Bursitis : Symptoms, Causes, Management, and Prevention

- Bursitis
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Bursitis ?
Bursitis means inflammation of a bursa. Bursae are confined, fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions and smooth surfaces between organs. In close proximity to the tendons surrounding the big joints (shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees), you’ll find the primary bursae. Most cases of bursitis resolve on their own. Movement may be restricted, but malformation is rare for this disorder. 1Overview | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
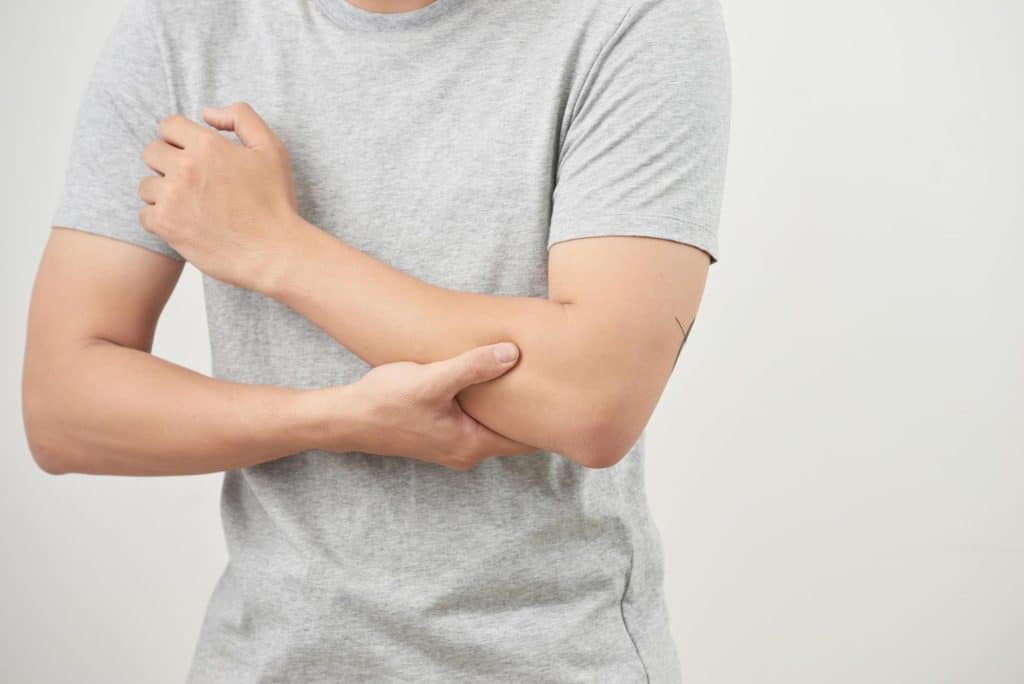

Types
Types of Bursitis
Although bursitis can affect any bursa in any part of the body, certain kinds are more prevalent than others.
Retro malleolar tendon bursitis
- Bursitis of this kind is also known as Albert’s illness. Injuries, illnesses, and wearing shoes with too much arch support are all potential causes. The Achilles tendon, specifically its bottom portion, is stressed more by these. Calf muscles are connected to the bottom of the foot by this tendon. This can cause the bursa at the tendon’s foot attachment to become inflamed. 1Types | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Posterior Achilles tendon bursitis
- Bursitis of this type occurs in the bursa between the skin of the foot and the Achilles tendon; this condition is also known as Haglund deformity. The leg muscles are connected to the foot via the tendon.
- The condition is made worse by certain walking styles that force the heel’s delicate tissue against the shoe’s rigid back support. 1Types | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Hip bursitis
- This type is also known as trochanteric bursitis. It can develop as a result of trauma, excessive use of the hip muscles, spine anomalies, arthritis, or surgical procedures.
- Women and individuals in their middle to late 30s and elderly are more likely to experience this form of bursitis. 1Types | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Elbow bursitis
- Inflammation of the bursa between the tissue and bones of the elbow causes elbow bursitis. Injury or repetitive stress on the arm can lead to bursitis. 1Types | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Knee bursitis
- Goosefoot bursitis, also known as Pes Anserine bursa, is another name for bursitis that affects the knee. This bursa is located on the inside of the knee, between the thigh bone and the three hamstring ligaments.
- Lack of flexibility before exercise, tense hamstring muscles, excess body fat, arthritis, and knee or lower limb out-turning have all been linked to this form of bursitis. 1Types | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Kneecap bursitis
- This form of bursitis, also known as prepatellar bursitis, is prevalent in individuals who spend a lot of time kneeling, like plumbers or carpet layers. 1Types | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Symptoms
Symptoms of Bursitis
Pain and tenderness in the area of the afflicted bone or muscle are classic symptoms of bursitis. When the bursae sacs enlarge, it can be painful to move. Bursitis can also cause other symptoms, such as: 5Symptoms | Researched based study from Pennmedicine.org
Shoulder
- Discomfort is felt in the shoulders when the arms are raised overhead, especially when sleeping.
- Restricted mobility .
Elbow
- Pain is worse when the arm is flexed.
- This sac is prone to infection.
Hip
- Walking Causes Hip Pain
- Pain or discomfort in the groin
- Aching from the front and center of the thigh down to the knee, made worse by bending or twisting the hip.
Knee
- Kneecap swelling
- Discomfort with bending the knee
- Worsen intensity of pain at night .
Causes
Causes of Bursitis
Inflammation of the bursa, a sac containing a jellylike fluid, between a bone and a muscle, is the root cause of bursitis. 2Causes | Researched based study from Versusarthritis.org When healthy, this fluid shields your bones and joints from damage caused by impacts. There are various issues that bursitis is linked to. These conditions include
- Excessive use of bursa
- Injury
- Infection
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Diabetes
- Gout
- Tendonitis
- Arthritis 1Causes | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Risk
Risk factors of Bursitis
Bursitis can affect anybody; however, women and middle-aged to elderly persons are often affected by it. Younger individuals and males are at lower risk.
