Sinusitis: Symptoms, Causes and Management

- Sinusitis
- 29 Aug 2023
Introduction
What is Sinusitis?
Sinuses are hollow cavities within the facial bones connected to the laser passageways. The sinuses’ lining tissue becomes irritated. It frequently happens due to a bacterial or viral infection, allergies, or other conditions that result in blocked, fluid-filled sinuses.
We will delve into the intricate aspects of sinusitis in this post, shedding light on its numerous manifestations, potential triggers, effects on everyday life, and the most effective management techniques. This thorough manual gives readers a firm foundation for comprehending and dealing with this common health problem.
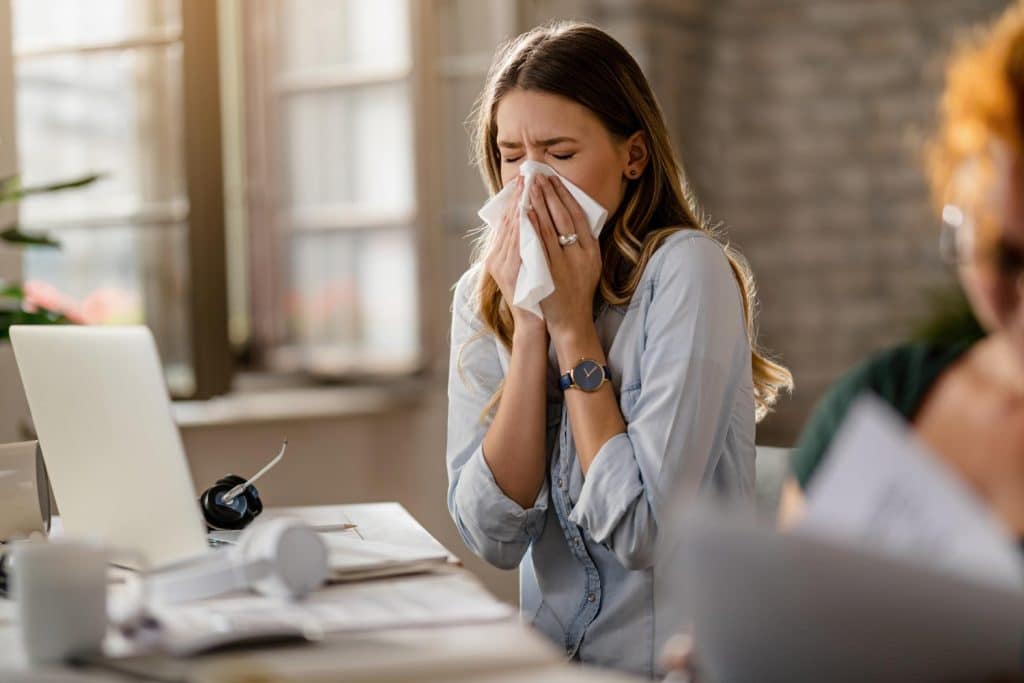

