lead to physical assault later in life.
Overwhelmed anger
Overwhelmed anger is an anger type
- Which accumulates over time and has no way to express them
- Which is uncontrolled and
- One gets the feeling of total disheartenment and disappointment
- The overwhelmed anger precipitates due to uncertain life situations and too much personal burden and can impact the mental status leading to sudden anger outbursts.
Judgmental anger
Judgmental anger (also called righteous anger) is an anger type which results from
- Continuous injustice against ourselves or somebody else
- It can be an ethical fault observed in others
- One gets the feeling of being superior or inferior feelings than others
- Sometimes the affected person humiliates others publicly to justify his viewpoints as unique.
Retaliatory anger
Retaliatory anger is an anger type which
- Arises for retaliation for some wrongdoing of the past
- Being assaulted by someone else
- It can be intentional and determined
- It can be emotional or verbal abuse and, at times, aggressive and physical.
- The person feels contented at first, but it ultimately damages any relationship.
Self-abusive anger
Self-abusive anger (also called shame-based anger) is an anger type which results from
- Hopelessness
- Humiliation
- Pessimistic thoughts
- The person takes the embarrassment internally and expresses it in ways detrimental to oneself by
- Harming oneself
- Taking alcohol or drugs intake
- Messy eating, and
- Criticizing oneself
Destructive anger
Destructive anger is a dangerous anger type, which is
- Impulsive
- Express externally by destroying things and storming away from the room
- Shows extreme hatred
- Can be violent towards other people
- Can develop a criminal tendency
Silent anger
Silent anger(non-verbal anger) is an anger type characterized by
- Being completely silent and keeping things to oneself
- Restricted facial expression
- Silent anger can lead to
- Increased anxiety
- Extreme Stress
- Frustration, and
- Dissatisfaction
Deliberate anger
Deliberate anger (also called motivational anger) is an anger type characterized by
- Hurting the person who hurts them
- Ruins any relationship
- Deliberate anger is often common in work areas and sports teams to motivate people to do their duties and improve performance.
Addictive anger
Addictive anger is due to high adrenaline or dopamine secretion in the body. It is characterized by
- Extreme irritation even when everything is fine
- Anger outbursts when things don’t go their way
- Criticize most of the time about themselves or others
- He knows his anger problem but cannot stop changing his anger-driven behaviour 1Classification | Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com .
Symptoms
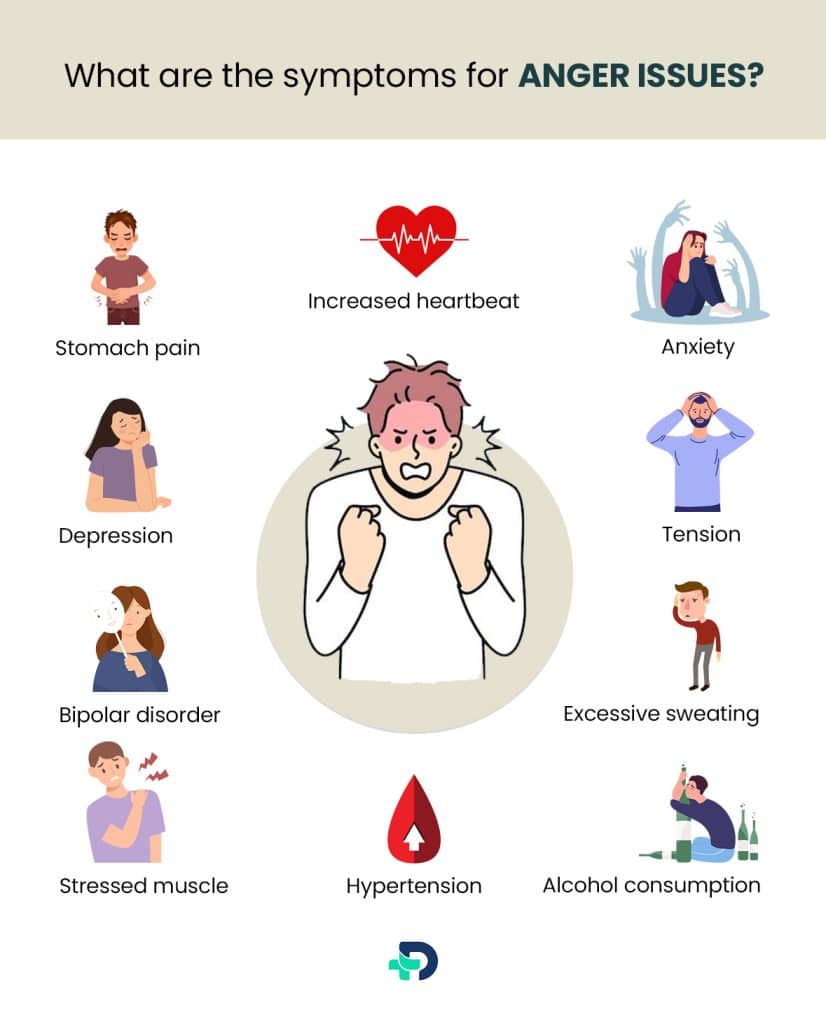
What are the symptoms ?
Symptoms of anger issues are
- Increased heartbeat
- Hypertension (increased blood pressure)
- Excessive sweating
- Face redness
- Hotness in face and neck
- Stinging sensation
- Body trembling
- Lightheadedness
- Stressed muscle
- Clutch fists and jaws
- Stomach pain
- Extreme irritability
- Anxiety
- High temper
- Extreme tension
- Causes for anger issues
- Family problem
- Financial crisis
- Tension
- Depression
- Alcohol consumption
- Sorrow (due to death, divorce or breakups)
- Bipolar disorder(brain disorder causing frequent mood changes)
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (caused due to inattention at a young age)
- Oppositional defiant disorder (behavioral disorder in young children)
- Intermittent explosive disorder ( one shows repeated episodes of violent behavior)
Management
How to Manage anger issues?
Management of anger issues
Identify the triggering factors like
- Long queue
- Traffic jams
- Criticism
Move away from the triggering circumstances, try
- Divert attention to other things
- Take a long breath and calm down
- Repetition of mantras to divert from angry feelings
- Expressing the emotions (disappointment or sadness) to another person might resolve the anger
Think before expressing concerns
- Take a break
- Go for a walk
- Once calm down, express the concerns
Identifying the anger signs in oneself like
- Increased heartbeat
- Feeling too hot
- Red face
Engage in things that give pleasure like
- Looking at natural landscape pictures
- Listening to soothing music
- Reading a religious book
- Taking a rapid exercise
Meditation(mind exercise)
- Stop thinking
- Do breathing exercise
Take help of supportive talks
- Tell about your emotions which hurt you rather than blaming other people
- Identify and implement solutions
- Try to forgive and forget
- Know when to talk to a doctor 2Management| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com .
Prevention
Preventing anger issues
Preventive measures for anger issues can be :
- Count to ten to calm oneself down and allow the heart to beat normally
- Taking a slow breath several times through the nose to avoid shallow breathing
- Do anything that calms the nerves, like bicycling, walking or playing games
- Move to a quiet room for relaxing
- Listen to soft music
- Keep quiet for some time to relax the brain
- Write in a notebook what made you angry
- Prepare oneself by finding a solution to tackle the situation wise fully and prevent future recurrence
- Look for ways to cheer oneself like
- Thinking of good moments
- Watching a comedy episode on television
However, it is always advisable to talk to a doctor when managing and controlling anger is challenging.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Anger | Classification
-
Science Direct
Anger Management | Management


































