Hip Pain : Causes, Symptoms, and Management:

- Hip Pain
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is hip pain?
Hip pain is a broad term for pain in and around a person’s hip joint. People may feel pain in the knee, groin, or thigh rather than in the hip. The hip joint is able to endure constant movement in addition to minor strain and wear. It is the body’s largest ball-and-socket joint and fits snugly toto allow for fluid motion. Hip discomfort is widespread, especially among older people. It can occasionally be due to medical conditions in other parts of the body, like the lower back, and is called referred pain.
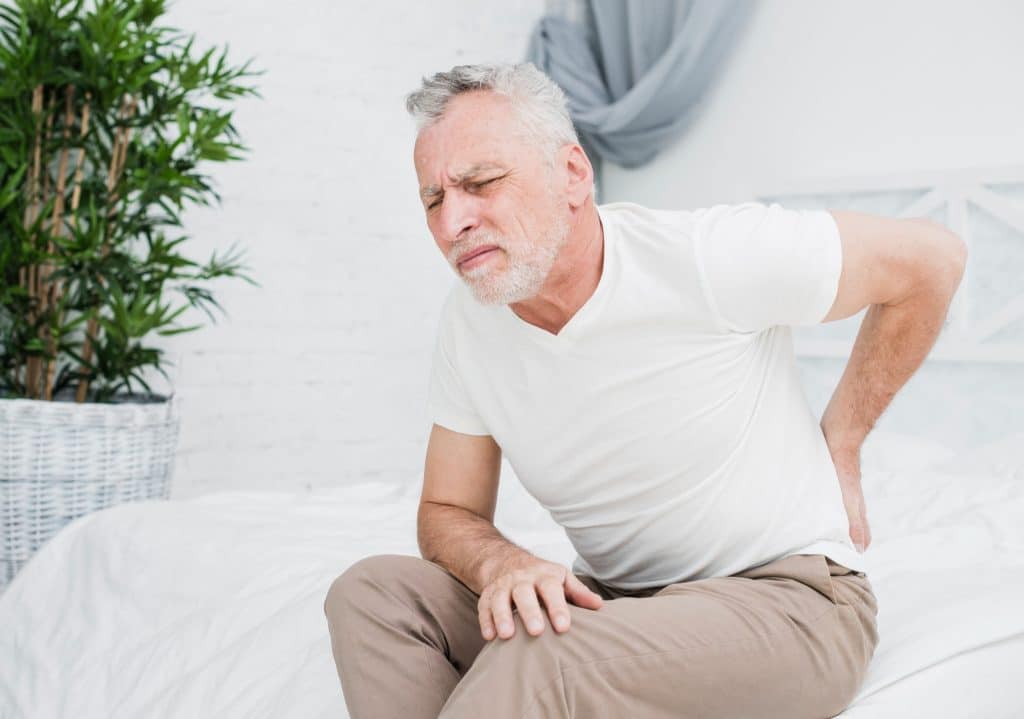

Causes
What are the causes of hip pain?
Hip pain may be caused by various reasons, as follows
Hip joint inflammation
- Idiopathic arthritis in children1Causes | Researched based study from Mayoclinic.org
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Psoriatic arthritis.
- Sacroiliitis2Causes | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Synovitis.
Any injuries, including
- Dislocated hip.
- Fracture of the hip bone.
- Labral tear of the hip.
- Hamstring strain.
- Hip flexor strain.
- Sprain.
- Bursitis.
Nerve injury or compression
- Sciatica.
- Meralgia paresthetica.
Referred pain
- Inguinal hernia
- Back pain.
Cancer
- Leukemia.
- Bone cancer.
Other conditions
- Legg-Calve-Perthes disease in children – rare.
- Snapping hip syndrome.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Osteonecrosis.
- Osteoporosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with hip pain
The symptoms of hip pain might differ depending on the underlying reason and could consist of any of the following
- Pain in the knee, groin, buttocks, or hip.3Symptoms| Researched based study from Betterhealth.vic.gov.au
- Pain that worsens when a person moves.
- Tight joints that typically worsen in the morning and after rest.
- A grinding sound made when moving the hip.
- Reduced hip range of motion may result in a limp and limit mobility.
- A joint ache that gets worse by rain or cold weather.
- Swollen, warm, and tender joints.
- Rarely, weakness, fever, and appetite loss.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of hip pain
To identify the cause, the doctor will interview the patient about their symptoms, conduct a physical exam, and order imaging tests.
Physical examination
- A visual inspection of the hips may indicate an abnormality or injury.
- The physician will move the patient’s leg in various directions while checking for pain, popping, or stiffness.
- These might point to the origin of the hip issue.
Imaging tests
The following standard imaging tests are used to find the cause of pain:
- X-rays – used to look for fractures or other abnormalities.4Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Ultrasound – to find soft tissue damage in the tendons, ligaments, and cartilages connected.
- Bone scan – to find any anomalies in the bone, especially in conditions affecting the bones.
- MRI scan – can distinguish between pain from the belly and cartilage tears or fraying.
