Cavities
Cavities : Prevention and Management

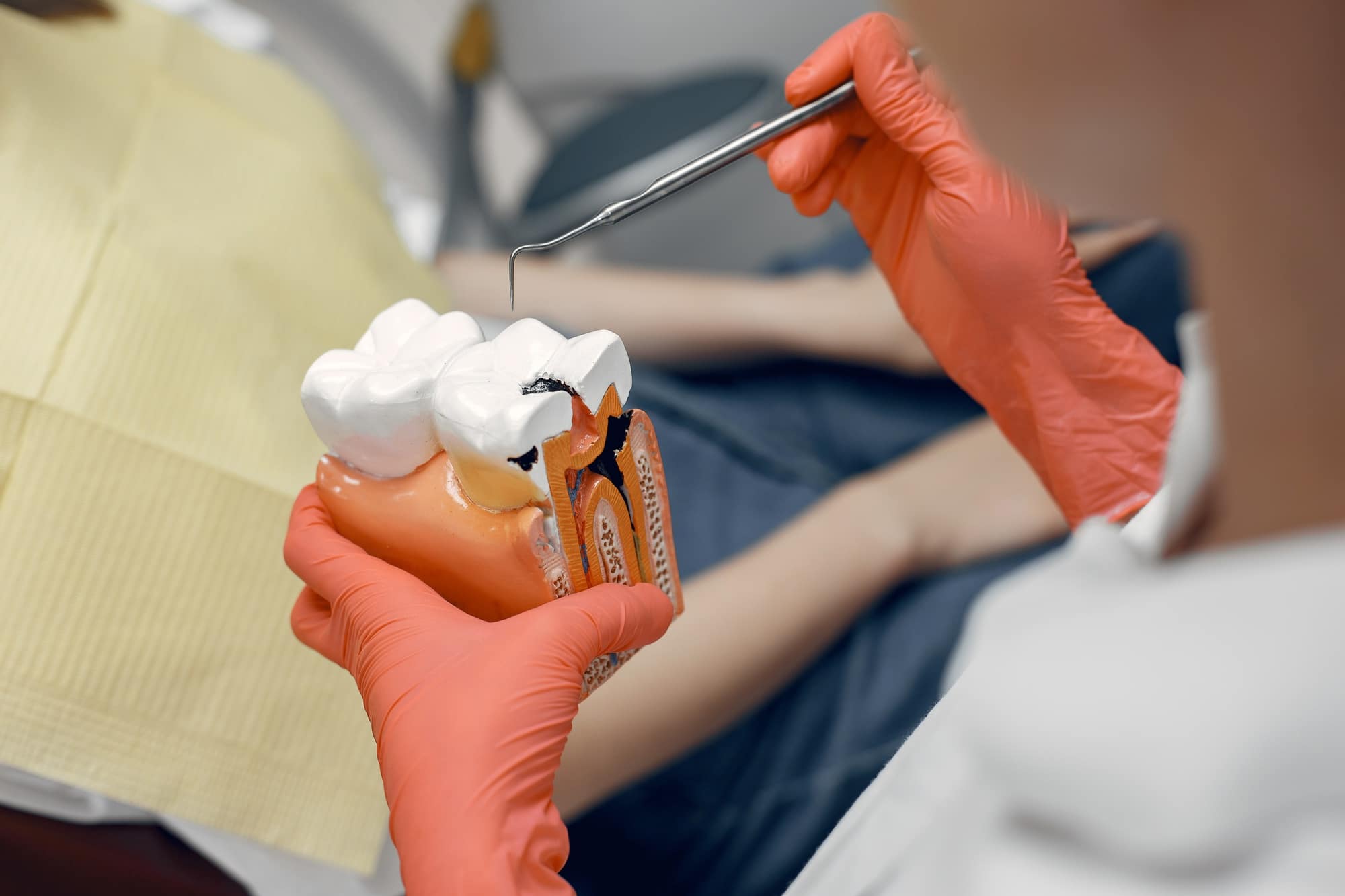
Cavities, dental caries, or teeth decay are holes in the hard surfaces of the teeth. They are indications of irreversible structural damage to the teeth. They begin small, but if ignored, they continue expanding and can lead to pain and infection.
Tooth decay symptoms include:
A variety of variables like the following might cause cavities to form:
Here are some steps to prevent dental cavities
If left untreated, cavities may result in the following complications: