Know About Rectal bleeding: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention

- Rectal Bleeding
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
About Rectal bleeding
Rectal bleeding also known as hematochezia, refers to the passage of blood through the rectum and is a concerning symptom that should not be ignored. It may show up as fresh blood on the toilet paper or in the feces. Rectal bleeding can be frightening, but it’s important to recognize its potential causes, get the right kind of medical care, and follow the right course of action.
In this article, we will look at the symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, consequences, and prognosis of rectal bleeding.

Symptoms
Symptoms of Rectal bleeding
Rectal bleeding can present with various symptoms, including:
- Stool with blood in it
- The toilet paper has blood on it
- Blood seen in the toilet bowl
- Any discomfort or pain
Stool with blood in it
- Bright red blood may be visible in the stool without any pain.
Toilet paper has blood on it
- After wiping, some may notice fresh blood on the toilet paper.
Blood seen in the toilet bowl
- Blood may be seen in the toilet bowl after passing motion.1Symptoms| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Any discomfort or pain
- Rectal bleeding could also be accompanied by pain, anal itching, or a feeling of fullness in the rectum.
Causes
Causes of Rectal bleeding
Problems with the lower gastrointestinal tract, such as those with the colon, rectum, or anal canal, can lead to rectal bleeding.
Common causes of rectal bleeding may include:
- Anal fissures – Bleeding can occur from tiny cracks or tears in the anal lining.
- Hemorrhoids – when ruptured can cause bleeding from the rectum.
- Diverticulosis – The formation of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon can lead to bleeding.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) – Rectal hemorrhage can be brought on by illnesses including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.2Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Gastrointestinal infections – Infections such as bacterial or viral gastroenteritis can lead to rectal bleeding.
- Anal or colorectal trauma – Injury or trauma to the anal or rectal area can cause bleeding.
- Medications and other medical conditions – Certain medications, such as blood thinners, and conditions like liver disease or clotting disorders can contribute to rectal bleeding.
- Colorectal polyps or cancer – can cause abnormal bleeding from the rectum.3Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Sexually transmitted infections – in the anal area can cause bleeding.4Causes| Researched based study from Nidirect.gov.uk
Risk factors
Rectal bleeding risk factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing rectal bleeding, including:
- Age and Gender – Rectal hemorrhage was more common in women between the ages of 18 and 39 and above 60, while it was more common in men between the ages of 40 and 49.3Risk factors| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Family history – Having a family history of colorectal cancer or other gastrointestinal conditions can increase the risk.
- Constipation that persists over time – can cause hemorrhoids or anal fissures to form when people strain during bowel movements.
- Obesity – Being obese or overweight might put more strain on the area around the genitals.
- Living a sedentary lifestyle – can make you constipated and make you more likely to experience rectal bleeding.
- Poor diet – A low-fiber diet can lead to constipation and increase the risk of rectal bleeding.
- Dehydration – when people don’t drink enough water every day, it results in hardening of stools.
Consultation
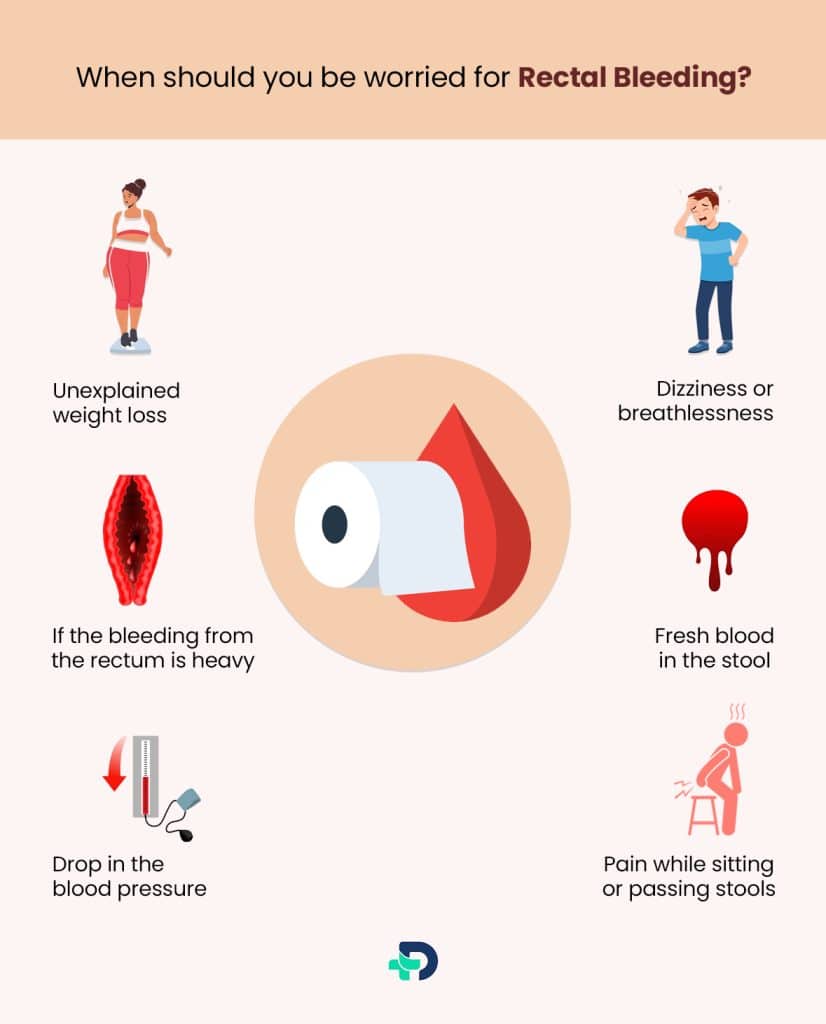
When should you be worried?
