CT Scan: From Uses and Advancements to Procedure and Potential Side effects

- CT Scan
- 04 Sep 2023
Overview
What is a CT Scan?
Computed tomography (CT) is a medical imaging technique that makes use of X-rays and computerized processing to produce precise cross-section pictures of the internal structures. The X-ray beam during a CT scan travels in a loop around the body. Modern medical practice frequently uses CT scans for diagnosis and treatment planning. There are many uses for a CT scan, but it’s particularly useful for quickly analyzing individuals who may have internal injuries due to car accidents or other trauma. A CT scan is capable of capturing almost all parts of your body. 1Overview | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
CT scans play a critical role in advance medicine, helping to diagnose and manage various medical conditions. The decision to have a CT scan is determined by the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the specific diagnostic inquiries that need to be examined. 1Overview | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Uses
Uses of CT scan
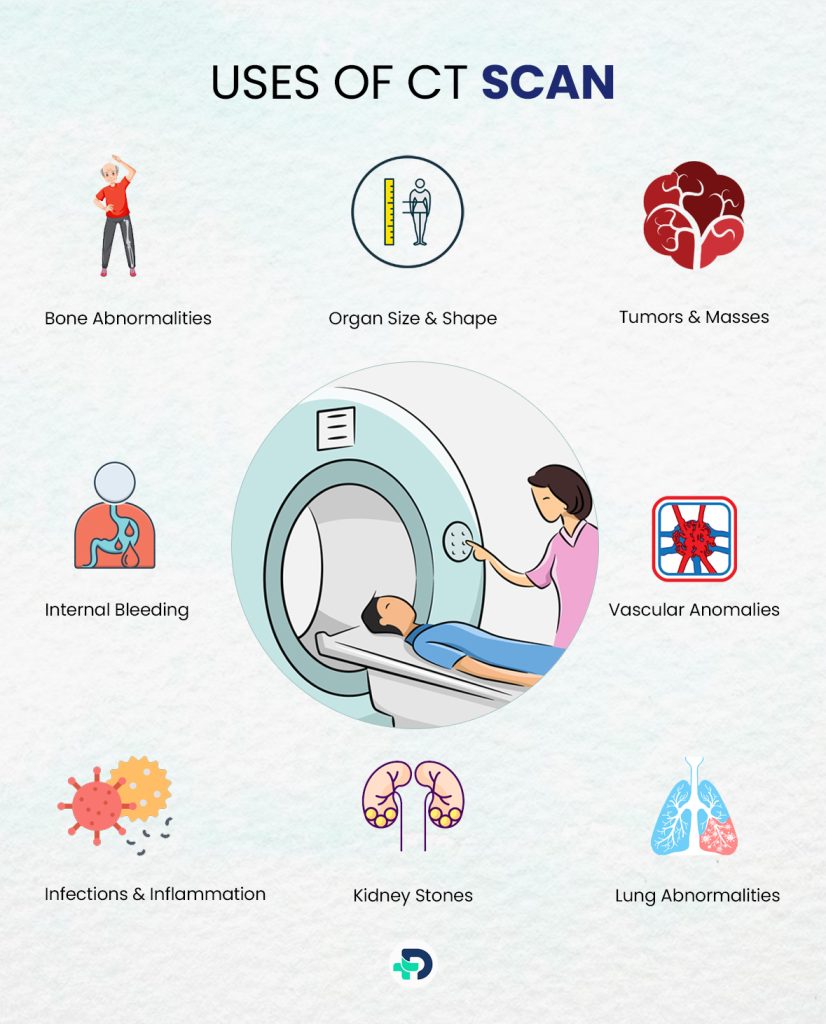
It provides a clear view of the bones, soft tissues, blood vessels, and organs, allowing healthcare professionals to assess and diagnose various medical conditions.
Here are some specific details that a CT scan can reveal:
- Bone Abnormalities: CT scans can detect fractures, bone tumors, and other abnormalities in the skeletal system.
- Organ Size and Shape: The scan can show the size, shape, and position of organs such as the brain, lungs, liver, kidneys, and others.
- Tumors and Masses: CT scans are useful for identifying tumors, cysts, or other abnormal growths in different parts of the body.[2]
- Internal Bleeding: CT scans can detect internal bleeding and identify the source or location of the bleeding.
