Neuropathy: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

- Neuropathy
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is characterized by nerve injury or dysfunction, which causes various symptoms and problems, such as pain, numbness, and tingling sensations in one or more body regions. It commonly starts in either the hands or legs and progresses.1Overview| Researched based study from Cancer.gov It significantly impacts the quality of life for many people worldwide. This article will delve into the various aspects of Neuropathy, including its symptoms, causes, types, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, complications, and prognosis.

Types
Types of Neuropathy
There are many types of neuropathies, each with its causes and problems:
- Peripheral Neuropathy – affects the nerves in the extremities, like feet and hands, and is the most common type of Neuropathy.2Types| Researched based study from Diabetes.org
- Autonomic Neuropathy – It affects the nerves that control involuntary bodily functions like heart rate, digestion, and bladder function.3Types| Researched based study from Niddk.nih.gov
- Focal Neuropathy involves damage to a specific nerve or group of nerves, resulting in weakness or pain in a particular area4Types| Researched based study from Diabetes.org
- Proximal Neuropathy – It affects the nerves in the hips, thighs, or buttocks, causing weakness and pain.5Types| Researched based study from Niddk.nih.gov
Symptoms
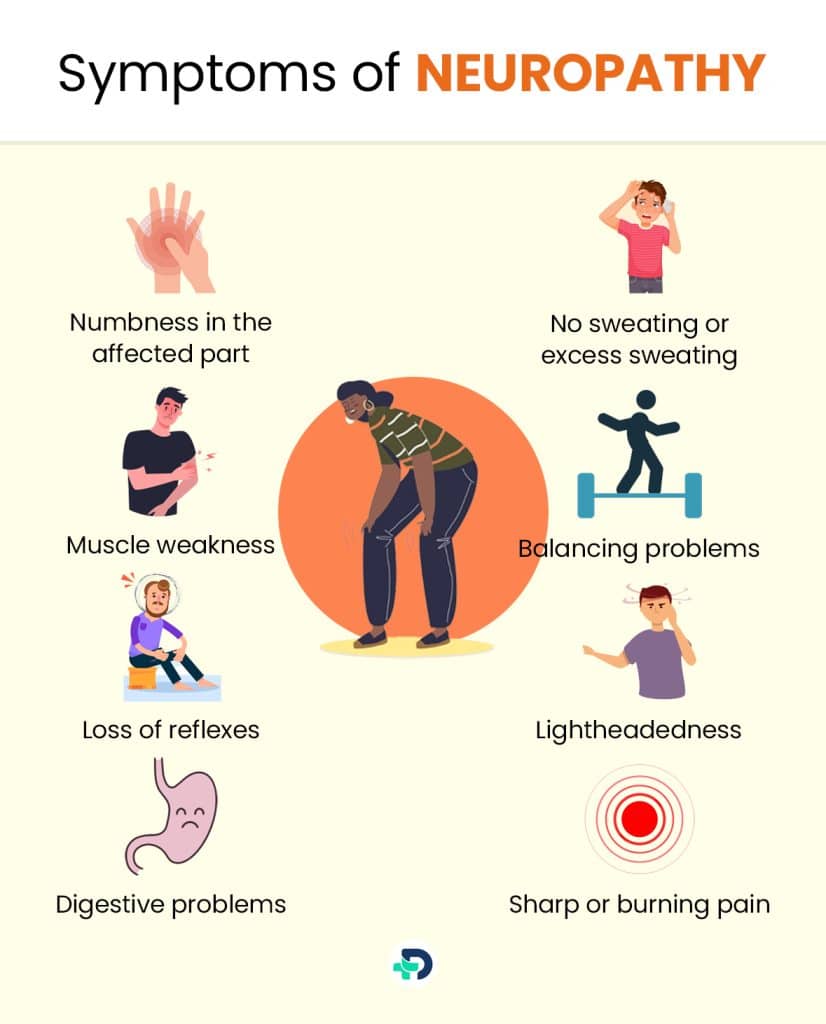
Symptoms of Neuropathy
The symptoms of Neuropathy can change based on the nerves affected and may include:
- Numbness in the affected part
- Pain that gets worse at night
- Sharp or burning pain
- Tingling sensation or pins and needles
- Muscle weakness
- Paralysis of muscles
- Balancing problems
- Loss of reflexes
- Lightheadedness
- Digestive problems
- Loss of bladder control
- Sexual dysfunction 6Symptoms| Researched based study from Healthdirect.gov
- Muscle cramps or twitching
- Increased sensitivity to touch
- No sweating or excess sweating
- Intolerance to heat
Causes
Causes of Neuropathy
Any of the following can cause Neuropathy:
- Diabetes – may cause Diabetic Neuropathy, a typical form induced by high blood sugar levels causing nerve damage.7Causes| Researched based study from Niddk.nih.gov
- Trauma or injury – Physical injury, road traffic accidents, or excessive use of a body part can hurt the nerves.
- Infections – Certain infections like Lyme, shingles, or HIV/AIDS can lead to Neuropathy.
- Autoimmune conditions – like lupus, Guillain-Barre syndrome, or rheumatoid arthritis can trigger Neuropathy.
- Tumors – Growths, cancerous and noncancerous, can develop and press on nerves causing Neuropathy.8Causes| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Cancers – such as multiple myeloma, and cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, can result in neuropathies.
- Other medical conditions – like thyroid issues, high cholesterol levels in the blood, liver, and kidney disease, and other hereditary disorders can also cause Neuropathy.