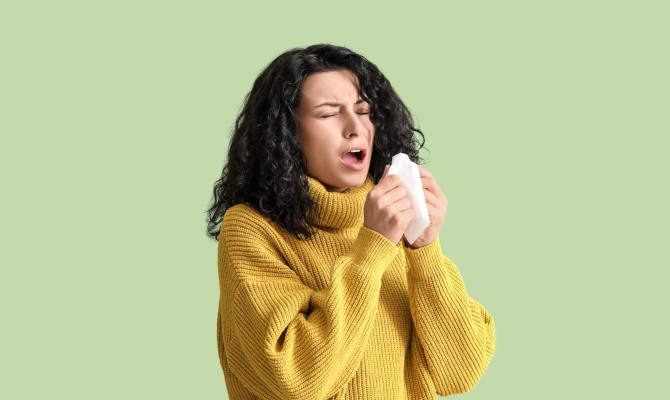
Symptoms

Symptoms of Sinusitis
- Nasal congestion
- Headache
- Discharge
- Post nasal drip
- Reduced sense of taste and smell
- Weakness
- Foul breath
- Fever
Nasal congestion
- A blocked airway that makes using the nose to breathe difficult.
Sinusitis headache
- Usually localized to the forehead region and made worse by bending or quick movements. Headache or pressure in the cheekbones or the area surrounding the eyes are two examples of facial discomfort.
Discolored nasal discharge
- Thick mucus dripping from the nose that is yellow or green.
Nasal post-drip
- Throat congestion is brought on by mucus drips that cause a cough or sore throat.
Reduced ability to taste and smell
- A common problem is when the sinuses are involved.
Fatigue
- Feeling worn out or exhausted due to the body’s efforts to combat the infection.
- Bread with a fall-like aroma is caused by bacteria in the sinuses.
Fever
- It can occasionally result in fever when brought on by a bacterial infection.
Toothache
- Upper tooth pain is frequently misdiagnosed as a dental problem. 2Symptoms | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Causes
Causes of Sinusitis:
There may be several underlying causes, which are often grouped as follows:
Infections
- Viral illnesses like the common cold frequently bring on the most frequent reason of bacterial infections can cause sinusitis, particularly if the symptoms worsen or persist.
Allergies
- Allergies to dust mites, pollen, pet dander, or other allergens can cause sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinuses.
Nasal polyps
- They are tiny growths that can obstruct the sinus passages and cause chronic sinusitis.
Structural issues
- Normal sinus drainage might be obstructed by a deviated septum, nasal bone spurs, or other anatomical anomalies, increasing the risk of infection.
Environmental factors
- Changes in air pressure, smoke, and pollution exposure can irritate the passageways and aggravate the condition.
Immune system conditions
- Immune system-compromising conditions like HIV or autoimmune illnesses can increase the risk.
Medical procedure
- Sometimes nasal discomfort and eventual sinusitis are caused by nasal intubation or regular use of nasal sprays. 5Causes | Researched based study from Science Direct
Types
Types of Sinusitis
Following the length and underlying causes, it can be divided into several types. The primary types consist of:
Acute sinusitis
- This often lasts for less than four weeks and is frequently brought on by a viral infection like a cold. Acute sinusitis symptoms range from heavy nasal discharge, face discomfort, and nasal congestion. 1Types | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Chronic sinusitis
- When symptoms persist for 12 weeks or more, chronic sinusitis is diagnosed.
- Allergies, nasal polyps, or structural problems impeding drainage can all contribute to this problem.
Subacute sinusitis
- This form lasts less than 12 weeks but longer than acute sinusitis. A persistent viral infection or a subsequent bacterial infection could cause it.
Recurrent sinusitis
- It is deemed recurrent if a person has several episodes of acute sinusitis within a calendar year or if chronic sinusitis symptoms continually reappear.
- A physical examination, evaluation of the patient’s medical history, and other testing go into making the diagnosis. This is how the process usually works. 1Types | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health 2Types | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Diagnosis
How is Sinusitis Diagnosed?
Medical history
- The doctor will ask you about your symptoms, their length, and whether or not you have ever had allergies, infections, or other conditions of a similar nature.
Physical examination
- The doctor may do a physical exam, which may include looking for facial pain and examining passageways and evidence of congestion.
The nasal endoscopy
- An endoscopy of the nose may be performed sometimes.
- This entails looking within your sinuses and tubes using a tiny flexible tube with a camera.
- This can aid the physician in identifying anomalies, such as polyps or structural problems, through imaging tests.
Imaging tests
- Tests like X-rays, CT scans are used in some cases.
- These give clear pictures of the sinuses that can be used to spot obstructions, inflammations, or other problems. 3Diagnosis | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health 4Diagnosis | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Treatment
Management of Sinusitis
The cause and severity of the disease determine the management in most cases. Here are a few typical methods:
Hydration and sleep
- To help your body fight infections and accelerate your recovery, get plenty of rest and drink lots of water.
Nasal sprays
- Saline nasal sprays or a neti pot can clear congestion and remove mucus.
Steam inhalation
- Nasal congestion can be eased, and the nasal passages can be soothed by inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water.
Decongestants
- Decongestants sold over the counter may offer momentary relief.
Pain relief
- Over the counter drugs like acetaminophen, or ibuprofen can help alleviate headaches and facial pain.
Allergy management
- Regulating and figuring out the allergens can be useful if allergies are a contributing part.
Antibiotics
- A healthcare provider might prescribe antibiotics if a bacterial illness is identified.
Nasal corticosteroids
- When nasal polyps or chronic sinusitis are present, these prescription nasal sprays may help reduce nasal irritation.
Surgery
- Surgery may be considered in extreme cases to enhance drainage, especially when polyps or structural problems are present.
Consult with a medical expert.
- It’s essential to see an ear, nose, and throat expert for a proper evaluation and individualized treatment suggestions if symptoms persist, worsen, or occur frequently. 3Treatment | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health 4Treatment | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Prevention
How to Prevent Sinusitis?
There are various activities you can do to lessen the likelihood of having it, even if the risk may not be eliminated:
Maintain proper hygiene
- Wash your hands frequently to lower your chance of contracting viruses.
Keeping hydrated
- To lessen irritation, keep your nasal passages wet by drinking plenty of water.
Prevent irritants
- Reduce your exposure to environmental irritants like smoke and other potential irritants.
Allergies
- If you have allergies, engage with your healthcare provider to determine the triggers and create a strategy for effective management.
Use humidifiers
- Using a humidifier in dry surroundings can keep your nasal passages wet.
Nasal spraying
- When used frequently, saline nasal sprays can help clear mucus and lower the risk of illness.
Stop smoking
- You should consider giving it up if you smoke because it might harm and irritate your respiratory system.
Vaccinations for pneumococcal and influenza
- Immunization can help lower the risk of diseases such as the flu and pneumonia.
Dental care
- Practice good oral hygiene to avoid tooth infections, which can occasionally spread to the sinuses. 6Prevention | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Outlook
The outlook and prognosis may change depending on the nature, underlying causes, and management style. Acute sinusitis typically resolves independently, either without therapy or with it. Chronic sinusitis can also be efficiently controlled with proper care.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Types
- National Library of Medicine
- National Library of Medicine
-
National Library of Medicine
Diagnosis | Treatment
-
Science Direct
Causes
-
National Health Service
Prevention