A Gentle Approach: How To Massage Ear Wax Out For Safe Removal

- Ear Pain
- 15 Sep 2023
Introduction
Ear Wax
Cerumen, also referred to as ear wax in medicine, is a naturally occurring material created by glands in the ear canal. Its purpose is to protect and lubricate the ear, preventing the entry of dirt, debris, and harmful bacteria. Ear wax typically flows gradually from the inner ear to the outer ear opening, where it dries and gently comes out. However, occasionally, it can build up and become impacted, causing an issue called cerumen impaction or ear wax blockage. The wax accumulates and obstructs the canal for the first time, generating a variety of symptoms and probable discomfort.

This article thoroughly overviews ear wax obstruction, including its causes, symptoms, and potential side effects. It’s vital to remember that while home care techniques may provide some relief, a precise diagnosis and treatment plan depend on consulting a trained healthcare expert. 1 Introduction | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of Ear Wax build up?
- Hearing impairment
- Earache or discomfort
- Tinnitus
- Dizziness or Vertigo
Here is a bit more detail about each sign:
Hearing impairment
- A gradual or sudden hearing loss was one of the most typical ear complaints.
- Hearing in the affected ear may feel muted or diminished due to the impacted wax’s ability to prevent sound waves from reaching the ear drum.
Discomfort or earache
- Wax buildup can make you feel unwell or uncomfortable.
- This discomfort, which can be slight to severe, is frequently brought on by the wax buildup pressing against the canal.
Tinnitus (Ringing in the ears)
- In the absence of external sound, it is the perception of ringing, buzzing, hissing, or other sounds in the ear.
- By obstructing the flow of sound waves and leading the brain to produce these phantom noises, the blockage might indirectly cause tinnitus.
Dizziness or vertigo
- Ear wax obstruction may occasionally cause vertigo or dizziness.
- This happens when the inner ear’s balance organs are damaged, which causes instability, spinning, or loss of balance.
While these symptoms may point to a block, it’s crucial to remember that other ear-related disorders might also bring them on. Visiting a healthcare professional if you encounter any of these symptoms is advised for an accurate evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. 2 Symptoms| Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Ear Anatomy
Anatomy of the Ear
The outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear are the three primary sections.
- The visible pinna and ear canal are both parts of the outer ear.
- The eardrum and the ossicles, which are small bones that transmit sound vibrations, are in the middle ear.
- The inner ear transforms these vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain for interpretation.
Causes
Causes for Wax build up
Producing excessive ear wax
- Overproduction of wax, some people create more wax than others by nature.
- Genetics might affect wax’s consistency and quantity.
Improper cleaning methods
- Cleaning the ears with cotton swabs, fingers, or other things may cause impaction by pushing back further into the canal.
Narrow or curved ear canals
- It may be more difficult for wax to naturally migrate out of the ear if the canals are narrow or odd.
Use of earplugs or headphones frequently
- The natural discharge of wax can be hindered by headphones, hearing aids, or earplugs, which force the wax further into the canal.
Aging
- Wax’s consistency can alter with age, becoming dryer and more prone to buildup.
Hairy canals
- In the ear canal, excessive hair growth can trap your wax and cause obstructions.
Skin issues
- A few skin conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema. It can affect wax mobility and the skin of the canal.
Foreign substances
- Wax can become trapped when foreign things, such as hearing aid molds, are placed within the Ear.
Medical conditions
- Medical diseases, including temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ) or persistent ear infections, may influence wax buildup. 2 Causes | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Treatment
Treatment options for Ear Wax
A doctor’s removal of ear wax
- Ear wax can be safely removed by medical professionals like an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or a primary care doctor using specialized equipment and methods.
- After using an otoscope to see the canal, they may carefully remove the wax using forceps or curettes. For wax that is obstinate or severely impacted, this technique works well.
Micro suction
- It includes removing wax with a microscope equipped with a soft suction instrument.
- This technique offers exact control for those with delicate ear canals, perforated eardrums, or those who have had ear surgery.