Check with a doctor if you go notice any of the following:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Dizziness or breathlessness
- Lack of control over passing stool
- Fresh blood in the stool
- If blood in the stool lasts more than 1-2 days
- If the bleeding from the rectum is heavy
- Drop in the blood pressure
- Pain while sitting or passing stools
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Rectal bleeding
When experiencing rectal bleeding, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation. The diagnosis may involve:
A detailed medical history
- Medical history of the patient is asked by the healthcare professional which may include the individual’s symptoms, history of any other health conditions, family history, etc.
Physical examination
- Heart rate, blood pressure and the respiratory rate are all monitored. Also, a digital examination of the rectum is done by the doctor to identify any abnormalities.5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
Diagnostic tests
Additional tests may be done to evaluate the cause if rectal bleeding and may include:
- Blood test
- Anoscopy 6Diagnosis| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Colonoscopy
- Proctoscopy
- Sigmoidoscopy
- Upper endoscopy
- Stool tests
- Bleeding scans 7Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment
Treatment of Rectal bleeding
Rectal bleeding may be treated with different treatments based on the cause:
Conservative measures
- For minor cases, conservative treatments such as dietary modifications, increasing fiber intake, and managing constipation can be effective.
Medications
- Topical creams, suppositories, or ointments may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms associated with hemorrhoids or anal fissures.8Treatment| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
Surgical interventions
- In cases where conservative treatments are ineffective or when the cause of rectal bleeding requires intervention, surgical procedures may be recommended. These can include procedures to remove hemorrhoids, repair anal fissures, or address other underlying conditions.3Treatment| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment for underlying conditions
- If rectal bleeding is caused by conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer, specific treatments targeting these conditions will be implemented.
Prevention
How to prevent Rectal bleeding?
While not all cases of rectal bleeding can be prevented, certain measures may help reduce the risk or recurrence:
- Maintain a healthy diet – Regular bowel movements can be encouraged and constipation can be avoided by eating a high-fiber diet that is rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Avoid processed food – like cheese, bread, processed meat, etc.
- Drink enough water – to soften feces and avoid straining when going to the toilet9Prevention| Researched based study from Healthdirect.gov
- Regular exercise – can help to support good bowel function and lower the possibility of constipation.
- Good toilet habits – include not straining during bowel movements and not sitting on the toilet for extended periods of time.
- Manage stress – Chronic stress can contribute to gastrointestinal issues, including constipation. Use stress-reduction strategies for general wellbeing.
Complications
Rectal bleeding complications
Ignoring rectal bleeding or delaying medical evaluation can lead to potential complications, including:
- Anemia – Because of blood loss, chronic or serious rectal bleeding can cause iron deficiency anemia.
- Progression of underlying conditions – If rectal bleeding is caused by conditions such as colorectal cancer, delaying treatment can allow the condition to advance and worsen prognosis.
- Recurrence or chronicity – Without proper treatment and management, rectal bleeding may recur or become a chronic issue.
- Metastasis of the cancer – to the draining lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated or undetected.3Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Prognosis
Rectal bleeding prognosis
Rectal bleeding is a symptom that shouldn’t ever be overlooked. While it can be alarming, understanding the potential causes, seeking medical evaluation, and following the recommended treatment plan are essential for a proper diagnosis and management. The underlying reason will determine the prognosis for rectal bleeding. In many cases, rectal bleeding can be effectively managed and treated, especially when detected early. Early diagnosis and treatment can enhance results and decrease the likelihood of complications.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Factors identifying higher risk rectal bleeding in general practice | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Life-Threatening Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in Pediatric Crohn's Disease | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Rectal Bleeding | Causes | Treatment | Complications
-
NiDirect
Rectal bleeding | Causes
-
Mount Sinai
Rectal bleeding | Diagnosis
-
Medline Plus
Anoscopy | Diagnosis
-
National Library of Medicine
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Scan | Diagnosis
-
Cleveland Clinic
Rectal Bleeding | Treatment
-
Health Direct
Rectal bleeding | Prevention