Functional MRI (fMRI): Uses, Process, Benefits and Limitations

- Functional MRI (FMRI)
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Functional MRI?
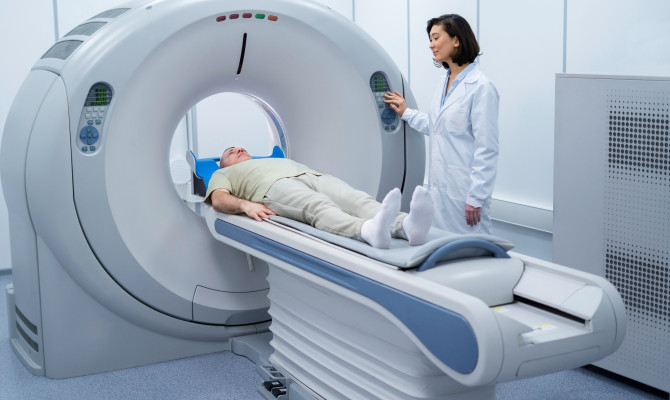
With cutting-edge imaging methods like Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), neuroscience has recently made incredible gains in comprehending the complexity of the human brain. Using FMRI, a unique non-invasive neuroimaging technique, researchers and medical practitioners may see and analyze brain activity in real time. This article examines the mechanism of functional MRI and its applications, benefits, drawbacks, and limitations. It also discusses what to anticipate during the operation and how to prepare for it.

How does fMRI work?
- The imaging technology known as functional MRI, or fMRI for short, monitors brain activity by spotting variations in blood oxygenation and flow.
- It is based on the idea that variations in blood flow to active brain areas are correlated with neuronal activity.1Overview| Researched based study from Open.edu
- A specific brain area needs more oxygenated blood to meet its energy needs when doing cognitive tasks or responding to inputs.
- This relationship between neural activity and blood flow is taken advantage of by FMRI to produce precise maps of brain activation throughout diverse tasks.
Preparation
How to prepare for it?
To achieve the best outcomes, various preparations must be made before having an fMRI scan:
- Remove All Metal Objects – Because fMRI employs strong magnets, removing all jewelry, piercings, and hairpins is essential.2Preparation| Researched based study from Radiologyinfo.org
- Let your doctor know about any existing medical conditions – Patients with particular health conditions, such as claustrophobia, metal implants, pacemakers, replacement joints, stents, etc., should let their doctor know ahead of time so they can determine whether fMRI is safe for them.2Preparation| Researched based study from Radiologyinfo.org
- Remain Still – Keeping still during the fMRI scan is essential to preventing motion artifacts that could skew the results.
- Follow Directions – Patients will be given detailed directions depending on the type of investigation and the duties they must carry out throughout the scan. These directives must be carefully followed; therefore, they must pay special attention.
Process
The Process of fMRI
A functional MRI procedure could include any of the following steps:
- Informed consent – Before the fMRI scan, the patient will receive a detailed explanation of the process, its purpose, and any potential risks. A form describing their comprehension and approval to move forward will be given to them for signature.
- Positioning – The patient will be made feel as comfortable as possible before being placed on the exam table, which is typically resting on their back.2The Process| Researched based study from Radiologyinfo.org
- Head coil – A customized head coil will be positioned around the patient’s head to detect magnetic signals coming from the brain.3The Process| Researched based study from Clevelendclinic.org
- Calibration – To pinpoint the exact location of the brain, a brief localizer or calibration scan will be conducted before the main scan.
- Functional scans – The patient will next be asked to perform particular tasks or react to stimuli given visually or audibly as part of the functional scans. The study’s objective determines these duties.
- Resting state scans – With the patient lying down and their eyes closed during a resting-state fMRI, researchers can examine the intrinsic functional connectivity of the brain.
- Post-Processing and Analysis – After the scan, the fMRI session’s raw data will be post-processed and statistically analyzed to produce brain activation maps.
- Interpretation – The results of the fMRI will be interpreted by trained experts, such as neuroscientists or radiologists, who will make judgments based on the brain activity seen during the tasks.
How is it different from a standard MRI?
- Activity is the primary distinction between an fMRI scan and a conventional MRI, as medical professionals may urge you to talk, tap a finger, or perform other easy tasks during an fMRI scan.3The Process| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- The fMRI monitors your brain’s blood flow as you perform these tasks to determine which regions are most active and compare that information to what you were doing then.
Uses