Bursitis is linked to the following risk factors: 6Risk | Researched based study from Aaos.org
- Injuries caused by abuse or continual tension- This is a common problem for people who run, ascend stairs, ride bikes, or stand for extended stretches of time.
- Injured hip- When you fall on your hip, hit your hip, or lay on one side of your body for a long time, you increase the risk of a hip injury.
- Spinal disorder- Other conditions that can impact your gait include scoliosis and arthritis of the lumbar (lower) vertebrae.
- The disparity in shin-length – When one of a person’s legs is noticeably shorter than the other, it can alter their gait and cause pain in the hip bursa.
- Rheumatoid arthritis- Bursitis is more likely to develop with this condition.
- Prior surgical history- Bursitis can be caused by trauma to the bursa, such as that which occurs during surgeries.
- Calcium deposits or bone spurs- Tendonitis of the trochanteric region is a common disorder. They can trigger bursitis by irritating the bursa.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Bursitis
Bursitis can be diagnosed with a variety of procedures, including but not limited to a thorough patient history and physical examination. 1Diagnosis | Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
- X-ray: A diagnostic procedure that employs rays of invisible electromagnetic radiation to create images of organs, bones, and other interior structures.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A diagnostic imaging procedure that creates high-resolution images of the human body using a computer, radio waves, and very strong magnets.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is a diagnostic procedure that employs high-frequency sound pulses to examine the body from the inside.
- Aspiration: In order to rule out infection or gout as potential reasons for bursitis, a fine needle is used to drain fluid from the enlarged bursa and examine it.
- Blood tests: To corroborate or rule out other diseases, laboratory testing may be performed.
Management
Treatment and Management of Bursitis
Your healthcare practitioner will discuss a treatment strategy with you that will help you get back to normal.
What to do to relieve bursitis?
- Apply cold three to four times a day for the first two or three days. 4Management| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Wrap a cloth around the painful spot and apply ice or an ice pack to it for 15 minutes.
- Take some time off to heal the joint.
- If you suffer from bursitis, avoid resting on the affected side.
Hip, knee, or foot bursitis treatment:
- Avoid staying in one position for too long.4Management| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Put your full weight onto both of your feet and stand equidistant from the floor.
- When laying on your side, putting a pillow between your legs can provide some relief from discomfort.
- Cushioned flat shoes can make a big difference in relieving pain.4Management| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Losing weight may also be beneficial if you are overweight.
- Avoid doing things that require you to repeatedly move the same bodily area.
Additionally, there are therapies such as
- Altering one’s activities- Stay away from activities that make your condition worse.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, piroxicam, naproxen, celecoxib, and others may be helpful. Be careful and don’t take NSAIDs for too long. Get your doctor’s opinion on the NSAIDs you’ve been taking. If you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking a certain drug, you may experience serious negative effects from NSAIDs.6Management| Researched based study from Aaos.org
- Assistive aids- When moving around is difficult, use a cane or walker for at least a week.
- Physical rehabilitation and therapy- Your doctor may recommend a stretching program for the affected part of your body. Your physical therapist may also recommend additional therapies, such as rolling therapy (massage), ice, heat, or ultrasound, in addition to the movements you perform to stretch the affected muscles.6Management| Researched based study from Aaos.org
- Injection of corticosteroids and bursal fluid drainage
- Your doctor may recommend strengthening and motion routines as the discomfort subsides.
- Injection of steroids- Bursitis pain can sometimes be relieved by injecting cortisone and a local anesthetic into the affected area.
Surgical Management
- Surgery is only done very rarely. After exhausting all other options for relieving discomfort and inflammation, your doctor may suggest surgical removal of the bursa. The joint will recover to regular function after the bursa is removed.6Management| Researched based study from Aaos.org
- An arthroscopic bursectomy is an emerging method of treating hip bursitis, for example. This method involves making a tiny cut (about 1/4 inch) over the hip in order to extract the bursa.6Management| Researched based study from Aaos.org
Prevention
Prevention of Bursitis
- Maintain your weight. Extra weight can adversely impact your joints. 3Prevention | Researched based study from nhs.uk
- Disinfect any scrapes or cuts you get on your elbows or knees to avoid infections.
- Cushion your joints with padding if you need to apply force on your joints
- If you’re doing something that could cause joint damage, like squatting, make sure to take frequent pauses and warm up first.
- When starting a new activity or fitness program, do so gradually. Raise the bar you’re setting for your body slowly but surely. 3Prevention | Researched based study from nhs.uk
- When doing a task that is repetitive, stop and rest frequently.
- Use elbow and leg cushions to protect vulnerable joints.
- Do not perform activities that worsen your condition or symptoms.
- Maintain an upright position. Always use correct posture when performing common tasks. 3Prevention | Researched based study from nhs.uk
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Bursitis is an unpleasant inflammation of the bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that act as shock absorbers for the bones, ligaments, and muscles around your joints.
- Bursitis most frequently manifests in the shoulder, elbow, and hip. It can occur anywhere including the knee, the foot, and the big toe joint. Bursitis is common around joints that endure repeated stress.
- The afflicted joint should be protected from further damage and rested as part of the treatment. Pain from bursitis typically subsides after a few weeks of therapy, though recurrence is frequent.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Bursitis | Overview | Types | Diagnosis
-
Versus Arthritis
Bursitis | Causes
-
National Health Service
Bursitis | Prevention
-
Medline Plus
Bursitis | Management
-
Penn Medicine
Bursitis | Symptoms
-
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Hip Bursitis | Risk | Management