- Micro suction is typically regarded as secure and cozy.
Professional ear irrigation
- It also goes by “ear syringing,” which entails flushing ear wax out with water or saline solution.
- A healthcare practitioner uses a specialized irrigation tool or syringe to carry out this approach.
- It’s crucial to remember that not everyone can benefit from ear irrigation, especially if they have a history of ear infections or surgery.
Manual removal with instruments
- Medical practitioners may occasionally manually remove the wax using specialized tools.
- Typically, an otoscope is used in direct visualization when performing this. The ear canal and eardrum are protected from harm. 3 Treatment | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health ,4 Treatment | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Home Remedies
Home remedies for blocked Ear
Ear wax lubrication
- Removing ear wax yourself or a medical professional may be more straightforward if it has been softened.
- To soften and loosen ear wax, you can use over-the-counter ear drops. These include salt, mineral oil, glycerin, or hydrogen peroxide.
- If you have a history of ear infections or an eardrum perforation, use ear drops only as directed on the product’s box.
Ear irrigation
- You can try gentle ear irrigation at home if you prefer; however, professional ear irrigation is only done by healthcare professionals.
- Warm water is flushed into the canal using a bulb syringe or a commercial kit. Letting the water drain out, tilt your head to the side and gently squirt it into the ear.
- However, it would help if you used this technique cautiously and only when you are sure there is no infection or eardrum perforation. Before attempting this at home, speaking with a healthcare professional is best.
Avoiding Q-tips and objects
- It is essential to avoid inserting objects like cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other items in your ears. These can push the wax deeper into the canal, potentially causing blockages, injury, or irritation.
- Because the ears are made to clean themselves, using things to clean them naturally can interfere with this design feature. 3 Home Remedies | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health , 4 Home Remedies | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health , 5 Home Remedies | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health , 7 Home Remedies | Researched based study from Research Gate
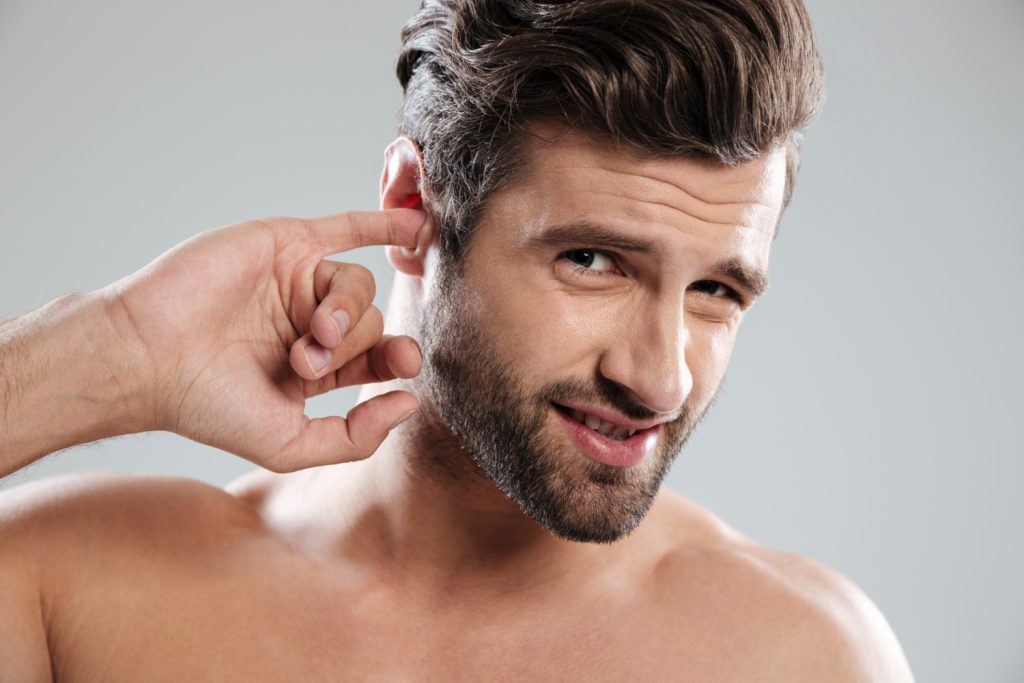
How to massage my ear?