- Some medicines – such as platinum drugs such as cisplatin, plant alkaloids such as vinblastine and vincristine, proteasome inhibitors, and immune modulators, may produce Neuropathy.9Causes| Researched based study from Cancer.org
Risk factors
Neuropathy risk factors
Certain factors may raise the likelihood of an individual developing Neuropathy, including:
- Genetic factor – People with a family history of Neuropathy or other hereditary disorders are at an increased risk.
- Age – Neuropathy becomes increasingly common as people age.10Risk factors| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Long-term alcohol misuse – can injure the nerves and raise the risk.11Risk factors| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Nutritional deficiencies – Vitamin B1, B6, B12, E, folate, and niacin deficits, as well as a lack of these vitamins, can result in Neuropathy.
- Toxins – like heavy metals, chemicals, and some drugs can raise the risk.12Risk factors| Researched based study from Foundationforpn.org
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Neuropathy
Diagnosing Neuropathy may involve a complete evaluation of medical history, clinical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Blood tests – identify underlying conditions like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies.
- Nerve conduction studies (NCS) – evaluate the electrical activity in the nerves.13Diagnosis| Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
- Imaging tests – X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to determine other possible causes.
- Electromyography (EMG) – Assesses the muscles for their proper electrical activity.
- Nerve biopsy – to look for inflammation that could be damaging the nerve.14Diagnosis| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
Treatment
Treatment of Neuropathy
Neuropathy treatment’s primary goal is to control symptoms, limit progress, and deal with the underlying cause and may include the following options:
- Pain relieving medicines – like over-the-counter painkillers, including acetaminophen or certain prescription pain relievers, may help neuropathic pain.
- Anti-seizure drugs – like gabapentin, pregabalin may help manage neuropathic pain and may also have some side effects like drowsiness.
- Other medicines – like topical creams, including lidocaine, may be prescribed to address pain in specific areas.
- Physical Therapy – and exercises can help improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination. They may also help alleviate pain and improve overall functioning.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) – applies low-voltage electrical currents to the skin, relieving pain and improving nerve function.15Treatment| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Surgery – may be needed in individuals with tumors pressing on nerves as a cause for Neuropathy. This type of pain may decrease when the tumor is removed or when the pressure is reduced.
Lifestyle modifications for Neuropathy
Making specific changes to one’s lifestyle, such as the following, can alleviate symptoms and decrease the rate of progression of neuropathy:
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly
- Exercise regularly
- Quit smoking or do not smoke
- Reduce alcohol consumption or quit drinking
- Maintain a healthy diet 16Treatment| Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Take a warm bath to relax and reduce pain
Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative medicine can provide relief for some people and may include:
- Therapeutic massage
- Herbal drugs
- Acupuncture
However, consulting with a healthcare professional before seeking alternative therapies is essential.
Prevention
Prevention of Neuropathy
While it may not always be possible to prevent Neuropathy, specific measures can reduce the risk or delay its onset:
- Managing underlying conditions – Proper management of diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions can help prevent or minimize Neuropathy.
- Eating a well-balanced diet – with all the key nutrients, particularly vitamin B, can benefit nerve function.
- Avoiding toxins – Taking precautions to minimize exposure to toxins or chemicals can help prevent nerve damage.
- Staying active – Regular exercise and physical activities can improve circulation and overall nerve health.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption – Limiting or avoiding alcohol can reduce the risk of developing alcoholic Neuropathy.
Complications
Neuropathy Complications
Neuropathy can lead to several complications, including:
- Foot ulcers and infections – Nerve damage in the feet can result in reduced sensation, making individuals susceptible to foot injuries and infections, which may progress to severe infections that may need amputation. 17Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Falls and injuries – Muscle weakness and lack of coordination may increase the risk of falls and related injuries like fractures.17Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Autonomic dysfunction – Autonomic Neuropathy can lead to complications such as irregular heart rhythm, digestive problems, and bladder dysfunction.
- Emotional and psychological impact – Chronic pain and functional limitations can contribute to anxiety, depression, and decreased quality of life.18Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Prognosis
Neuropathy prognosis
The prognosis for Neuropathy varies depending on the underlying cause, the extent of nerve damage, and the effectiveness of treatment. Early intervention and adequate management can help reduce symptoms and slow disease development in some circumstances. However, certain types of neuropathies may be chronic and require long-term management. People need to consult with a medical professional for a precise diagnosis and specific treatment plan.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Cancer Institute
neuropathy | Overview
-
American Diabetes Association
Peripheral Neuropathy | Types
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Autonomic Neuropathy | Types
-
American Diabetes Association
Additional Types of Neuropathy | Types
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Proximal Neuropathy | Types
-
Health Direct
Neuropathy | Symptoms
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Diabetic Neuropathy | Causes
-
Mayo Clinic
Peripheral neuropathy | Causes
-
American Cancer Society
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy? | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Age as an Independent Risk Factor for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes | Risk factors
-
National Library of Medicine
Alcoholic Neuropathy | Risk factors
-
The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy
Toxic Neuropathy | Risk factors
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Nerve Conduction Studies | Diagnosis
-
Mount Sinai
Nerve biopsy | Diagnosis
-
Cleveland Clinic
Peripheral Neuropathy | Treatment
-
Mayo Clinic
Peripheral neuropathy | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Neuropathy | Complications
-
National Library of Medicine
A Review of the Emotional Aspects of Neuropathic Pain: From Comorbidity to Co-Pathogenesis | Complications