Cholecystitis: Symptoms, Causes and Management

- Cholecystitis
- 14 Aug 2023
Overview
What is cholecystitis?
Cholecystitis is the swelling, irritation and soreness of the gall bladder. Usually, the bile passes from the gallbladder to the small intestine. When the bile flow passage is blocked due to gallstone, the bile fluid accumulates within the gallbladder, causing enlargement, pain and probable infection. A person may suffer from either of the two forms of cholecystitis 1What is cholecystitis| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com i.e.
- Acute cholecystitis
- Chronic cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is a gallbladder infection causing sudden severe pain in the upper right side of the belly and extending up to the right arm. The affected belly part is usually very tender, and inhaling hard can make the pain severe.
Chronic cholecystitis is the recurring mild attacks of acute cholecystitis causing thickening and decrease of the gallbladder wall resulting in bile storage inability.

Gallbladder
Facts of the gallbladder
- The gall bladder (or cholecyst) is a tiny organ below the liver on the right of our upper stomach.
- The gall bladder is a bag-like structure with a narrow end connecting a small tube called a cystic duct through which bile is released into the small intestine.
- The function of the gall bladder is to store the bile juice secreted by the liver. Bile juice helps in the fat digestion of our body.
- The gallbladder secretes bile through the cystic duct, which travels through the common bile duct and finally into the small intestine.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cholecystitis
Generally, cholecystitis pain lasts for 2 to 3 days. Symptoms may differ from person to person. Some of them are: 1Symptoms of cholecystitis | Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
- Severe stomach aches in the upper right side of the center
- Pain radiate to the shoulder and back
- Tenderness
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- The stomach hurts during intense breathing
- Pain persists for hours after heavy meals
- Gassy stomach (bloating)
- Jaundice (yellowish eyes and skin)
- Loose and light-colored stool
Acute cholecystitis symptoms
- Severe pain starts suddenly and gets worse with deep breathing.
- The pain moves to the right arm and around the back
- Excessive perspiration
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach bloating
- Stomach tenderness
- Fever with chill
- Moreover, meals containing high fat worsen the acute cholecystitis symptoms
Chronic cholecystitis symptoms
- Chronic cholecystitis patients experience pain usually during the evenings or night hours.
- The symptoms appear slowly in frequent intervals (weeks or months). The pain may transform into an acute form with time.
- Cholecystitis symptoms look similar to other health issues, so it is always advisable to approach a physician to confirm its symptoms.
Causes
What are the causes ?
- Family history of gallbladder infection
- Gallstones (crystal-like substances formed by bile juice) or gall bladder sludge (a mixture of cholesterol and calcium of bile) get trapped in the bile duct.
- Reduced blood supply to the gall bladder (happens in diabetic patients)
- Infection in the common bile duct (common duct carrying bile from the liver, gall bladder and pancreas to the small intestine)
- Obstruction of the common bile duct
- Lump in the gall bladder (which is generally rare)
- Bump in the liver and the pancreas
- Excess cholesterol deposition in the gall bladder, usually during pregnancy or weight loss
- Consumption of high-fat diets such as oil, fat, chocolate, ice cream, egg yolk
- Extended fasting for long hours
- Abdominal injury due to surgery, sepsis(body’s extreme response to injury) or burns
- Infection in the blood vessels (vasculitis)
- Immune-deficiency individuals like diabetics, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infected or immunocompromised individuals
- Extreme illness that damages blood vessels1What are the causes | Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of cholecystitis
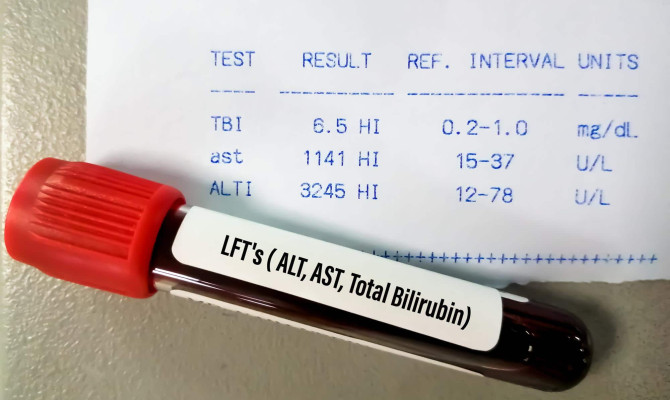
Blood test
- Complete blood count (CBC)-CBC test is done to see for increased WBC (white blood cells), alkaline phosphatase, serum aminotransferase, and bilirubin levels in the blood samples
- Liver function test (LFT)-LFT tests are done to confirm if the liver is functioning normally
Ultrasound
- Ultrasound is done to get an internal picture of the gall bladder for any probable infection.
Abdominal X-ray
- It uses high-energy radiation to get images of internal organs, bones and tissues.
CT (computed tomography ) scan
- It uses computers and X-rays to get a clear picture of the internal organs of the body
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- MRCD is used to get a clear picture of the gallstones, cystic duct and gallbladder
HIDA(Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid) scan (also called hepatobiliary scintigraphy or cholescintigraphy),
- HIDA scan uses a radioactive tracer to detect abnormalities in bile ducts, gall bladder, and liver.
- It can track the bile flow from the liver to the small intestine.
ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
- (ERCP) uses both upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy (a thin tube with a camera is passed inside of the body through the mouth) and X-ray to identify liver, gall bladder, bile and pancreatic duct problems.
PTC (percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography)
- PTC visualizes any blockage in the bile ducts using dye and X-ray
Management