fMRI Uses
Functional MRI is used for the following:
- Brain mapping
- Diagnosis and treatment planning
- Cognitive studies
- Drug development
Brain Mapping
- Brain mapping, which entails pinpointing specific brain areas in charge of diverse processes like language processing, motor abilities, memory, and sensory perception, is one of the main applications of fMRI.
- This aids in the understanding of how various brain regions cooperate to carry out challenging tasks.4Uses| Researched based study from Frontiersin.org
Diagnosis and treatment planning
- The therapeutic use of fMRI for diagnosing and treating neurological and psychiatric diseases is considerable.
- It facilitates the identification of brain function anomalies linked with illnesses such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and depression.5Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Additionally, fMRI plays a significant part in presurgical planning by highlighting essential functional regions to keep clear during brain procedures.
Cognitive Studies
- Using fMRI, cognitive neuroscientists can examine how the brain responds to various inputs, mental processes, and emotional states.
- These investigations advance our knowledge of how people behave, make decisions, and learn.6Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Drug Development
- FMRI is employed in the pharmaceutical sector to assess how medications affect the brain. 7Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- It aids in evaluating whether novel drugs have the expected effects on brain activity.
Benefits
fMRI Benefits
Using an fMRI has the following benefits:
- Non-invasiveness – fMRI is non-invasive, meaning it doesn’t require any injections or surgical procedures, unlike other brain imaging methods that might need them. Patients can feel safer and more at ease because of this.
- High Spatial Resolution – Because fMRI has a great spatial resolution, researchers can identify the precise brain areas engaged during particular tasks.
- Versatility – It’s a flexible tool for neuroscience research because it may be used to examine various cognitive processes and brain functions.
- Real-time observation – Real-time monitoring of brain activity by fMRI enables studying dynamic processes as they occur.8Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Disadvantages
fMRI Disadvantages
The following limitations and drawbacks exist to fMRI:
- Expensive equipment – Because fMRI needs specialized and pricey equipment, its use in some hospitals and research facilities may be constrained.
- Indirect measure – FMRI measures blood flow changes and is a proximate indicator of brain activity. In contrast to electroencephalography (EEG), it does not directly assess the brain’s electrical activity.
- Motion artifacts – Results can be distorted and artifacts introduced even by slight movements made during the fMRI scan. Studying populations like youngsters or people with mobility disabilities presents significant difficulties9Disadvantages| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Limited temporal resolution – Even though fMRI has good spatial resolution, it has poor temporal resolution compared to other methods like EEG, which can precisely record brain activity in milliseconds.
Bottom line
The Bottom Line
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has substantial benefits for clinical and neurological research. It offers distinctive insights into the human brain’s workings, enabling us to investigate cognitive processes, comprehend neurological illnesses, and improve medical procedures. Despite its drawbacks, fMRI continues to transform our understanding of the complexity of the brain and provides optimism for future advancements in neuroscience and medicine. We should expect even more exciting improvements in studying the human brain as technology improves and fMRI becomes more widely available.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
The Open University
How FMRI works | The Prcess
-
Radiology Info
Functional MRI (fMRI) | Preparation
-
Cleveland Clinic
Functional MRI | Procedure
-
Frontiers Media
Pre-surgical Brain Mapping: To Rest or Not to Rest? | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Functional magnetic resonance imaging in neurology | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Combining fMRI and Behavioral Measures to Examine the Process of Human Learning | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
The role of fMRI in drug development | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Functional MRI and other non-invasive imaging technologies: Providing visual biomarkers for spinal cord structure and function after injury | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
A. Reducing the Effects of Motion Artifacts in fMRI: A Structured Matrix Completion Approach | Disadvantages