- Arthrogram – aids in diagnosing joint diseases like hips or shoulders by clearly displaying ligaments, tendons, and cartilage concerns.5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
- Bone biopsy – the doctor may choose to extract a tiny portion of bone to perform a bone biopsy to check for irregularities in the structure of the bone and surrounding tissues.
Vulnerability
Who are at risk?
The following individuals may have an increased chance of experiencing hip pain:
- Older adults, as bone and joint disorders are brought on by aging.
- People who are obese.6Vulnerability| Researched based study from Hopkinsarthritis.org
- Women primarily following menopause.7Vulnerability| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- A history of arthritis in their families.
- Individuals with prior hip injuries.
- Those who have osteoporosis.
- Young kids suffering from Perthes disease.
- People who engage in a physically demanding sport.
- Those whose jobs place a lot of stress on their hips.
Complications
What are the associated complications of hip pain?
Complications of hip pain may include
- Impaired capacity to walk.
- Disparities in limb length.
- Persistent discomfort.
- Permanent Hip abnormalities.
- Pain-related anxiety, depression, and sleeplessness.8Complications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Management
Management strategies for hip pain
Depending on the degree of pain experienced, an individual may be treated both medically and at home
Self-care advice are
- Rest – Don’t stand, sit, or bend at the hips to give the joints a break.9Management| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
- Ice – To apply cold therapies to the hip, use ice blocks or a package of frozen veggies covered in a towel.
- Heat – On the other hand, a warm shower or bath may help the muscles get ready for stretches that can ease the pain.
- Over-the-counter medicines for pain like ibuprofen and acetaminophen, may decrease pain.
- Keep away from activities that aggravate pain.
- Lay a pillow between the legs and choose the side of the body that will not hurt when sleeping.
- Put on cushioned, comfy flat shoes.
- Schedule a visit with a doctor if self-care remedies are ineffective.
Medical management
The type of medical treatment depends on the primary cause
Medicine
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may lessen inflammation and ease discomfort. Ibuprofen and naproxen are two examples.
- Corticosteroids – These potent anti-inflammatory medications can be administered orally or injected directly into the affected joint to relieve inflammation-related discomfort.
Physiotherapy and occupational therapy
- Consult a physiotherapist for additional assistance with pain-relieving stretches and exercises. For instance, arthritis.
- Request occupational therapy; an OT might help with items that will make your life easier, like walking sticks or other walking aids.
- Specialized braces, casts, and slings that hold the joint firmly in place while the hip heals are typically effective in treating DDH and Perthes disease.
Surgical management
- Surgery to replace the hip – partially or totally.
- Hip resurfacing.10Management| Researched based study from Aaos.org
- Hip labrum or tendon repair.
- Osteotomy.
Prevention
How to prevent hip pain?
Following are some ways that people might avoid hip pain from straining during exercise and movement
- Before working out or participating in any sport, always warm up.
- Following a workout, practice, or game, take some time to stretch and cool yourself down.
- Choose a diet that emphasizes the development and maintenance of bone health.
- Avoid running down hills straight and walk instead.
- If given the option, consider routinely swimming instead of biking or running.
- Run on a soft and smooth surface, like a track.
- Try using arch supports and specialized shoe inserts if you have flat feet.11Prevention| Researched based study from Pennmedicinec.org
- Wear well-made, well-fitting, and well-cushioned running shoes.
- Avoid going too far with your physical activity.
- After a challenging workout or demanding game, take a lot of time to rest and recover.
- Always remember that taking a day off enables the body to recover, heal, and repair.
- People whose jobs need them to spend hours in a chair all day long must take brief breaks to go for walks.
- Don’t neglect to treat small wounds. No matter how minor the discomfort may seem, you should see a doctor if it persists.
Prognosis
Prognosis of hip pain
The prognosis of hip pain is largely determined by its primary cause and how effectively it responds to treatment. Doctors can manage hip pain successfully after identifying the cause and applying appropriate treatments. On the other hand, until one receives therapy, the symptoms of more severe problems, like fractures, necrosis, and arthritis, are likely to worsen. To get assistance with a treatment plan, consult a doctor. There is a healing period following hip surgery of any kind. The kind of surgery performed determines how long recovery and rehabilitation will take.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Mayoclinic
Hip pain | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Sacroiliitis | Causes
-
Better Health Channel
Hip disorders | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Imaging of Hip Pain: From Radiography to Cross-Sectional Imaging Techniques | Diagnosis
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Arthrography | Diagnosis
-
Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center
Role of Body Weight in Osteoarthritis | Vulnerability
-
National Library of Medicine
Low back pain in women before and after menopause | Vulnerability
-
National Library of Medicine
Anxiety and insomnia in young- and middle-aged adult hip pain patients with and without femoroacetabular impingement and developmental hip dysplasia | Complications
-
Cleveland Clinic
Hip Pain | Management
-
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Osteoarthritis of the Hip | Management
-
Penn Medicine
Hip Pain | Prevention