- Infections and Inflammation: The scan can show signs of infections or inflammation in organs and tissues.
- Vascular Anomalies: CT angiography can view blood vessels and identify issues like blood clots or aneurysms.
- Trauma and Injuries: In cases of accidents or trauma, CT scans can reveal the extent of injuries and guide appropriate medical intervention. 2Uses of CT scan | Researched based study from SAGE Publications
- Kidney Stones: CT scans are effective in identifying kidney stones and their location within the urinary system.
- Lung Abnormalities: CT scans have the ability to detect lung diseases, nodules, or masses that may not be visible on standard X-rays.
- Abdominal and pelvic complaints: CT scans allow detailed images of the abdomen and pelvis, making it easier to diagnose various diseases affecting these areas.
Limitations
Limitations of a CT scan
Few types of cancers, such as the following are completely difficult to scan for –
- Prostate cancer.
- Uterine cancer.
- Some Hepatocellular cancers.
- Biliary tract cancer.
Developments
New Developments in CT Technology
Today, the radiology uses the CT scan technology, which was developed in 1974, as their fundamental device for daily hospital work. There are countless noteworthy advancements in CT technology: 3New developments in CT technology | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- Dual-Energy CT (DECT): This technology allows for better tissue characterization by simultaneously using two different energy levels, providing more information about the composition of scanned tissues.
- Iterative Reconstruction: Enhanced algorithms for image reconstruction have been developed, which reduce image noise and improve image quality while maintaining lower radiation doses.
- Cone Beam CT: Originally used in dental and interventional procedures, this technology has expanded to applications like image-guided surgery and orthopedics. 3New developments in CT technology | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- Portable and Compact CT Scanners: These smaller, more mobile scanners are useful for point-of-care imaging and in places with limited space.
- Photon-Counting Detectors: These detectors offer improved spatial resolution, spectral imaging capabilities, and potentially lower radiation dose. 3New developments in CT technology | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- Artifact Reduction Techniques: Advances in software and hardware have helped reduce artifacts caused by metal implants or patient movement during scanning.
- Cardiac CT Imaging: Enhanced scanners and techniques have allowed for better visualization of coronary arteries, improving non-invasive cardiac assessment.
- Functional CT Imaging: Combining CT with functional information, such as blood flow or tissue perfusion, provides more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI algorithms are being included to help in image reconstruction, noise reduction, and automatic detection of anomalies.
- Ultra-High-Resolution CT: These systems can provide extremely detailed images, which is particularly useful in areas like lung imaging.
Preparations
Preparing for a CT scan
Preparing for a CT scan may involve several steps to ensure a successful and accurate imaging procedure. These are some points to consider:
- Notify Your Physician: Make sure your healthcare assistant knows about any medical conditions, allergies, or medicines you are taking. Also, inform them if you have had a previous allergic reaction to contrast dye used in imaging studies. 1Preparing for a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Fasting: The type of CT scan may require you to fast for a specific period before the scan. For 4 hours before your test, please do not eat solid foods. You can drink liquids such as water, juice or caffeinated black coffee or tea.
- Contrast Dye: In the event that your CT scan requires contrast dye, the healthcare provider may request that you drink the contrast material or receive it through an intravenous (IV) line beforehand. The dye enhances the images and makes it easier to see certain structures. 1Preparing for a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Wear clothing that is comfortable: You may be asked to change into a hospital gown, but wearing loose and comfortable clothing without metal zippers or buttons can be helpful. 4Preparing for a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Dispose of Metal Objects: Make sure to remove any metal objects, such as jewelry, eyeglasses, dentures, or hearing aids, before the CT scan as they can meddle with the imaging process.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Notify your doctor if you are pregnant or nursing, as precautions may be required for some CT scans.
- Follow the pre-scan guidelines. You have to follow specific guidelines based on the CT scan you’re undergoing.
- Maintain a calm and relaxed state: CT scans are usually a quick and pain-free procedure. To get clear images, try to relax and remain calm during the scan.
It’s important to ask any questions or describe any concerns before the CT scan. Having a well-prepared and informed mindset can lead to a smooth and successful imaging experience.
Procedure
During a CT scan
During your CT scan, you can expect the following process:
Positioning on the Scanner:
- You will be positioned correctly by the technologist to assure that the area of interest is in the center of the scanner.
