Beta-carotene : Sources and Significance

- Beta-carotene
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is beta carotene ?
Plants contain a pigment called beta-carotene. It is a Vitamin A precursor known as provitamin A carotenoid, a member of the carotenoid family. The provitamin, the most well-known carotenoid, is beta carotene. Yellow- or orange-colored fruits and vegetables acquire their vibrant colors from them. Foods like margarine are colored with it as well. 1Overview | Researched based study from Mountsinai.org Beta carotenes’ functions, requirements, health benefits, side effects, deficiencies, and interactions are discussed in this article.

Facts to know about beta-carotene
- A reddish-orange pigment called beta-carotene is present in various fresh vegetables and fruits.
- High beta carotene intake may not result in hypervitaminosis, unlike vitamin-A. 2Facts | Researched based study from Nutri-facts.org
- The more beta-carotene a fruit or vegetable has, its color is more vibrant.
- Beta carotene may aid in maintaining lung health as people age.
- Beta-carotene, unlike vitamin A, is not a required nutrient in and of itself.
- Beta-carotene is converted by the body into retinol/ vitamin A.
- We can obtain vitamin A in supplement form or through food such as beta carotene. 2Facts | Researched based study from Nutri-facts.org
- Dietary beta carotene has the advantage that the body only transforms what it requires.
Functions
Biological functions of beta-carotene
The following are the biological functions of beta-carotene:
- Boosts immune system performance.
- Effective antioxidant that inhibits tissue damage caused by free radicals.
- Assists in the prevention or reduction of the body’s oxidative stress.
- Effective against the oxidation of lipids in cell membranes.
- They support skin health, mucous membrane, vision, and immune function.
- It is crucial to the reproductive process.
Sources
Sources of beta-carotene
Natural sources
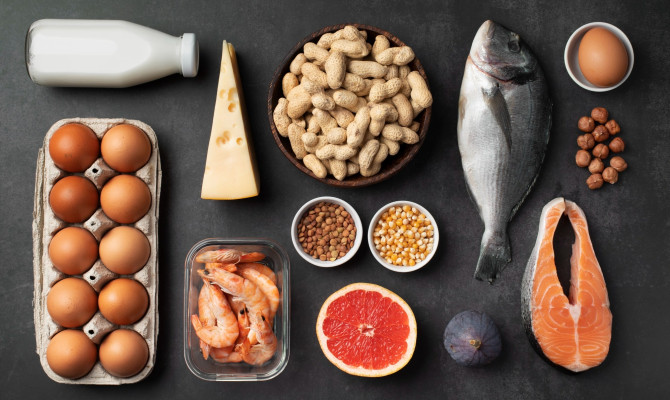
The following list of foods contains a good amount of B-carotene:
- Vegetables – spinach, kale, parsley, tomatoes, sweet potato, broccoli, carrots, green leaf lettuce, peas, and red and yellow peppers.
- Fruits – mangoes, apricots, butternut squash, winter squash, cantaloupes, and squash.
- Herbs and spices include paprika, cayenne, chilies, parsley, cilantro, sage, and coriander.
- Animal sources include fish oil, milk, eggs, and beef liver.
As beta carotene is a fat-soluble substance, consuming these foods along with healthy fat like olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds will help the body absorb them more effectively
Dietary supplements
Beta carotene supplements are available in the following forms:
- Capsules.
- Chewable tablets.
However, Doctors or dieticians do not prefer supplements over dietary sources.
Requirement
How much beta-carotene do I need to take?
For kids
- 3 to 6 mg of beta-carotene, or 5,000 –10,000 units of daily vitamin A activity.
Adults and adolescents
- 6 -15mg of beta-carotene, or 10,000 – 25,000 units of vitamin A activity daily. 3Requirement | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Benefits

