Ovarian cyst: Causes, Symptoms, Types and Treatment

- Ovarian Cysts
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
Overview
An ovarian cyst is a fluid filled sac that can be formed either on one or both the ovaries. Women in the reproductive age group have functional ovarian cysts. These are usually benign and do not require surgical management.
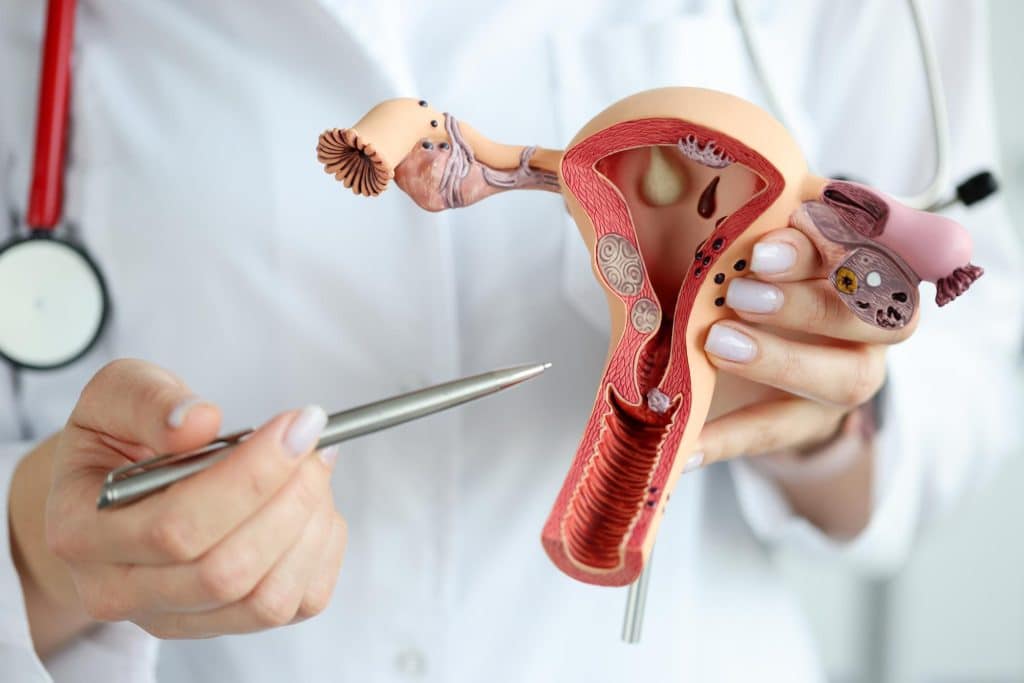
What is an ovarian cyst?
Female reproductive system consists of the uterus, a pair of ovaries and a fallopian tube. The ovaries manufacture many follicles in a month. One dominant follicle matures and ovulates. Due to ovulation a fluid filled cystic sac can form on the ovaries. The cyst size varies from 1-4 inches or even larger.
Causes
Causes of Ovarian cyst
Ovarian cyst causes are :
- Ovulation
- Medicines
- Pelvic diseases
Ovulation
- A follicle develops on the ovary each month throughout the menstrual cycle. Hormone estrogen is secreted by the follicles of the ovary. The egg is released from the follicle after maturity. This is the ovulation process.
- If the follicle remains futile, the follicle becomes fluid filled leading to the formation of a cyst. This type of cyst is called follicular cyst.
- After the release of an egg, a corpus luteum cyst can also be formed. It secretes estrogen and progesterone hormones. This cyst might contain trace amounts of blood.
Fertility Medicines
- Use of fertility medications can also lead to the formation of multiple cysts in ovaries.
Pelvic infections
- Pelvic infections due to Chlamydia can also form a cyst or abscess.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Abnormal cell proliferation due to dermoid and serous cystadenomas.1Causes| Researched based study from Pennmedicine.org
Types
Types of Ovarian cysts
Most of the cysts are non cancerous and are usually related to menstrual changes. They settle down within a few weeks.
The various types of ovarian cysts include:
- Functional ovarian cyst
- Endometrioma
- Cystadenomas
- Dermoids
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Functional ovarian cysts
- Functional ovarian cysts are seen only in females of reproductive age group. It is the most common type of ovarian cyst.
