Spinal Stenosis: Causes, Treatment and Complications

- Spinal stenosis
- 30 Aug 2023
Introduction
What is Spinal Stenosis?
The narrowing within the spinal canal is known as spinal stenosis. There is a tunnel present that connects the spine’s vertebrae to the spinal canal. The spinal cord is present inside it. A constricted area can result in pinching, compression, and irritation of the spinal cord and can be due to various traumas and diseases.It can also result in nerve problems, like sciatica, and back pain. When the area surrounding the spinal cord becomes too small, spinal stenosis develops. Back or neck discomfort and tingling in the legs and arms are signs of spinal stenosis. 3Introduction | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic

Symptoms
Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
For the majority of people, symptoms appear and worsen gradually over time, and in certain cases, there may be no symptoms at all. 3Symptoms | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Lower back spinal stenosis may give rise to the symptoms present below:
- An aching and burning sensation that travels through the buttocks all over the legs. This pain worsens while walking or standing and can be better with bending.
- Numbness, tingling, and cramping of legs and feet
- Lower back pain
- Weakness and heaviness in legs and feet
- Bowel movement difficulties
- Difficulty to hold urine 1Symptoms | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Cervical spinal stenosis may give rise to the following symptoms:
- Problems with balancing
- Stiff neck
- Numbness and tingling sensation (which travels down the arms and into the hands)
- Weakness in fingers, arms, and hands
- Pain that can get worse while standing, and walking
- The pain can be reduced by bending the neck and lower back or by sitting 1Symptoms | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
More serious symptoms are:
- Bowel dysfunction
- Sexual dysfunction
- Bladder dysfunction 1Symptoms | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Types
Types of Spinal Stenosis
Based on the regions of the spine that are affected, spinal stenosis can be:
Lumbar spinal stenosis:
- Anatomically and pathologically, lumbar spinal stenosis involves a narrowing of the lower spinal canal.
- The lower back’s lumbar spine is made up of five vertebrae and are among the largest of the spine. 3Types | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Cervical spinal stenosis:
- A number of symptoms that might arise from the neck’s spinal canal narrowing is called as cervical spinal stenosis.
- The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrates.
Causes
What Causes Spinal Stenosis?
Acquired and congenital etiologies can lead to spinal stenosis. Congenital etiologies account for just 9% of the cases. As spinal stenosis often develops as a person ages, some patients have smaller spinal canals from birth itself. The causes include: 4Causes | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- The spinal disks dry out, begin to protrude, and occasionally rupture
- The spine’s bones and ligaments thicken and enlarge
- Spinal arthritis, which typically affects middle-aged or older adults
- Bone conditions like Paget disease
- Spine issue or growth that has existed since birth
- Hereditary multiple exostoses
- Narrow spinal canal at birth
- Herniated or slipped discs, which frequently occur in the past
- An injury that puts pressure on the nerve roots and the spinal cord
- Tumor of the spine
- Osteoarthritis
- Spinal cysts
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Spinal dysraphism
- Injury or fractured spine
- Congenital kyphosis
- Posterior longitudinal ligament ossification
- Congenital stenosis
- Osteopetrosis
- Spinal curvature or scoliosis
- Morquio syndrome
- Achondroplasia 1Causes | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Diagnosis
How is Spinal Stenosis Diagnosed?
The healthcare professional will examine the person physically, inquire about their symptoms, and get a detailed medical history. The healthcare professional could press on various parts of the spine to feel any pain. They will probably ask to bend in various ways so they can check to see if different spinal postures cause any symptoms. 3Diagnosis | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
They will advise a few imaging tests:
X-ray of the spine:
- X-rays can display changes in bone structure like bone spurs, or a reduction of disk height.
MRI:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) produces cross-sectional images of the spine using strong magnets and radio waves.
- The spinal cord, nerves, and disks can all be observed in MRI.
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan:
- It is also called a CT myelogram.
- Cross-sectional images of the spine are created using a CT scan.
- A contrast dye is used during a CT myelogram to view the spinal cord and nerves more clearly. 3Diagnosis | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Treatment
Treatment
The treatment of spinal stenosis depends upon the location, severity, and cause. It may include the following methods.
- Non-surgical techniques
- Surgical methods
- Home remedies
Non-surgical remedies:
Physical therapy:
- Physical therapy improves balance, flexibility, spine stability, and strength.
- The spine will become more resilient and may aid with back and core muscle strengthening.
- The spinal canal can be opened up by proper walking technique, which can assist relieve strain on spinal nerves.
Steroid injections:
- When given to the affected area, they may help lessen discomfort, irritation, and swelling, discomfort, around the pinched spinal nerves.
Oral medications:
- Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can help lessen discomfort, inflammation, and pain that is associated with spinal stenosis.
- Medications can include tricyclic antidepressants and muscle relaxants.
Surgical remedies:
Laminectomy:
- Laminectomy is the most common and preferred surgery for spinal stenosis.
- It entails taking off the lamina, a piece of the vertebra, ligaments, and bones.
Laminotomy/ partial laminectomy:
- The lamina that is pressing the nerve the most is only partially removed by the surgeon.
Laminoplasty:
- In order to provide additional canal space, the surgeon removes a portion of the lamina.
- They build a hinged bridge over the area where they removed bone using metal screws and plates.
Foraminotomy:
- This technique entails removing bone or tissue from this region.
Interspinous process spacers:
- For some patients with lumbar spinal stenosis, interspinous process spacers is a minimally invasive procedure.
- The spinous processes, which are the bones that protrude from the rear of each vertebra, are separated by spacers inserted by the surgeon.
Spinal fusion:
- Two vertebrae are permanently joined (fused) together during spinal fusion surgery. 3Treatment| Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Home remedies:
Exercise:
- Exercising increases flexibility and balance while bolstering the muscles that support the spine.
