Lung cancer: Types, Stages and Treatment

- Lung Cancer
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Lung cancer?
Lung cancer is a critical health concern affecting millions of people worldwide. It is a particular type of cancer that usually results from smoking and starts in the lungs. Nonsmokers, on the other hand, can get lung cancer due to a variety of other factors, including secondhand smoke exposure, and environmental contaminants.
In this article, we will delve into lung cancer’s causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, treatment options and prognosis.
Symptoms
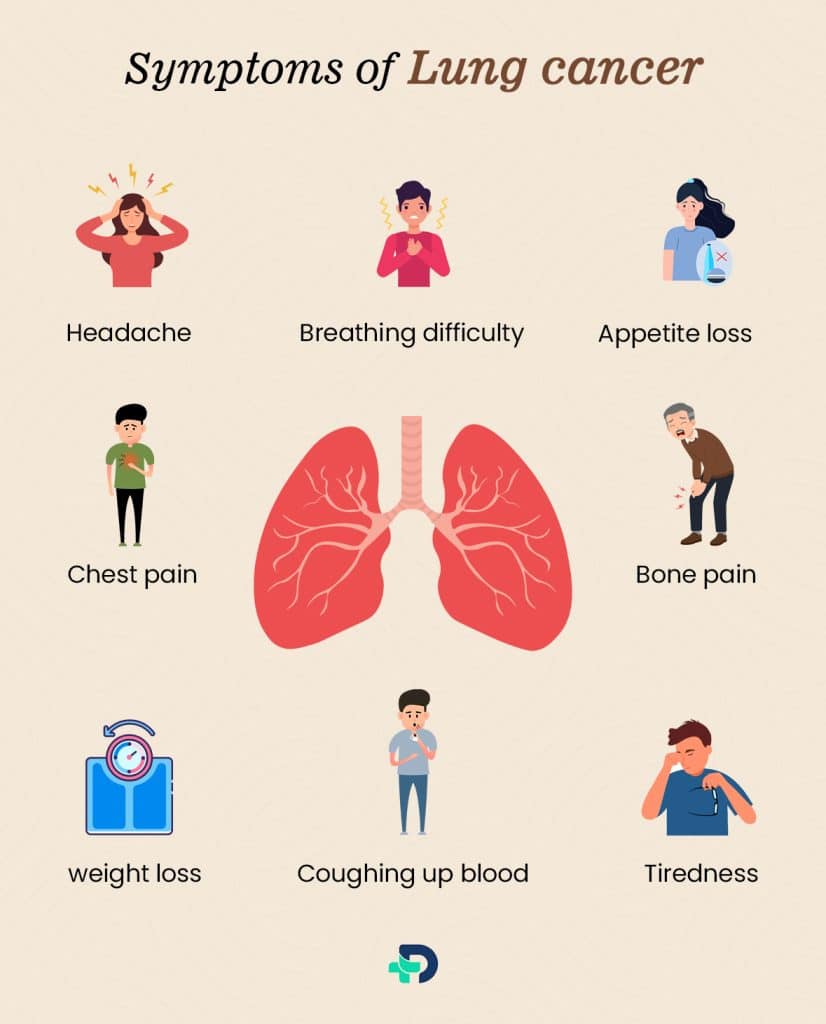
Symptoms of Lung cancer
Initially there are no specific signs of a lung cancer and when individuals exhibit the symptoms listed below, the majority of patients already have an advanced condition:
- Persistent cough that worsens with time.
- Headache.
- Appetite loss.
- Breathing difficulty.1Symptoms| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Coughing up blood.
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Tiredness.
- Bone pain.
Types
Types of Lung cancer
They can be of broadly two types based on where it begins:
- Primary type
- Secondary type
Primary lung cancer
If the cancer originates inside the lung, it is called as primary lung cancer. There are two subtypes of primary lung cancer :
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
Secondary lung cancer
- It is when the cancer has moved from a different part of the body to the lungs.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
- Approximately 15% to 20% of all the lung cancers.
- These tumors frequently spread quite quickly.2Types| Researched based study from Cancerresearchuk.org
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Nearly 80% to 85% of lung cancers are NSCLCs or non-small cell lung cancer2Types| Researched based study from Cancerresearchuk.org
The three main kinds of NSCLC are:
- Large cell carcinoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
The following less frequent non-small cell cancers could also exist:
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
Stages
Stages of Lung cancer
Cancer staging describes how far this illness has gone and how bad it is. Staging of NSCLC and SCLC can be performed in various methods.
Lung cancer of the NSCLC type may be staged as follows:
- Stage 0 – The top layer of the lungs or bronchi is affected by cancer. It hasn’t spread to the outside of the lungs or other type of lung tissue.
- Stage I – The cancer is still in the lungs and has not spread to other parts.
- Stage II – Bigger than Stage I, has spread to internal lymph nodes, or has multiple tumors in the same lung lobe.
- Stage III – Bigger than Stage II, has spread to nearby lymph nodes or structures, or has many tumors in various lobes of the same lung.
- Stage IV – Spread to the other lung, or the fluid around the lung, fluid around the heart, or other organs of the body.1Stages| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
Staging SCLC
Lung cancer of the SCLC subtype’s staging may comprise :
- Limited-stage SCLC – only one lung is affected and may have spread rarely to the lymph nodes in the center of the chest or just above the collarbone on the same side.
- Extensive-stage SCLC – spread throughout one of the lungs, or to the other lung, or to the lymph nodes on the opposite side, and other parts of the body.