Immobilization: 1During a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health 4During a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Pillows, straps, or foam pads may be used by the technologist to keep you still during the procedure.
Scanning Process:
- Multiple X-ray images from different angles will be taken by the CT scanner as it rotates around your body.
- You could hear buzzing and clicking sounds during this process.
Communication:
- The technologist will use an interphone to communicate with you during the scan.
- To reduce motion blur in the images, they will instruct you to hold your breath for a brief period at certain points.
Scan Duration:
- CT scans are usually quick, and the entire process may take only a few minutes to complete. 1During a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Post-Scan:
- After the scan is finished, the technologist will review the images to ensure they are of high quality.
Contrast dye and recovery:
- If you were given contrast dye, wait for a brief period to make sure there are no adverse reactions to it.
- Contrast is well tolerated by most people, but some may experience slight side effects like a metallic taste or a feeling of warmth.[1]
Average time for the CT scan:
- It usually takes 24 to 48 hours to obtain the results of the CT scan.
- On the whole, most CT scans are usually fast and take only a few minutes.
- The scanning process involves rotating the X-ray machine around the body to capture images from various angles and it usually lasts for a few seconds.
- Usually, the CT scan process can be completed in 10 to 15 minutes.
- However, more complex scans or scans of larger areas may take slightly longer.
Outcomes
Outcomes of having a CT scan
Although CT scans are generally safe, considerations must be given to some side effects.
Some possible side effects of CT scans are listed below:
- Radiation Exposure: A small risk of long-term effects is posed by exposure to ionizing radiation during CT scans, if multiple scans are performed over time. 5Outcomes of having a CT scan | Researched based study from SAGE Publications
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience mild to severe allergic reactions to the contrast dye. 1Outcomes of having a CT scan | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: Contrast dye can stress the kidneys, leading to a temporary decline in kidney function, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney issues.
- Sickness and vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting due to the use of contrast dye.
- Itching or Rash: Allergic reactions to contrast dye may cause itching, hives, or a rash. 5Outcomes of having a CT scan | Researched based study from SAGE Publications
- Metallic Taste: Some patients report a metallic taste in their mouth after receiving contrast dye.
- Feeling hot: In certain individuals, the contrast dye can cause a warm sensation or feel hot.
- Discomfort: Patients may experience mild discomfort during the scan due to the positioning on the CT table or holding their breath at certain intervals.
- Over diagnosis: CT scans can detect minor abnormalities that may not require treatment, leading to over diagnosis and unnecessary concerns.
Discussing the potential risks and benefits of a CT scan is crucial, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or concern about the procedure.
CT Scan Vs. MRI
CT Scan Vs. MRI
CT scan and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) are two medical imaging techniques that are used to view and identify different conditions within the body.
Despite their shared purpose, there are some significant differences between them. These are:
Imaging rule:
- CT scans: Cross-sectional images of the body are produced by X-rays in a CT scan. To create in –depth pictures, a computer processes the rotating X-ray beams around the patient.
- MRI: MRI consists of using a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce precise images of internal structures of the body. The use of ionizing radiation like X-rays is not involved in it.
Contrast rule:
- CT scan: Contrast dye (iodine-based) is often used to improve certain structures or highlight specific areas on a scanner.
- MRI: Contrast dye (gadolinium-based) can be utilized in MRI, but it is not used as frequently as CT scans.
Visualizing the soft tissue:
- CT scan: Bones, lung tissue, and dense structures are more visible in CT scans due to the use of X-rays.[6]
- MRI: The use of MRI is beneficial for visualizing soft tissues, including the brain, spinal cord, muscles, ligaments, and organs, as it offers excellent contrast between different soft tissues.
Radiation Exposure:
- CT scan: The risk of exposure to ionizing radiation is small, particularly with repeated scans.
- MRI: Because MRI doesn’t use ionizing radiation, it’s a safer option for repeated imaging studies, notably in young individuals or pregnant women. 6CT Scan Vs. MRI | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
Suitability for Specific Conditions:
- CT scan: CT scans are often preferred for evaluating trauma, detecting fractures, and identifying conditions that involve the lungs, abdomen, and bones.
- MRI: It is valuable for diagnosing neurological disorders, spinal cord injuries, brain tumors, joint and soft tissue problems, and pelvic conditions.