Management of Cholecystitis
Non surgical methods
- Prevent eating and drinking for some time to relieve the stressed gall bladder and ease the symptoms
- Injecting intravenous fluids to avoid dehydration
- Painkillers to relieve pain
- Antibiotics to fight gallbladder infection
- Gallbladder drainage(percutaneous cholecystostomy) is done when surgery cannot be performed due to severe illness and to prevent the spread of infection
Gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy)
It is done by any of the following:
- Open abdominal procedure the long cut is done in the belly
- Laparoscopy(Laparoscopic cholecystectomy)small cuts are made in the abdominal skin area through which a camera is placed in the cuts to guide the surgical procedure and tools for surgical removal of the gall bladder through other incisions
Patient experiences less pain and fast recovery after the laparoscopic procedure, after the gallbladder surgical removal, the bile directly flows from the liver into the small intestine and does not affect the overall patient’s health, but some may experience diarrhea 2Management of cholecystitis | Researched based study from Surgeryscience.com .
Other treatment measures
- Cholesterol-lowering medicines viz; statins to prevent gall bladder stones from forming
- Living on a very low-fat diet (fish or poultry)
- Medicines viz; ursodiol to dissolve the gallstone (oral dissolution therapy)
Alternatives
Alternative treatment
Cleansing of the gallbladder
- By consuming herbs, apple juice and olive oil for around five days.
Apple cider vinegar in apple juice
- It has anti-inflammatory properties and relieves pain and swelling.
- Its acidic nature can dissolve gallstones.
- But limited evidence is available for the effects on gallstones
Turmeric
- It helps the body fight infections
- It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and hence is beneficial for gallstones.
Milk thistle
- It is a herb having high levels of antioxidants and hence helpful in detoxifying the blood.
- Its anti-inflammatory properties help reduce the pain and swelling of cholecystitis.
Dandelion
- It is a herb containing antioxidants that helps to treat cholecystitis
Artichoke
- Artichoke plant extract stimulates bile production and improves gallbladder and liver function.
Psyllium husk
- Psyllium husk Plant fibre helps lower the cholesterol in our body and hence helps prevent gallstones.
Castor oil
- When placed in the belly area, a warm castor oil pack somewhat relieves the cholecystitis pain.
Acupuncture (technique of inserting a thin needle in the skin)
- Acupuncture can give relieve cholecystitis symptoms, but there is limited evidence for it.
Yoga (exercises with breathing techniques)
- Yoga is said to control cholecystitis symptoms, but further research is warranted to prove the fact.
Complications
Complication related to cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis complication
- Gallstones in the bile duct
- Liver and bile duct injury
- Lumps within the stomach
- Intestinal injury
- Bleeding
- Infection
Chronic cholecystitis complication
- Pancreatitis is an infection of the pancreas causing redness and swelling, and leads to pancreatic duct blockage
- Gallbladder-duodenal Fistula-It is an opening that occurs when gallstone destroys the gall bladder wall linked to the first part of the small intestine, and Causes leakage of stomach acid
- Gall bladder enlargement-The gall bladder wall becomes thicker, more diminutive and scarred, leading to decreased bile storage capacity and release.
- Gall bladder perforation (due to infection)
- Cholestasis (decreased or complete stoppage of bile juice flow through the bile duct )
- Gall bladder cancer (rare case)
- Gall bladder outburst
- Belly infection( in some cases)
- Gallbladder tissue death(gangrenous cholecystitis)
- Pus formation within the gallbladder
Prevention
Preventing cholecystitis
- Avoid skipping meals
- Avoiding foods with high cholesterol and fats (saturated and trans fats)
- Doing regular exercise( as exercise decreases the cholesterol in our body)
- Maintaining the correct body weight as per height
- Losing one’s weight gradually as rapid weight loss increases the chances of gallstones.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Cholecystitis - An overview | Introduction | Causes | Symptoms
-
International Journal of Surgery Science
Acute cholecystitis: Severity assessment and management | Management