- The two subtypes of functional cysts: Follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst.2Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Endometrioma
- Endometriosis is a phenomenon where the tissue lining inside the uterus known as endometrium is observed outside of the uterus. Women with endometriosis will develop ovarian cysts.
- Endometrioma may form blood filled cysts. The blood appears like the color of a chocolate. Hence, they are also called chocolate cysts.2Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cystadenomas
- It develops from the outer layer of cells of the ovary. It can be serous cystadenoma – has thin fluid and mucinous cystadenoma- has thick fluid containing mucus. They can be benign or malignant.2Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dermoids
- These are mature cystic teratomas that contain gross contents like hair, teeth, fat, bone etc. Dermoid cyst develops from the egg making cells of the ovaries.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- PCOS affects women in the reproductive age group. It is the primary reason for infertility in females. PCOS means presence of numerous small cystic follicles and enlargement of ovaries. It causes hormonal imbalance leading to acne, obesity, irregular menses etc.
Risk factors
Risk factors
Factors increases the probability of developing ovarian cysts are:
Age
- Ovarian cysts are more common in females of reproductive age group.
History of ovarian cysts
- You can develop ovarian cysts if you have already had before.
Medical conditions
- Ovarian cyst can be seen if you have: endometriosis, hormonal imbalance or if you’re taking ovulation medications like clomiphene citrate.
Pelvic infections
- Pelvic Inflammatory disease can form cysts or abscess in the ovaries.
Pregnancy
- Cysts can be seen during pregnancy and usually subside after the birth.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Ovarian cyst
Most of the cysts do not cause any discomfort and remain asymptomatic but some may show features such as;
- Pain in abdomen: An ovarian cyst causes pain if the cyst becomes enlarged, bleeds, ruptures, disrupts the blood supply to the ovary or due to torsion of the ovary. The pain can be dull and sharp. It will come and go after your periods.
- If the cyst breaks open, you may experience nausea and vomiting.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Urge to pee frequently
- Back pain
- Indigestion
- Heartburn
- Painful periods
- Irregular periods
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Weight gain
- Constant dull aching pelvic pain
- Spotting/bleeding in some cysts
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Hirsutism: Increased growth of hair on the body specially pubic areas.
- Acne
Most of the ovarian cysts are functional and subside within a few days. You must do a regular follow up and monitor your symptoms closely.3Symptoms| Researched based study from Nhs.uk
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Ovarian cyst
You must visit your OB/GYN doctor as soon as you experience the above mentioned symptoms. Abnormal and painful menses is the primary feature of an ovarian cyst.
A physical examination is necessary to rule out other medical conditions. This includes pelvic examination to detect any swelling on the ovary. If you have an ovarian cyst then you might need diagnostic tests to rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The tests include:
Transvaginal Ultrasound
- This diagnostic test utilizes magnetic waves to know the size, location and shape of cysts. The probes scan the ovaries to tell if the cystic growth on solid or fluid filled.
Transabdominal ultrasound
- This diagnostic test scans the abdomen to check for infections in the pelvic area and assess blood flow. Cyst size more than 10 cm, papillary projections, thick walls, ascites, solid components, complex masses or high vascularity suggests malignancy.
Pregnancy test
- This is done to know if pregnancy is the cause for development of cyst.
Blood tests
- Ovarian marker is the CA125 test. If this test is normal then the cyst is non cancerous. CA125 test in combination with ultrasound will help in ruling out malignancy. CA125 is high in ovarian cancer. A blood level of slightly less than 35U/ml is considered normal.3Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nhs.uk
Urinalysis
- Urinalysis is done to exclude urinary tract infections and kidney stones (renal stones).
Biopsy
- A thick piece of ovary is extracted. It is then visualized under the microscope for the presence of cancerous cells. Your doctor may advise biopsy if he suspects any growth on an ultrasound scan of the ovary.
Hormone levels (LH, estradiol, FSH and testosterone)
- These hormones are liable to alter in case of polycystic ovarian disease. Higher levels of testosterone, DHEA sulfate (DHEAS), androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) are seen in PCOS.