Health Benefits
Some of the health benefits may include the following
- Sun sensitivity – Beta-carotene is used to lessen sun sensitivity in persons with the rare genetic disorder erythropoietic protoporphyria. 4Benefits | Researched based study from Biomedcentral.com
- Beta carotene reduces the risk of diabetes and heart disease due to metabolic disturbances.
- Reduces cholesterol – reduces blood triglycerides and body fat.
- Age-related eye problems – When taken with vitamins C and E, zinc, and copper, beta carotene may help to delay age-related vision problems. 5Benefits | Researched based study from Nih.gov
- Better cognitive function – beta carotene may help lower the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease by improving cognitive performance.
- Breast cancer – Beta carotene-rich diets may minimize the chance of developing breast cancer among premenopausal women. 6Benefits | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Prevents cancers – like pancreatic and lung cancer. 7Benefits | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- After-birth complications – might lower the chance of postpartum fever and diarrhea. It also lessens the incidence of pregnancy-related death.
Vulnerability
People at risk of deficiency
The chance of developing beta carotene deficiency may arise in the following circumstances:
- Cystic fibrosis. 3Vulnerability| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Prolonged diarrhea.
- Chronic illnesses.
- Serious injury.
- Malabsorption.
- Pancreatic disorder.
- Pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding mothers.
- After multiple pregnancies.
- People with kidney disease. 8Vulnerability| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Deficiency
Deficiency symptoms
Symptoms may be very similar to that of vitamin A as beta carotene is eventually converted by the body into vitamin A and any deficiency of beta carotene results in a deficit of vitamin A. Symptoms may include the following:
- Nighttime blindness.
- Ulcers in the cornea.
- Dry eyes.
- Dry, scaly or irritated skin.
- Delayed growth in kids.
- Infertility.
- An ongoing cough.
- Continual infections.
- Digestion issues.
Side effects
Side effects of beta carotene
As the body only transforms as much beta-carotene into vitamin A as it requires, using beta-carotene is generally safer than taking vitamin A tablets.3Side effects | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
On the other hand, taking supplements with an excessive amount of beta-carotene occasionally poses a risk and can have the following adverse effects:
- An orange or yellow discoloration of the skin.
- May raise the risk of some cancers.
- Loose stools.
- Joint ache.
- Bruising.
- Dizziness. 3Side effects | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
Precautions
Precautions to be taken while consuming beta carotene
It is best to consult a doctor before taking beta-carotene supplements in individuals with the following conditions:
- Allergies – people who are allergic to this supplement or any medications as such, or to particular food, dyes, preservatives, or animals should inform their doctor about it.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women – Beta-carotene supplements should only be consumed by pregnant or nursing women if prescribed by a physician. Studies on humans do not demonstrate its advantages for pregnant or nursing moms.
- Liver or kidney diseases – may result in elevated beta-carotene levels in the blood, which could increase the risk of adverse consequences.
- Smokers – Taking beta-carotene supplements could increase the chance of lung cancer in long term or past smokers. 9Precautions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Alcoholics – Beta-carotene and alcohol may interact, raising the danger of liver damage.
Interactions
Beta carotene Interactions with other medicines
The following medicines may interact with beta-carotene supplements:
- Statins – Statins like simvastatin and atorvastatin may be less effective when combined with antioxidants like beta-carotene, vitamin E, and C. People who use statins to decrease their cholesterol should see their doctor before taking beta-carotene supplements. 1Interactions | Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
- Cholestyramine and Colestipol – Cholesterol-controlling drugs like cholestyramine or colestipol can lower beta-carotene levels in the blood. 10Interactions| Researched based study from Peacehealth.org
- Orlistat (a weight loss drug) – may decrease beta-carotene absorption, resulting in reduced beta-carotene levels in the body. People taking Orlistat might want to consider taking a multivitamin. People should give a gap of at least two hours between these two medications to avoid interaction. 11Interactions | Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Mineral oil – may cause beta-carotene levels in the blood to drop when taken to treat constipation. 12Interactions | Researched based study from Peacehealth.org
Takeaway
Takeaway
People can increase their beta-carotene intake and gain additional advantages from antioxidants and other nutrients by consuming more vegetables and fruits. Supplemental beta carotene is generally risk-free; however, smokers and former smokers may be in danger from them. Beta-carotene is a crucial dietary component and an essential form of vitamin A. Before taking a supplement, always check with a doctor to ensure it’s a good fit and safe for overall health.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Mount Sinai
Beta-carotene | Overview
-
NUTRI-FACTS
Beta-Carotene | Facts
-
Mayo Clinic
Drugs and Supplements-Beta Carotene (Oral Route) | Dietary requirements
-
BioMed Central Ltd
Erythropoietic protoporphyria | Benefits
-
National Institutes of Health
Vitamin A and Carotenoids | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Plasma carotenoids and risk of breast cancer over 20 y of follow-up | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Association between vitamin A, retinol and carotenoid intake and pancreatic cancer risk: Evidence from epidemiologic studies | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin A Deficiency | Vulnerabilty
-
National Library of Medicine
β-Carotene Supplementation and Lung Cancer Incidence in the Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study: The Role of Tar and Nicotine
-
Peace Health
Colestipol | Interactions
-
Medline Plus
Orlistat | Interactions
-
Peace Health
Mineral Oil | Interactions