Heart failure : Causes, Symptoms and Management

- Heart Failure
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Heart failure?
When the heart becomes weak and is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body’s needs, this condition is called heart failure.
This constant and moderate illness influences a great many individuals all through the world. Many patients with heart failure may have active, whole lives with the proper care.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov

Types
What are the types of heart failure?
Systolic heart failure
- When the heart muscle is damaged and unable to contract normally, this occurs. As a result, the heart is unable to pump the body’s required amount of blood. This is brought on by heart muscle injury from a heart attack, chronic high blood pressure, or other heart-stressing disorders.
Diastolic heart failure
- When the heart muscle becomes tight and unable to fully relax, this occurs. During the resting phase of the cardiac cycle, the heart cannot pump enough blood.
- Conditions including excessive blood pressure, diabetes, or coronary artery disease are frequently responsible for this.
- t’s significant to remember that some individuals could have both. Heart failure with decreased ejection fraction or intact ejection fraction is the two terms used to describe this.1Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Left-sided heart failure
- It happens when the left ventricle, the part of the heart delivering oxygen-rich blood to the body, malfunctions.
Right-sided heart failure
- It occurs when the right ventricle, which transports oxygen-rich blood to the lungs, fails to function properly. Inflammation and discomfort may result from an accumulation of fluid in the body, especially in the legs, ankles, and feet.
Acute cardiac failure
- A medical emergency might arise from this unexpected occurrence.
Chronic heart failure
- This gradually worsens over months or years as it develops over time.1Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Causes
What are the causes of heart failure?
Several conditions that impair the heart’s capacity to pump blood efficiently can result in heart failure. Among the most frequent causes are:
Coronary artery disease
- This is the most frequent reason. It happens when the arteries carrying blood to the heart constrict or are clogged, lessening the availability of nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle.3Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Hypertension, or high blood pressure
- It may result in muscle thickening and stiffening, making the heart’s blood pumping more difficult.
Cardiomyopathy
- The heart muscle may expand, thicken, or stiffen due to this. Genetics, infections, alcohol misuse, and certain medications are potential causes.
Arrhythmias
- Abnormal cardiac rhythms can negatively impact the heart’s ability to pump.
Diabetes
- The blood arteries and nerves that regulate the heart can be harmed by uncontrolled diabetes.
Obesity
- The heart may work harder if a person is overweight.
Sleep apnea
- Episodes of low oxygen levels during sleep may result from this.
Smoking
- It might damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.3Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Symptoms
Symptoms of heart failure
Breathing difficulty
- Feeling out of breath, especially after exercising or resting at night.
Weakness
- Even after adequate sleep, weakness and fatigue still feel weak and exhausted.
Swelling
- Swollen ankles, feet, legs, or abdomen.2Symptoms| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Irregular or fast pulse
- Experiencing a racing or fluttering sensation in the chest.
Persistent cough
- A cough that discharges blood-tinged mucus, either white or pink.
Reduced capacity for exercise
- Finding it challenging to execute once-easy physical tasks.
Faint or dizzy
- Feeling weak or lightheaded, particularly while standing up.
Reduced appetite
- Even after eating very little, feeling bloated or full.2Symptoms| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Risk factors
What are the risk factors?
Age
- With age, the risk rises, especially after age 65.
High blood pressure
- The cardiac muscle can get damaged by chronic hypertension.2Risk factors| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Cardiovascular disease
- Blood flow is decreased as a result of artery plaque formation.
Diabetes
- Heart disease is more likely to affect diabetics.
Obesity
- The heart can be strained by excess weight.
Smoking
- Blood vessel damage results from smoking.
Family history
- You may be at a greater risk if you have a family member with heart failure.
Sleep apnea
In this condition, breathing is disrupted when sleeping, which might increase your chance of developing heart disease.2Risk factors| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Alcohol
- Alcohol abuse can weaken the heart’s muscles.
Certain Medicines
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), certain chemotherapy medications, and chest radiation treatment can increase the risk.2Risk factors| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Diagnosis
Diagnosing heart failure
Physical exam
- Your physical health might be checked, and a doctor could ask about your symptoms and medical history.
Tests
Doctor could also suggest specific diagnostic procedures, like:
Echocardiogram
- Doctors can check the heart’s size, shape, and function with this test, which uses sound waves to produce a picture of the organ.
ECG: electrocardiogram
- This gauges the heart’s electrical activity and can find irregular heartbeats or other indications of heart disease.4Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
A chest X-ray
- It may indicate cardiac failure if the heart is enlarged or if there is an accumulation of fluid in the lungs.
A blood test
- These can test the blood for specific proteins and enzymes that could point to heart failure or other disorders.
Stress test
- This involves working out on a treadmill or stationary cycle while your blood pressure and heart rate are being tracked. It can assist in locating cardiac issues that might not be seen while at rest.4Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cardiac catheterization
- To do this, a small, flexible tube must be inserted into a blood artery in the arm or groin and directed toward the heart. This might be used to identify cardiac blockages or other issues.
CT or MRI scan
These examinations can offer precise pictures of the heart and its supporting components, enabling medical professionals to assess its function and find any anomalies.4Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment
Treatment strategies for heart failure
Medications
- ACE inhibitors-These medications increase blood artery diameter and reduce blood pressure, which lightens the stress on the heart.5Management| Researched based study from Nhs.uk
- Angiotensin receptor blockers-They are used in people who cannot take ACE inhibitors and have effects similar to ACE inhibitors.