Causes
What are the major causes of Lung cancer?
- Smoking – is the primary cause of lung cancer, accounting for 90% of all cases.3Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Genetic alterations – DNA alterations can turn on or off tumor suppressor genes, which help regulate cell division and induce cells to die at the appropriate moment, or oncogenes, which enable cells to grow, increase, or remain alive. Lung cancer typically requires alterations to numerous genes.4Causes| Researched based study from Cancer.org
- Environmental Factors – Lung cancer risk can be considerably increased by exposure to environmental contaminants such as radon gas, secondhand smoke, asbestos fibers, diesel exhaust, and certain chemicals.
Risk factors
Risk factors
- Genetic Predisposition – Some people may be more prone to developing lung cancer due to an inherent genetic predisposition, even if they are not exposed to other known risk factors.
- Family history – individuals with one of their parents or a sibling with lung cancer are at a higher chance of developing it.
- Smoking – increases the likelihood of developing a lung cancer drastically.
- Secondhand smoke exposure – can increase the likelihood of an individual even if they do not smoke.
- Previous chest radiation therapy – for any other type of cancer raises a person’s risk of acquiring lung cancer, especially if they smoke.
- Radon gas exposure – Radon is formed naturally by the disintegration of uranium in soil, rock, and water and eventually includes a component of the air we breathe. Radon levels that are unsafe can build up in any structure, including residences.3Risk factors| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Asbestos and other cancer-causing substances – Workplace exposure to uranium, asbestos, and other carcinogens like silica, arsenic, vinyl chloride, chromium, diesel smoke, and nickel can raise a person’s risk of developing lung cancer, especially if they smoke.5Risk factors| Researched based study from Cancer.org
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Lung cancer
Early detection of lung cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes.
The following diagnostic tests and procedures are used to diagnose lung cancer after a thorough medical history and a family history:
- Imaging Tests – include chest X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and computed tomography (CT) scans, used to visualize the lungs and identify abnormalities.6Diagnosis| Researched based study from Cancer.org
- Sputum Cytology – to check for cancer cells, where the sputum sample is examined under a microscope.
- Biopsy – A tissue sample is obtained through bronchoscopy, needle biopsy, or surgery to determine the presence of cancer cells and their type.
- Molecular Testing – of the tumor cells helps identify specific genetic mutations or changes that may guide treatment decisions.
- Staging – Once lung cancer is diagnosed, staging tests, such as positron emission tomography (PET) scans, are conducted to determine the extent of cancer spread and plan appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of Lung cancer
The treatment depends on various factors, including the stage and type of cancer, overall health and the patient’s preferences.
The following are the common treatment modalities:
- Surgery – aims to remove the tumor and nearby affected tissues. It may involve a lobectomy, wedge resection, or pneumonectomy, based on the size and location of the cancer.7Treatment| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
- Radiation Therapy – High-energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, are directed at the tumor to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy – Anti-cancer drugs are given through mouth or through veins to kill cancer cells throughout the body and is often used in advanced stages of lung cancer or before surgery to shrink tumors.
- Targeted Therapy – given to stop specific genetic changes or abnormalities in cancer cells and can be highly effective in treating certain types of lung cancer.8Treatment| Researched based study from Cdc.gov
- Immunotherapy – helps the immune system locate and destroy cancer cells and has shown promising results in treating advanced lung cancer.
- Palliative Care – focuses on increasing the patient’s quality of life by treating signs and symptoms, controlling pain, and giving emotional support.
Prevention
Prevention of Lung cancer
While some risk factors for lung cancer cannot be avoided, like genetic predisposition, specific preventive measures, such as the ones listed below, can help lower the risk :
- Avoid smoking.
- Reduce exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Minimize exposure to environmental pollutants, such as radon gas, asbestos, and other chemicals.
- Eat a diet high in vegetables and fruits and get physical exercise most days of the week.9Prevention| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Get regular checkups to catch any health issues early.
Complications
Complications associated with Lung cancer
Lung cancer and its treatment can affect the body in various ways as it progresses and may include the following:
- Shortness of breath.
- Changes in pupil size.
- Droopy eyelids
- Increased blood calcium level.
- Coughing up blood. (Mild to severe)
- Fluid accumulation in the chest.10Complications| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Swelling of the face.
- Spinal cord compression.
- Unexplained weight loss.3Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Dizziness.
- Anemia
- Loss of consciousness.
- Spread to the bone, causing bone pain.
- Spread to different sites of the body like bones or the brain.
- Anxiety and depression.
Prognosis
Prognosis of Lung cancer
Lung cancer prognosis is determined by various factors, including the stage of diagnosis, general well-being, and response to treatment. When compared to advanced-stage lung cancer, early-stage lung cancer has a better outlook. When lung cancer has spread to nearby structures, it is often incurable. However, there are treatments to improve symptoms and life expectancy of people with advanced lung cancer. If any symptoms or risk factors are present, get medical assistance immediately.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Cleveland Clinic
Lung Cancer | Symptoms
-
Cancer Research UK
Types of lung cancer | Types
-
National Library of Medicine
Lung Cancer | Causes
-
American Cancer Society
Lung Cancer | Causes
-
American Cancer Society
Lung Cancer | Risk factors
-
American Cancer Society
Lung Cancer | Diagnosis
-
Medline Plus
Lung Cancer | Treatment
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
How Is Lung Cancer Diagnosed and Treated? | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
A Healthy Dietary Pattern Reduces Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | Prevention
-
Mayo Clinic
Lung cancer | Complications