Differential diagnosis
Cysts require proper medical checkup and intervention because Ovarian cysts can be confused with few medical conditions like:8Differential diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Appendicitis
- Pelvic kidney
- Gastric cancer
- Nephrolithiasis
- Abscess
- Urinary Tract Infection
- Kidney stones.
Treatment
Treatment of Ovarian cyst
Management of ovarian cysts depends on the age of the patient, menstrual status, cyst size and location.
Watchful intervention:
- Unilocular ovarian cysts of size less than 10 cm are considered benign and resolve spontaneously without surgical treatment. If it doesn’t resolve then further investigations are indicated.
- Functional ovarian cysts will go away by 8-12 weeks.
- Pregnancy associated ovarian cysts like corpus luteal cysts and follicular ovarian cysts, will resolve by 14 to 16 weeks of gestation with conservative treatment.
- Endometriosis should have imaging follow ups every 6-12 weeks until surgically removed.
Medications
- Birth control pills are usually prescribed to prevent ovulation. Chances of developing ovarian cysts in future will be prevented by stopping ovulation. Metformin is also given to patients to reduce insulin resistance.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated if there is:
- Torsion to the ovaries.
- Persistent adnexal mass.
- Malignancy suspicion.
- Acute sharp pain in abdomen.
- Increasing size of cysts
- Complex cysts.
An ovarian cyst is surgically removed by Keyhole surgery or Open surgery. It is best decided by your gynecologist.
Keyhole surgery (laparoscopy)
- Small ovarian cysts can be removed using keyhole surgery. In this surgery, small incisions are made in the abdomen and instruments are inserted along with a laparoscope (thin tube like camera) through the cuts. Then your ovaries are examined and cysts removed. It is usually done in haemo-dynamically stable patients.
Open surgery (laparotomy)
- A single wide cut is made on the abdomen. It is done in case of large ovarian cysts or cancerous cysts. It is usually utilized when the patient is hemodynamically unstable. It is done for early visualization of the structures.
Oophorectomy
- In the case of extensive cystic masses an entire ovary can be removed, known as Oophorectomy.
Post-surgery care
- These surgical procedures might cause bruising, pain, discomfort, pain in the shoulders, slight, vaginal bleeding etc for which your doctor will prescribe over-the-counter medications.
- It will require enough time for your body to heal and recover after a laparoscopic or laparotomy surgery. You must take short walks of 15-20 minutes in the initial few days. After a week of surgery you can stand and walk upto 60 minutes.
- You will be able to cope up and go back to routine work after 2-3 weeks of surgery. However, recovering from an open surgery will requ more time.
Some possible complications of surgery are:
- Bleeding
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Infection
- Damage to bladder
- Hernia
Home remedies

Home remedies to relieve Ovarian cyst pain
Home remedies for the management of ovarian cyst are:
Over-the-counter medication
- Ibuprofen like NSAIDs are helpful in the treatment of period, cramps and cyst pain.
Exercise and stretching
- Regular exercise along with proper dietary regime, has a successful impact on managing PCOS symptoms. You must improve your lifestyle changes by increasing physical activity. Perform yoga to release the muscle tension and cystic pain. It is shown that yoga reduces the risk of cyst4Home remedies| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov formation in females.
Heat application
- Applying heat will significantly decrease pain and soreness. It also increases blood flow and decreases inflammation.
Massage
- The tensed up muscles due to pain can be soothed by massaging the upper and lower back, buttocks and stomach.
Weight loss
- Losing a significant amount of weight can help in regulating the hormones that will prevent the development of cyst. This will also improve period pain and fatigue.
Dietary changes
- Many females who develop ovarian cysts are usually insulin resistant. This can be a prevalent condition for developing diabetes. Insulin resistance can be managed by reducing sugar intake. You must avoid sugary food that contains high amounts of carbs such as pasta, carbonated drinks and bread. You must have healthy food and a balanced meal.
Drink chamomile tea
- Females with PCOS will develop cystic ovaries. They will also have testosterone levels above normal. Research 5Home remedies| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov shows that drinking chamomile tea helps in decreasing the levels of testosterone thereby decreasing the symptoms of cystic pain.