- Beta-blockers-These drugs improve heart health by lowering blood pressure and slowing heart rate.5Management| Researched based study from Nhs.uk
- Diuretics-They assist the body in eliminating extra fluid, which lessens edema and shortness of breath.
- Aldosterone antagonists-They lessen the body’s retention of salt and water, which reduces the strain on the heart.
- Digoxin-They assist the heart in beating more efficiently, which enhances its performance.
- Ivabradine-This lowers heart rate and may help with symptoms.5Management| Researched based study from Nhs.uk
Surgery
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- A treatment in which a healthy blood vessel is removed from another part of the body and utilized to go around a blocked or constrained cardiac artery.4Management| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Valve repair or replacement
- Surgery may be required to replace or repair a damaged heart valve because heart valve issues can contribute to heart failure.
Implantable devices
- Devices like pacemakers or defibrillators could be suggested in specific circumstances to assist in the control of the heart’s rhythm and prevent abrupt cardiac arrest.
A left ventricular assist device (LVAD)
- A mechanical left ventricular assist device (LVAD) pump can be implanted in the chest to aid the heart in pumping blood. It may be a temporary solution when someone is awaiting a heart transplant.
A heart transplant
- In severe cases, an organ transplant may be recommended. This involves switching out the patient’s diseased heart for a donor in good health.4Management| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Complications
Complications associated with heart failure
Arrhythmia
- It may disrupt the heart’s electrical impulses, resulting in an erratic heartbeat. Blood clots, strokes, and unexpected cardiac arrest become more likely.
Kidney injury
- Kidney injury as a result of fluid retention in the body.7Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Liver injury
- Due to fluid accumulation, the liver may also be impacted.
Pulmonary edema
- In extreme situations, fluid buildup in the lungs results in edema and shortness of breath.7Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cognitive dysfunction
- Memory loss, trouble concentrating and making decisions, and reduced blood supply to the brain are all effects of this condition.
Cardiac shock
- The result of insufficient blood pumping from the heart is organ failure and a severe decrease in blood pressure.7Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Death
- Some people may pass away from the illness or its consequences since it might be fatal.7Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Prevention
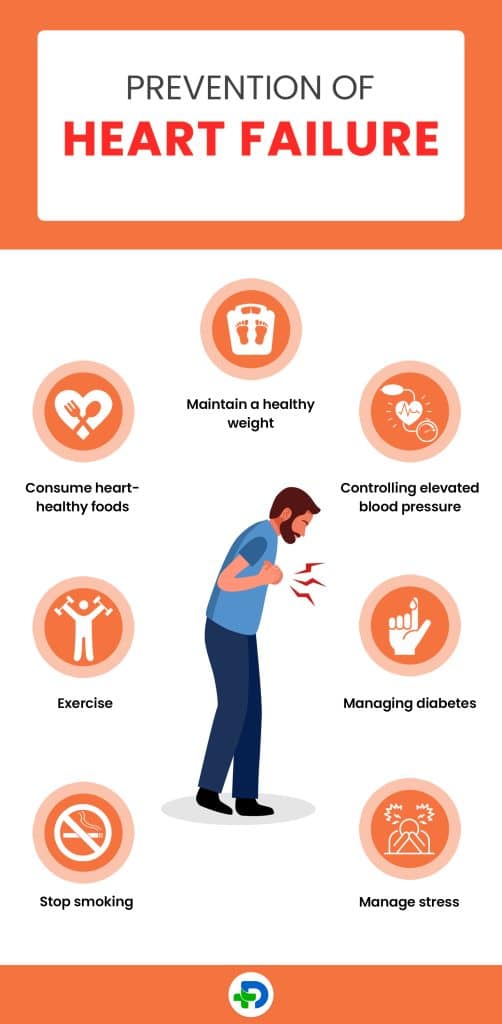
Prevention of heart failure
Maintain a healthy weight
- Keeping your weight in check requires a balanced diet and frequent exercise.
Consume heart-healthy foods
- Low salt and added sugar intake together with a nutritious diet can help decrease blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Controlling elevated blood pressure
- Medication and lifestyle modifications, such as a nutritious diet and regular exercise, can help manage hypertension.6Management | Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Exercise
- The risk of heart disease can be lowered by engaging in regular physical exercise.
Managing diabetes
- Keeping blood sugar levels under control might lessen this danger.
Stop smoking
- Quitting smoking can improve heart health and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
Manage stress
- Learning relaxation methods like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help manage stress.6Management | Researched based study from Cdc.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Millions of people worldwide suffer from the terrible medical illness known as heart failure.
- Working together with your doctor to create a treatment plan suited to your particular requirements and medical background is crucial if you have been diagnosed.
- It’s crucial to monitor your symptoms and inform your doctor immediately if anything changes. With the right care and treatment, you can live an active life.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Types of heart failure | Overview | Types
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Heart Failure | Risk factors | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Congestive Heart Failure | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Heart Failure: Diagnosis, Management and Utilization | Diagnosis | Management
-
National Health Service
Heart failure | Management
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Heart Disease | Prevention
-
National Library of Medicine
ABC of Heart Failure-Clinical features and complications | Complications