All About Personality disorders: Types, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment

- Personality Disorders
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
About Personality disorders
A person’s personality sets them apart from others regarding their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. An individual’s personality usually doesn’t change over time and is influenced by their experiences, environment, circumstances, and inherited traits. A category of mental health issues, personality disorders, impacts how people think, perceive, and interact with others. These illnesses can seriously affect a person’s relationships, daily life, and general health.
This article will delve into the types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, complications, and prognosis of personality disorders.

Types
Types of Personality disorders
Based on their shared traits, different types of personality disorders can be grouped into three clusters:
- Cluster A – Eccentric or Odd behavior.
- Cluster B – Erratic, Dramatic, or Emotional behavior.
- Cluster C – Fearful or Anxious behavior.1Types| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
Cluster A Disorders (Eccentric or Odd behavior)
- Paranoid Personality Disorder – This condition is characterized by disbelief, doubt, and a persistent conviction that others are out to get them.2Types| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Schizoid Personality Disorder – The condition is characterized by a lack of interest in social interactions, a lack of emotional expressiveness, and an affinity for solitary pursuits.
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder – involves peculiar thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors, often leading to discomfort in social situations.
Cluster B Disorders (Erratic, Dramatic, or Emotional behavior)
- Antisocial Personality Disorder – characterized by a disrespect for other people’s rights, impulsivity, a lack of empathy, and a propensity to act criminally.
- Borderline Personality Disorder – Individuals with this disorder experience intense mood swings, unstable self-image, relationship difficulties, and self-destructive behaviors.3Types| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Histrionic Personality Disorder – People with this disorder seek attention, exhibit excessive emotions, have a strong need for approval, and often engage in dramatic or provocative behaviors.
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder – refers to an exaggerated sense of one’s own value, a persistent desire for praise, and a lack of compassion for others.4Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cluster C Disorders (Fearful or Anxious behavior)
- Avoidant Personality Disorder – Due to their vulnerability to criticism and disapproval, those who suffer from this condition tend to avoid social situations and have low self-esteem.
- Dependent Personality Disorder – In relationships, those who have this illness exhibit dependent and clingy tendencies because they have a great desire to be taken care of.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder – Perfectionism, rigidity, obsessive attention to minutiae, and a need for total control are its defining traits.5Types| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
Symptoms
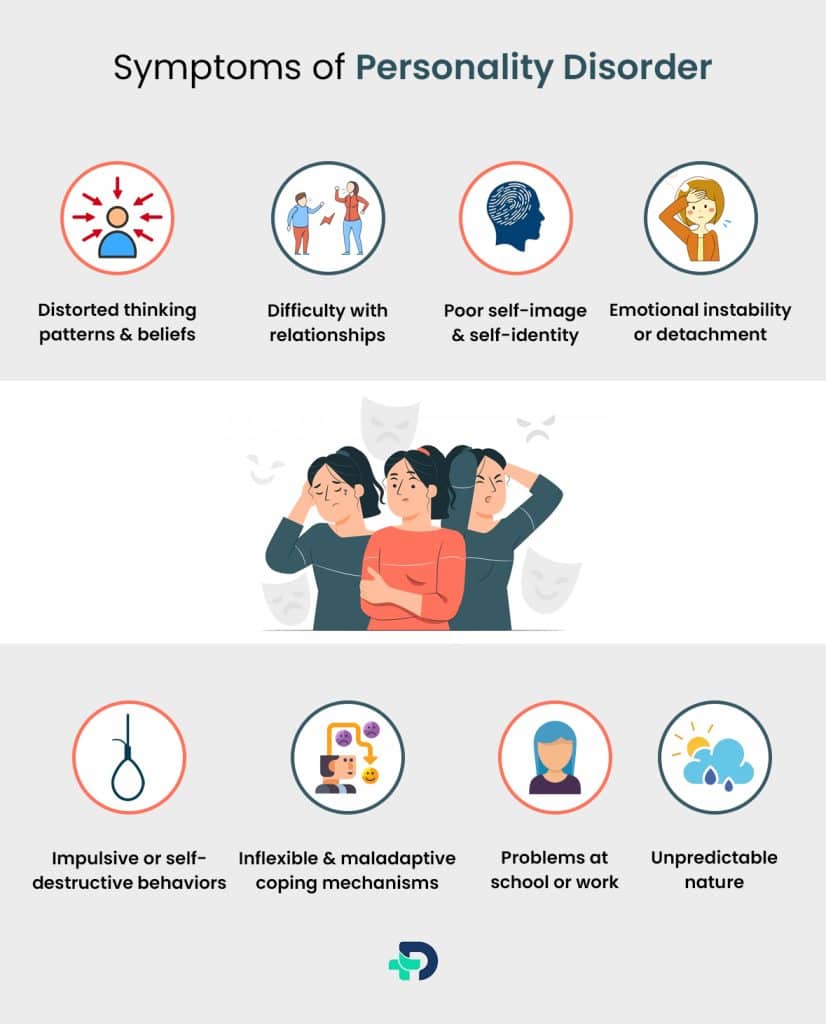
Personality disorder Symptoms
Each personality disorder has its specific symptoms, but some general signs may include:
- Distorted thinking patterns and beliefs.