Drink ginger tea
- Ginger is a great herb for relieving symptoms of cyst pain and also for naturally shrinking ovarian cysts.6Home remedies| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov Ginger not only helps in decreasing the size of cases but also helps in fighting ovarian cancerous cells.
Apple cider vinegar
- Apple cider vinegar helps in dispersing and decreasing the size of ovarian cyst that might have been caused due to deficiency of potassium. Mix 1 tablespoon of cider vinegar in a glass of warm water and drink it.
Diet
Dietary modification you have ovarian cyst
To get relief from the symptoms, you must include:
High-fiber foods
- They include pears, peas, oranges that prevent reuptake of estrogen hormone. This will help in maintaining hormonal balance.
Omega-3 foods
- Nuts, flaxseeds and fish are rich in omega 3. They help in maintaining hormonal balance.
Indole-3-carbinol foods
- These include vegetables such as broccoli, sprouts, cabbage and cauliflower. Regular consumption of vegetables will release estrogen and decrease testosterone.
Magnesium
- Almonds, dark, chocolate, avocados and bananas are magnesium rich foods. They will help in decreasing the pain caused due to an ovarian cyst.
Protein rich foods
- Chicken has a high amount of protein that will help in weight management and also hormonal balance.
You must avoid these foods if you have ovarian cyst:
- Fried foods-Food cooked in refined oils will promote weight gain. Excess weight gain will lead to the formation of ovarian cyst.
- Alcohol-Alcohol is known to disrupt the hormonal balance, thereby increasing the chances of ovarian cyst.
- Caffeine-It causes inflammation and dehydration.
- Refined Sugar-Rich Foods-These include canned beverages which are a major trigger source for hormonal imbalance leading to the formation of ovarian cyst. They also irritate the previously existing ovarian cyst (if any).
- Red meat-You must avoid lamb, beef and pork meat to avoid ovarian cyst formation.
Complications
Complications
The to serious complications of ovarian cyst are:
Ovarian torsion
- The cyst forces the ovary to twist resulting in cut off of the blood supply to the ovaries. You will encounter severe abdominal pain with vomiting. Ovarian cyst portion is very commonly seen more than 4 cm (larger cysts).
Rupture of cysts
- The cyst suddenly ruptures due to over enlargement, exercise or during sexual intercourse. Ruptured ovarian cyst when showing vaginal bleeding, nausea, and severe abdominal pain.
Hemorrhage
- Most of the cysts are uncomplicated with stable vital signs. But due to significant blood loss, there will be hemodynamic instability that will require urgent hospital admission and surgical intervention.
Fertility issues
- Usually small ovarian cysts do not affect fertility. Small ovarian cysts will vanish on their own. However, polycystic, ovarian disease, and endometriosis are gynecological issues that lead to formation of ovarian cyst leading to fertility issues
Prognosis
Prognosis of Ovarian cyst
Most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic and resolve on their own showing favorable prognosis. Some aggressive tumors of less malignancy show survival rates up to 86.2% at five years.7Prognosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov Malignant growth is suspected in medical conditions such as the polycystic ovarian syndrome and endometrial cysts.
Takeaway
Takeaway
Ovarian cysts are very common and the symptoms are treatable. Regular gynecological check ups and communication with your doctor will help in early intervention of the symptoms. With proper medical care, you can lead an improved quality of life.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Penn Medicine
Ovarian Cyst | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Ovarian Cyst | Types
-
National Health Service
Ovarian Cyst | Diagnosis
-
National Library of Medicine
Impact of yoga and exercises on polycystic ovarian syndrome risk among adolescent schoolgirls in South India | Home remedies
-
National Library of Medicine
Effect of chamomile capsule on lipid- and hormonal-related parameters among women of reproductive age with polycystic ovary syndrome | Home remedies
-
National Library of Medicine
Ginger inhibits cell growth and modulates angiogenic factors in ovarian cancer cells | Home remedies
-
National Library of Medicine
Adnexal masses in the pregnant patient: a diagnostic and management challenge | Prognosis
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560541/
Ovarian cyst | Differential diagnosis