Hives: Understanding and Management

- Hives
- 16 Aug 2023
Overview
What are Hives?
Hives are itchy pink, red, or flesh-colored raised areas on the skin’s surface. They occur due to allergic reactions in our bodies due to food, medication, or environmental irritants. Most hives are temporary and go away on their own. However, persistent hives with harsh allergic reactions require medical attention.

Facts of hives
- The medical terminology for hives is ‘urticaria.’
- The term ‘urticaria’ is derived from the Latin word ‘urtica’meaning nettle (irritation)
- Hives are non-contagious, meaning they cannot transmit from one person to another.
- Around 23% of adults experience an episode of acute (temporary) urticaria once in their lifetime.
- In adults, the prevalence of chronic(persistent) urticaria is around 0.5% to 5% 1Overview| Researched based study from Nature.com ,2Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov .
Types
Types of hives
Acute hives
- Acute hives appear suddenly due to the body’s allergic reaction to allergens.
- Allergens are foreign substances that induce the body’s immune response
- Acute hives may clear up within one day or sometimes within six weeks or less
Chronic Hives
- Chronic hives are repeated hives that occur twice a week and may last for more than six weeks and it has no definite cause and may return after several months or years.
- Chronic hives are not life-threatening but can be a symptom of diseases such as type1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and rheumatoid arthritis( a disease affecting joints)
- Chronic hives are also known as chronic spontaneous urticaria or chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Dermatographism
- Dermatographism is a mild itchy acute hive due to pressure or scratching on the skin.
- It clears up on its own without treatment within a short time.
Infection induced hives
- Infection-induced hives caused by viral or bacterial infection.
- Examples of bacterial infection hives are strep throat and urinary tract infection.
- Examples of viral infection hives are colds and hepatitis
Temperature-induced hives
- Temperature-induced hives are hives that develop due to extreme cold or heat.
- It can be long lasting
Urticaria vasculitis
- It is a rare condition that occurs due to swelling of the blood vessels
- The state is painful and can occur for more than 24 hours 3Types| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov .
Causes
Causes of hives
Hives occur due to allergic reactions to certain factors such as food, drugs, or infection.
When our body initiates an immune response due to allergens, the following events occur:
- The mast cells(immune cells) of the body first releases histamine protein to fight against foreign substances or infections
- The capillaries (tiny blood vessels) then leak fluids that accumulate under the skin and cause swelling and redness
- It causes itchy bumps and skin rash all over the skin 1Causes| Researched based study from Nature.com
Symptoms
Symptoms of hives
- Red, pink, or skin-colored bumps may also appear as tiny spots or thin raised lines in the skin.
- Bumps occur in batches
- The bump’s color fades when pressed in the middle
- Bumps combine with other minor blemishes and form a larger raised area.
- Mild or severe itchiness
- Painful swelling around cheeks, lips, and eyes
- Swelling under the skin causes puffed skin
- Developing bulges in response to heat and exercise
- Bumps appear, disappear, and reappear in a few days or even after months and years
- Swellings vary in shape and size 4Symptoms| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of hives
Allergy test
An allergy test determines the triggering factor for the allergic reaction. Allergy test is of two types-
Skin test
- In a skin test, the doctor tests different allergens on the skin. Any redness and swelling in the skin indicate an allergy to that particular allergen (substance).
- This test is also known as the prick test or scratch test
Blood test
- It checks for specific blood antibodies (proteins to fight infection)
- Blood tests can identify signs of underlying diseases such as thyroid problems or an autoimmune disease.
- Autoimmune disease is when the body attacks its healthy cells 5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Vulnerability
People at risk for hives
- People with an earlier history of an allergic reaction
- People on certain medications
- People unknowingly exposed to allergens such as pollen and food
- People with a bacterial or viral infection
- Young children and
- Women between the ages of 30 to 60 years 10Vulnerability| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Complications
Complication of hives
Anaphylaxis reaction
Anaphylaxis reaction is a harsh fatal allergic reaction in the body. One with an anaphylaxis reaction often experiences the following symptoms along with the hives:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breathing problem
- Severe swelling of the lips, tongue, mouth, and throat
- Lightheadedness, and
- Faint
Angioedema
- Angioedema is the severe swelling in the inner layer of the skin due to fluid build-up. It can impact any body part, including the eyes, hands, feet, and genitals.
- Angioedema swelling in the tongue or throat area causes difficulty breathing, which can be life-threatening 6Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment
Treatment of hives
Over-the-counter lotion
Calamine lotion
- It relieves itching and provides a cooling effect to the affected area
- Applying calamine with a cotton ball on the inflamed area and letting it dry gives much relief.