Even while removing earwax properly is crucial, you may do some easy steps to encourage the wax’s regular migration.
A warm compress
- For a few minutes, gently press a warm, damp towel against the outside of your ear.
- The wax may become softer as a result, making it more straightforward for it to move independently.
Choose a quiet environment
- Locate a peaceful, cozy area to unwind and concentrate on the massage.
Wash your hands
- Ensure your hands are clean before touching your ears to avoid introducing dirt or bacteria.
Warmth
- Cup your hands about your ears gently to impart a cozy and comforting feeling. This might encourage relaxation.
Earlobe massage
- Thumb and forefinger together, gently rub your earlobes. Work your way up and around the entire outer ear in circular motions.
Behind the ear
- Gently massage the region where the ear meets the head behind and around the Ear using your fingertips.
Finger tapping
- Tap the area around the ear gently, going from top to bottom and back up.
- This might help in promoting relaxation and blood flow. Avoid putting too much pressure on the object.
Tilt and pull
- Gently pull on your earlobe while tilting your head to one side. This may assist in somewhat straightening the canal and encouraging any softened wax to travel toward the ear opening.
Jaw movement
- When you chew, opening and closing your jaw can provide a slight movement in the ear canal that could help ear wax migrate.
Breathing
- Breathe deeply and slowly while massaging your ears. This might make the relaxing effect stronger.
Remember that these techniques should not involve harsh or combative actions. It is advised to speak with a healthcare provider if you feel discomfort or think you may have a severe ear wax obstruction. They can evaluate your circumstances and offer the proper advice or care to ensure safe and efficient wax removal. 4 Home Remedies | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health , 5 Home Remedies | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health ,6 Home Remedies | Researched based study from Research Gate
Risks
Complications & Risks of Ear Wax buildup
Affects hearing
- The transmission of sound waves to the eardrum might be hampered when earwax accumulations block the canal. This results in a discernible decline in hearing ability.
- Depending on the extent of the obstruction, the degree of hearing loss can vary. People may perceive sounds as distorted or muffled, and conversations could become challenging to follow.
- Untreated ear wax obstruction may occasionally cause social isolation and trouble engaging in activities that need good hearing.
Potential infections
- Extra ear wax contains moisture, which makes it ideal for bacterial and fungal growth. This makes ear infections more likely.
- Inflammation and canal infection may result from the trapped water and skin-surface microorganisms. Acute ear pain, redness, swelling, discharge, itching, and discomfort are all possible signs of an ear infection.
- They may worsen and possibly spread to surrounding structures if left unchecked.
Middle ear issues
- While obstruction predominantly impacts the ear canal, it can also harm the middle ear.
- The Eustachian tube, which connects the canal and middle ear, helps balance pressure inside and outside the middle ear.
- If the canal is closed, pressure variations impact the middle ear’s ability to operate. This could result in feelings of heaviness, pressure, vertigo, or imbalance. 8 Risks | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
When to seek medical help
- Severe or sudden hearing loss
- Severe pain signs of infection
- Dizziness
- Unsuccessful home treatments
It would help if you considered seeking medical help for ear wax issues in the following situations:
Severe hearing loss
- It is crucial to see a doctor if your hearing is seriously impaired and is interfering with your everyday life.
Chronic discomfort or pain
- You should consult a doctor if you experience chronic pain, discomfort, or a feeling of fullness in your Ear.
Ear infection
- See a doctor if you have a possible ear infection or have pain, discharge, redness, or swelling.
Nausea or vertigo
- If you have experienced imbalance or vertigo, especially when other ear-related issues accompany it, Speak with a doctor.
Ineffective home treatments
- It’s necessary to see a doctor if over-the-counter treatments don’t work or if your symptoms get worse. 2 Risks | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health , 3 Risks | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Prevention

Preventing Ear Wax Buildup
Hands of approach
- Avoid introducing anything like cotton swabs or items into your canal. This may push back further, increasing the risk of injury or obstruction.