- Difficulty with relationships.
- Poor self-image and self-identity.
- Emotional instability or detachment.
- Impulsive or self-destructive behaviors.
- Inflexible and maladaptive coping mechanisms.
- Problems at school or work. 6Symptoms| Researched based study from Healthdirect.gov.au
- Unpredictable nature.
Causes
Causes of Personality disorders
Despite the fact that the exact root causes of personality disorders remain unknown, studies indicate a combination of the following factors may be involved in their development:
- Genes.
- Neurobiology.
- Environment.
Genes
- Evidence suggests that certain personality traits and vulnerabilities may be heritable. 7Causes| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- People with a family member with personality disorders or other mental health conditions may have a higher chance of developing a personality disorder.
Neurobiology
- Abnormalities in brain structure and functioning have been associated with certain personality disorders.
- The brain regions in charge of controlling impulses and regulating emotions may differ in patients with borderline personality disorder, according to research. 8Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Environment
Environmental elements such as the ones listed below can have a significant effect on the formation of personality disorders :
- Childhood trauma – Physical, sexual, or emotional abuse, neglect, or early loss of a significant caregiver can contribute to developing personality disorders.9Causes| Researched based study from Apa.org
- Unstable or chaotic family environments – Growing up with inconsistent or unpredictable parenting, parental conflict, or substance abuse can increase the risk.
- Disrupted attachment – Insecure attachment styles, such as ambivalent, avoidant, or disorganized attachment, can influence the development of personality disorders.
Risk factors
Risk factors
Some common risk factors associated with personality disorders may include:
- Personality and Temperament – Some personalities and temperamental traits may make people more likely to acquire certain types of personality disorders. For instance, people who are more impulsive, emotionally unstable, or introverted may be more prone to certain disorders within the relevant clusters.
- Co-occurring Mental Health Conditions – Mood disorders like depression, anxiety disorders, and substance use disorders frequently coexist with personality disorders in people making it more difficult to diagnose and treat personality disorders.
- Cultural and Societal Factors – Cultural and societal influences can impact the expression and manifestation of personality disorders. Cultural norms, expectations, and social pressures may shape the development of maladaptive personality traits and coping mechanisms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
Because personality disorders are complex diseases, diagnosing them can be difficult.
Mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists and psychologists, rely on comprehensive assessments, including the following, to make an accurate diagnosis:
- Interviews
- Psychological tests
- Observation of behavior
The interview may include questions about history, relationships, previous work history, reality testing, impulse control, etc.10Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
The answers are then gathered and compared with the criteria for diagnosing personality disorders given in Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) to come up with a diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment strategies for Personality disorders
Personality disorders are usually managed with a combination of treatment including:
- Psychotherapy
- Medication
Psychotherapy
It is the main approach for treating most personality disorders.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) 11Treatment| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Psychodynamic therapy
- Psychoeducation 12Treatment| Researched based study from Psychiatry.org
- Group therapy
These treatments aid in the improvement of interpersonal skills, managing emotions, and better coping mechanisms in patients.
Medication
Even though medication is not a main treatment for personality disorders, it may include the following to treat few symptoms:
- Mood stabilizers – given to avoid intense mood swings, irritability and aggression.
- Anti-anxiety drugs – to decrease anxiety and sleeplessness.
- Anti-depressants – given to enhance mood and control anger and impulsivity.
- Neuroleptics or Antipsychotic drugs – decreases symptoms of psychosis like hallucinations and delusions if any.13Treatment| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Prevention
Prevention
- While preventing personality disorders is not always possible, early intervention and support can minimize their impact.
- Creating awareness about mental health, promoting healthy coping mechanisms, and addressing early signs of distress can help prevent complications.
Complications
Complications of Personality disorder
Complications arising from untreated or poorly managed personality disorders can be severe and may include:
- Chronic interpersonal conflicts and difficulties in relationships
- Challenges at an education facility
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Unemployment
- Homelessness
- Domestic abuse
- Societal crimes. (Especially those with antisocial personality disorder)
- Divorce 14Complications| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Substance abuse and addiction.
- Self-harm
- Suicidal death 10Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Prognosis
Prognosis of Personality disorders
Personality disorders are not only upsetting for the person but also a source of stress in society. The prognosis for personality disorders varies depending on several factors, including the specific condition, individual circumstances, and the effectiveness of treatment. With proper diagnosis, tailored treatment, and ongoing support, individuals with personality disorders can experience improvements in their symptoms and overall functioning.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Medline Plus
Personality Disorders | Types
-
Medline Plus
Paranoid personality disorder | Types
-
Mayo Clinic
Borderline personality disorder | Types
-
National Library of Medicine
Narcissistic Personality Disorder | Types
-
Cleveland Clinic
Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD) | Types
-
Health Direct
Personality disorders: an overview | Symptoms
-
Mayo Clinic
Personality disorders | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Trauma, genes, and the neurobiology of personality disorders | Causes
-
American Psychological Association
What causes personality disorders? | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Personality Disorder | Diagnosis | Complications
-
Cleveland Clinic
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Treatment
-
American Psychiatric Association
What are Personality Disorders? | Treatment
-
Mayo Clinic
Personality disorders | Treatment
-
Cleveland Clinic
Personality Disorders | Complications