Over-the-counter drugs
Antihistamine medication
Benadryl
- It relieves itchiness and skin rash within an hour or a day
- However, one must sincerely follow the dose instructions mentioned in the package as it might cause sleepiness.
Some antihistamines which cause less sleepiness include the following
- Allegra
- Loratadine
- Cetrizine
However, one must consult a dermatologist before consuming the medicines to get the correct dose and avoid unwanted side effects.
Topical steroids
- It helps relieves itching and discomfort.
Antiseptic creams
- It helps prevent secondary infection due to hives.
Omalizumab
- It is available as an injection to treat chronic hives.
- It blocks the immunoglobulin E responsible for the body’s allergic responses. Immunoglobulin E is a protein the immune system makes to help fight infections 7Treatment| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Natural remedies for hives
Aloe vera
- Applying topical aloe vera in the affected skin area a few times daily reduces swelling and redness.
- However, it is best to perform a patch skin test before application 8Treatment| Researched based study from Nccih.nih.gov
Witch hazel
- Applying witch hazel in the affected area, like a mask, twice to thrice daily relieves skin irritation.
- However, it is best to perform a patch test before applying witch hazel to the skin 9Treatment| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Home remedies
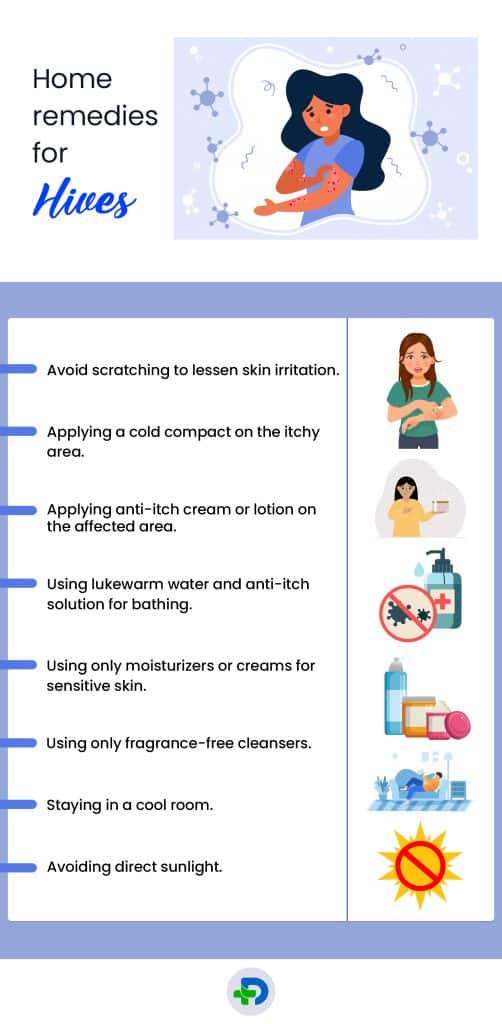
Home remedies for hives
- Avoid scratching to lessen skin irritation
- Applying a cold compact on the itchy area
- Applying anti-itch cream or lotion on the affected area
- Using lukewarm water and anti-itch solution for bathing
- Avoiding using of loofah or sponge to cleanse the body
- Using only moisturizers or creams for sensitive skin
- Using only fragrance-free cleansers
- Wearing light cotton clothing
- Staying in a cool room
- Avoiding direct sunlight
Prevention
Prevention of hives
- Avoid particular food that triggers hives
- Avoiding airborne allergens
- Avoiding highly humid areas
- Using scentless creams, soaps, and detergents
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes
- Relax when stressed
- Take a bath and change clothes if exposed to pollen or animals.
- Tracking the records of possible food triggers to avoid them in future 10Prevention| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Hives are uncomfortable itchiness on the body, which are generally not severe and disappear with time.
- Acute hives resolve within six weeks, while chronic hives might take months or years.
- One must take medical consultation for hives with a severe allergic reaction such as throat swelling.
- In rare cases, hives can lead to life-threatening anaphylaxis reactions, and one must immediately dial the emergency medical number to prevent any untoward situation.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Urticaria | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Urticaria With a Focus on Chronic Urticaria in Children | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
CHRONIC URTICARIA | Types
-
National Library of Medicine
An approach to the patient with urticaria | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Diagnosis of urticaria | Diagnosis
-
National Library of Medicine
Chronic Urticaria: An Overview of Treatment and Recent Patents | Complications
-
Science Direct
Chronic urticaria: new management options | Treatment
-
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Aloe Vera | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Contact Urticaria | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Chronic Urticaria | Prevention