Elimination diet: What do I need to know?

- Elimination diet
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is an Elimination diet?
Elimination diet is a dietary strategy that involves gradually returning various foods or food groups after removing them from your diet to detect any potential food allergies, sensitivities, or intolerances.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
In this post, we’ll set out to comprehend it, investigating its goals, advantages, and step-by-step methodology. We will examine each stage in detail, starting with the preparation phase, where you will discover the significance of speaking with medical experts and getting the necessary information before setting off.

Benefits
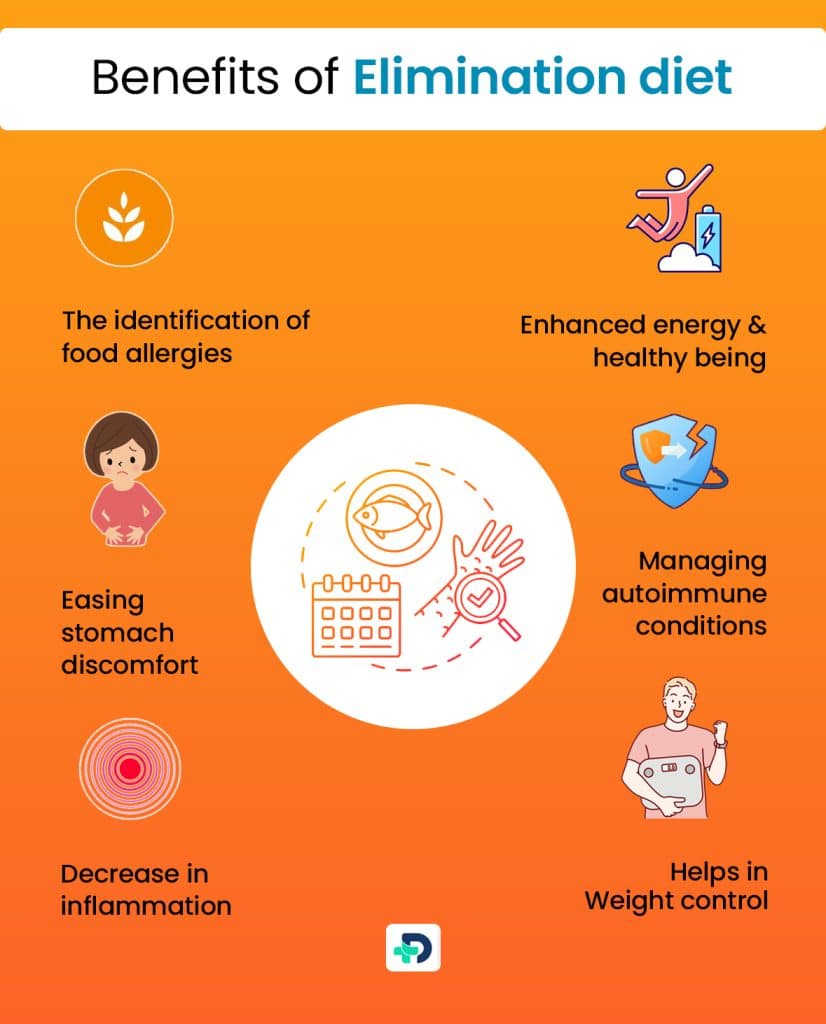
Benefits of Elimination diet
- Detecting food allergies or sensitivity
- Easing stomach discomfort
- Controlling autoimmune diseases
- Inflammation reduction
- Helps in Weight control
- Increased strength and well-being
Here are some broad advantages of an elimination diet, while the same benefits may differ based on personal circumstances:
The identification of food allergies
- One of its main advantages is its ability to identify specific foods that can generate adverse reactions in your body. You can identify and comprehend how particular foods affect your health and well-being by eliminating potential trigger foods and reintroducing them one at a time.1Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Easing stomach discomfort
- Constipation, diarrhea, gas, bloating, and other digestive issues are common. It can help you pinpoint the specific items that might be the source of these problems and offer relief by removing them from your diet.
Managing autoimmune conditions
- Certain foods may cause or worsen some medical disorders, including celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease. People may find a decrease in symptoms and an improvement in general health by identifying and avoiding these.3Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Decrease in inflammation
- In the body, chronic inflammation can be caused by specific diets, such as those high in artificial additives, harmful fats, or processed carbohydrates. By making these pro-inflammatory foods easier to recognize and avoid, inflammation and its accompanying symptoms may be lessened.4Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Helps in Weight control
- This might assist people in finding foods that might be impeding their success if they are having trouble reducing weight or battling unexplained weight gain. Maintaining a healthy weight is simpler by cutting out meals that could cause problems.2Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Enhanced energy and healthy being
- Some people claim to have more energy, mental clarity, better sleep, and general well-being. This can result from removing items that might trigger inflammations or mild unpleasant responses.1Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Why is a diet of elimination important?
- It can help locate the specific foods that may contribute to a person’s negative symptoms or reactions. These responses can vary and cause symptoms such as migraines, exhaustion, headaches, and digestive problems. It typically lasts for 2 to 6 weeks.1Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Method
Understanding the methodology of the Elimination diet
Preparation
- It’s essential to learn about your current diet and any symptoms or reactions you may be having before beginning.
Elimination phase
- You frequently cut out particular foods or food groups, resulting in adverse reactions during this phase. The most popular ones are meat, dairy products, and gluten. You must entirely forgo these foods for a set time, usually two to four weeks.
Phase of reintroduction
- The excluded foods will be gradually reintroduced one at a time, generally with a three-day interval between reintroductions. This enables you to watch for any potential reactions or symptoms.
Observation and monitoring
- You will closely observe how your body reacts to each item during reintroduction. Observe any changes in symptoms, including gastrointestinal problems, skin responses, headaches, exhaustion, or mood changes.
Personalization
- Once you’ve identified the triggers, you can modify your diet by minimizing or avoiding the foods that may result in adverse reactions. This enables you to keep a healthy diet while avoiding foods that are bad for you.8Method| Researched based study from Fammed.wisc.edu
Dietary Suggestions
Dietary suggestions to accomplish the benefits of the Elimination diet
What foods should you avoid?
Following is a list of typical foods that are frequently avoided:
Grains that contain gluten
- Wheat, barley, rye, baked goods, pasta, cereals, and bread are created from these grains.
Dairy goods
- Butter, milk, yogurt, cheese, and other dairy-based goods. Dairy products with and without lactose are included in this.7Dietary suggestions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Soy
- Soybeans, as well as soy-based foods, including tofu, tempeh, and soy sauce.
Eggs
- Whole eggs and meals like baked products, sauces, and dressings that use eggs as ingredients.
Nuts and seeds
- Tree nuts, including almonds, walnuts, cashews, and pistachios; peanuts; and seeds like sesame.
Fish and shellfish
- Fish such as salmon, tuna, mackerel, and shellfish such as prawns, crab, and lobster.
Certain veggies and fruits
- Some diets require avoiding foods strong in histamines, including citrus fruits, strawberries, tomatoes, and avocados. Also to be avoided are nightshade vegetables, including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and peppers.7Dietary suggestions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Artificial and processed foods
- Include preservatives, artificial sweeteners, colors, flavors, and additives.
Alcohol and caffeine
- Caffeinated or alcoholic items such as coffee, tea, energy drinks, etc.
Added sugars
- foods and beverages with added sugars include soda, candy, pastries, sweetened desserts, refined sugars, and high-fructose corn syrup.7Dietary suggestions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
What foods to eat?
List of food you need to add in your diet:
Gluten free food
- Rice (including white, brown, and wild rice) is gluten-free, oats without gluten, millet, amaranth, and quinoa.
Sources of protein
- Fish (apart from shellfish), such as salmon and cod, and lean meats like chicken, turkey, and lamb. Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are plant-based proteins that can be used.
Veggies and fruits
- Fruits and vegetables are generally in good condition. However, you should avoid a particular fruit or vegetable for a while if you think it causes an allergic reaction.
- To guarantee a healthy intake of vitamins and minerals, emphasize various colorful fruits and vegetables.
Non-dairy alternatives
- Include almonds, coconut, rice milk, and other substitutes without extra sugar or chemicals.
Healthy fats
- Olive oil, coconut oil, avocado, and modest quantities of nuts and seeds.
Spices and herbs
- Various herbs and spices can be used to flavor your food.
Alternative sweeteners
- Stevia plus modest amounts of honey or other natural sweeteners, such as maple syrup.7Dietary suggestions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Risks
Risks of Elimination diet
One should be aware of the possible risk associated with the elimination diet before choosing it.
Inadequate nutrition
- The diet may result in nutritional inadequacies if it is not carefully planned. For instance, skipping dairy products could cause a calcium shortage if substitute sources aren’t considered.5Risks| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Limited food choices
- It may be challenging to meet your nutritional demands and maintain a varied and enjoyable diet if it drastically limits your food options. This may result in diminished adherence and boredom.5Risks| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Social and practical challenges
- It can be not easy and socially isolating, particularly in social situations or dining out. It can call for meticulous meal planning, sharing information about your nutrition with others, and coming up with workable substitutes in various circumstances.6Risks| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Incorrect diagnosis of symptoms
- Interpreting symptoms throughout the elimination and reintroduction phases might be challenging and subjective. Maintaining correct records and collaborating closely with a healthcare practitioner is crucial.
Psychological and emotional effects
- It may have psychological and emotional implications, such as feelings of resentment or deprivation or stress about one’s dietary decisions.6Risks| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Role of the elimination diet in adults with food allergy | Overview | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
A Multi-Faceted Approach to Weight Loss: A Case Report | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
How to Tackle the Relationship between Autoimmune Diseases and Diet: Well Begun Is Half-Done | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Dietary Control of Inflammation and Resolution | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
The impact of the elimination diet on growth and nutrient intake in children with food protein induced gastrointestinal allergies | Risk
-
National Library of Medicine
Nutritional and Psychological Considerations for Dietary Therapy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis | Risk
-
National Library of Medicine
Diets for diagnosis and management of food allergy | Dietary suggestions
-
The UW Department of Family Medicine and Community Health
The Elimination Diet | Method