The decision to choose between a CT scan and an MRI is based on the specific clinical inquiry, the region of the body being examined, and the patient’s specific condition.
CT scan with contrast versus CT without contrast
They are two different types of computed tomography imaging procedures used for specific diagnostic purposes. Here are a couple of differences between them:
CT scan Without Contrast:
- A CT scan without contrast, also known as a non-contrast CT or plain CT, involves obtaining images of the body without the use of any contrast dye. 7CT scan with contrast versus CT without contrast | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- This type of CT scan is useful for evaluating conditions that do not require contrast enhancement, such as assessing fractures, detecting kidney stones, or evaluating lung and bone abnormalities.
Contrast based CT scan:
- A contrast dye (usually iodine-based) is administered through an intravenous (IV) line just before or during a CT scan with contrast.
- The contrast dye helps highlight blood vessels and certain organs or tissues, providing better visualization and differentiation between structures. 7CT scan with contrast versus CT without contrast | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- This type of CT scan is particularly valuable for evaluating blood vessels, detecting tumors, infections, inflammation, and providing better visualization of organs like the liver, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys.
It’s essential to discuss the need for contrast with your healthcare provider before the CT scan, especially if you have a history of allergies, kidney issues, or other medical conditions that may affect the use of contrast dye.
Regional CT Scans
Regional CT Scans
A limited or focused CT scan is a medical imaging procedure that focuses on a specific region or area of the body.
Compared to a full-body CT scan, which captures images of the entire body, a regional CT scan is more focused on checking a particular organ, joint, or part of the body without exposing the entire body to needless radiation.
Some common examples of regional CT scans include:
- Brain CT Scan: Used to evaluate the brain for head injuries, strokes, tumors, or other neurological conditions.
- Chest CT Scan: Used to examine the lungs, heart, and surrounding structures, helping diagnose lung conditions, infections, or abnormalities. 8Regional CT Scans | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- Abdominal CT: Focuses on the abdomen to assess organs such as liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas and intestine for a variety of conditions. 8Regional CT Scans | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- Pelvic CT scan: Used to assess the pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, prostate, and bladder, for abnormalities or diseases. 8Regional CT Scans | Researched based study from BioMed Research International
- Spine CT Scan: Focused on the spine to evaluate spinal fractures, disc herniations, or spinal cord compression.
Regional CT scans offer a more targeted approach to diagnostic imaging, reducing unnecessary radiation exposure to other areas of the body.
Safety
Safety during Pregnancy
- Medical imaging procedures, including CT scans, are usually not performed during pregnancy unless absolutely needed. 9Safety during Pregnancy | Researched based study from British medical journal
- During the first trimester of pregnancy, when the organs and tissues of the fetus are forming, there is a higher sensitivity to radiation.
- Therefore, if a CT scan is required during pregnancy, it is usually deferred to the second or third trimester when the risk to the fetus is lower. 9Safety during Pregnancy | Researched based study from British medical journal
Takeaway
Concluding Points
- CT scans are valuable tools for screening and evaluating various medical conditions, producing comprehensive images of bones, organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues. 10Concluding Points | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- The procedure is generally safe and well-tolerated, but it does involve exposure to ionizing radiation, which carries some risk, especially with repeated scans. 1Concluding Points | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Pregnant women and individuals with known allergies or kidney problems need to inform their healthcare provider before undergoing a CT scan, as precautions may be necessary. 9Concluding Points | Researched based study from British medical journal
- Advances in CT scan have led to higher image resolutions, enabling greater visualization of complex structures in the body.
- The field of CT scan technology is constantly evolving, with ongoing research going on latest innovations such as photon-counting detectors and improved contrast agents. 11Concluding Points | Researched based study from Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Overview | Preparing for a CT scan | During a CT scan | Outcomes of having a CT scan | Concluding Points
-
SAGE Publications
Use of CT Scan
-
BioMed Research International
New developments in CT Technology
-
National Institutes of Health
Preparing for a CT scan | During a CT scan
-
SAGE Publications
Outcomes of a CT scan
-
BioMed Research International
CT Scan Vs. MRI
-
BioMed Research International
CT Scan with contrast Versus without contrast
-
BioMed Research International
Regional CT Scans
-
British medical journal
Safety during Pregnancy | Concluding Points
-
National Institutes of Health
Concluding Points
-
Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology
Concluding Points