- In case of planning any exercise routine, consult a healthcare physician.
Applying cold:
- Apply a frozen gel pack, ice pack, or a frozen bag of peas, if heat is not alleviating the symptoms.
- Apply ice intermittently for 20 minutes.
- Ice helps to lessen swelling, inflammation, and soreness.
Applying heat:
- In most cases, applying heat to relieve osteoarthritis pain is preferable.
- Heat promotes blood flow, which eases painful joints and relaxes the muscles.
- Use heat with caution because a high setting can cause harm. 3Treatment| Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Prevention
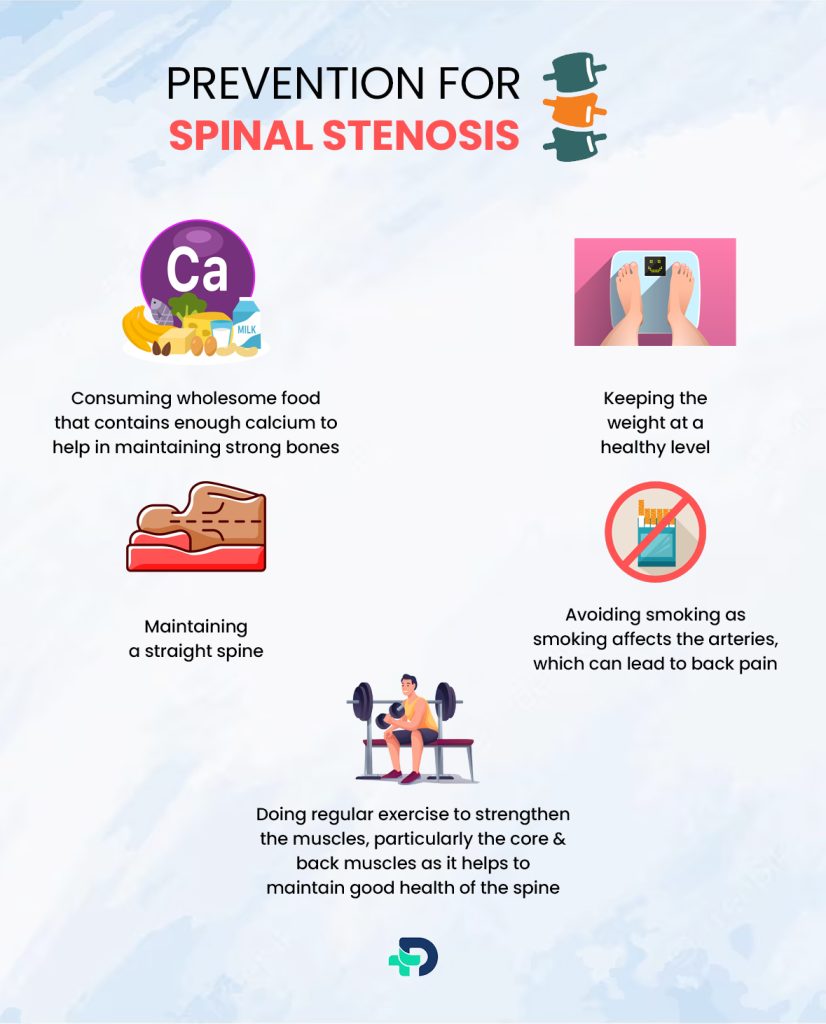
Can Spinal Stenosis be Prevented?
We cannot completely prevent spinal stenosis because the majority of its causes are common age-related “wear and tear” issues. But we can take certain actions to reduce the risk or halting the development of spinal stenosis as follows:
- Consuming wholesome food that contains enough calcium to help in maintaining strong bones.
- Keeping the weight at a healthy level.
- Avoiding smoking as smoking affects the arteries, which can lead to back pain.
- Maintaining a straight spine.
- Doing regular exercise to strengthen the muscles, particularly the core and back muscles as it helps to maintain good health of the spine. 2Prevention| Researched based study from MedlinePlus
Complications
Complications
- Loss of bowel and bladder control
- Sexual dysfunction including erectile dysfunction and anorgasmia.
- Partial or total leg paralysis. 3Complications | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
Prognosis
Prognosis
- The prognosis of spinal stenosis differs depending on a number of conditions, which includes:
- Severity
- Location
- Overall health of the person
- The outlook for spinal stenosis is generally favorable. With nonsurgical therapy, many patients with spinal stenosis can lead a normal active life.
- But it is crucial to keep in mind that each person’s experience with spinal stenosis is different, and every treatment is not effective for everyone. 2Prognosis | Researched based study from MedlinePlus
Takeaway
Takeaway points
- Treatment is typically not required if the patient is asymptomatic.
- Patients experiencing pain should be urged to start an exercise regimen, give up smoking, and keep their weight in check.
- People with spinal stenosis might need to adjust their jobs and interests, but many people with spinal stenosis are nevertheless able to lead active lives.
- The leg and arm problems may be partially or completely relieved by spine surgery.
- People who experienced chronic back pain before the surgery are likely to experience some discomfort after the surgery.
- Future issues can be more likely if one has had more than one type of back surgery.
- Future illnesses and arthritis are more likely to affect the parts of the spinal column that are above and below a spinal fusion. 4Takeaway | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Patients with spinal stenosis typically have a long and challenging recovery ahead of them, but the best results for patients can be accomplished with a team effort between the various healthcare teams and departments. 4Takeaway | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Causes | Symptoms
-
MedlinePlus
Prevention | Prognosis
-
Cleveland Clinic
Introduction | Symptoms | Complications | Treatment | Diagnosis | Types
-
National Institutes of Health
Causes| Takeaway