Natural cleaning
- Let the ear’s self-cleaning system operate. Frequently, ear wax will move from the canal to the outer Ear.
Keep your ears dry
- After bathing or swimming, bend your head gently to each side to allow water to escape your Ear. Dry the outer Ear by patting it with a towel. 6 Prevention | Researched based study from Research Gate,7 Prevention | Researched based study from Research Gate
Speak with a healthcare professional
- Consult a healthcare practitioner if you have symptoms, including hearing loss, discomfort, or strange feelings in your ears. They can establish whether ear wax is the root of the problem and suggest the best course of action.
Avoid DIY methods
- Refraining from cleaning your ears with cotton swabs, ear pins, or other things is crucial.
- These could force the wax deeper and raise the possibility of problems.
Specialist in Ear, Nose & Throat
- Consider consulting an ENT specialist if you frequently experience ear wax concerns or have a history of ear troubles.
- They can perform safe ear wax removal and offer expert guidance if required.
Regular examination
- Consider incorporating ear checks in your routine physical if you are prone to ear wax buildup. Doing so lets you monitor your health and identify any problems early. 6 Prevention | Researched based study from Research Gate, 7 Prevention | Researched based study from Research Gate
FAQs
Ear Wax-Frequently Asked Questions
What dissolves ear wax fast?
- Wax removal can be aided by over-the-counter Ear drops explicitly made to soften and dissolve wax.
- Chemicals like hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide soften and dissolve the wax. Additionally, it contains glycerin, recognized for its moisturizing effects, and aids in promoting the wax’s natural flow out of the Ear.
- While these drops may be helpful, the effects might take time. Regular use can take a few days before you see a difference.
How do you unblock a whole ear of wax?
- Some techniques that can help include using over-the-counter ear wax removal drops, warm water flushing, and expert ear wax removal.
Is it safe to massage your Ear?
- Yes, it is usually okay to give your pinna, also known as the Oracle, a little massage. It might encourage comfort and relaxation.
- However, it’s crucial to refrain from placing anything inside the canal. Additionally, it enhances blood flow and brings about a calming effect.
Can steam loosen ear wax?
Yes, steam can frequently help to loosen wax. It may aid a hard and wires and make it easier to move out of the Ear naturally if the moisture level is increased. You can do the following:
Boil water
- Once some water has reached a rolling boil, you can remove it from the heat source.
Create steam
- Place your face safely away from the pot so the steam will rise towards your Ear. To avoid burns, stay away from the hot water up close.
Inhale the steam
- Gently inhale the vapor through your nose. The wax may be softer due to the warmth and moisture.
Cover your head
- You can construct a tent by draping a towel over your head to help contain the steam around your face.
Drain and tilt
- After the procedure, return to the area and let any wax or moisture drain.
Can hydrogen peroxide damage your ears?
It should only be used in the Ear with caution. Although diluted one can occasionally soften ear walks and aid in their removal, it’s crucial to follow the proper procedures and avoid using it without professional advice.
Here are a few things to think about:
Concentration
- For ear treatment, hydrogen peroxide needs to be suitably diluted. Hydrogen peroxide used at maximum concentration can be harsh and potentially harmful to the canal’s delicate tissues.
Irritation
- Even when diluted, it might irritate certain people and make them uncomfortable. It could induce a stinging or bubbling feeling if it comes into contact with wax or the canal.
Perforated ear drum
- It’s crucial to avoid using it if you suspect you have a perforated eardrum. Putting any liquid into the Ear in such cases can lead to further complications.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Introduction
-
National Institutes of Health
Symptoms | Causes | Risks
-
National Institutes of Health
Treatment | Home Remedies | Risks
-
National Institutes of Health
Treatment | Home Remedies
-
National Institutes of Health
Home Remedies
-
Research Gate
Home Remedies | Prevention
-
Research Gate
Home Remedies | Prevention
-
National Institutes of Health
Risks