Hydrochlorothiazide: Uses, Side Effects, and Precautions

- Hydrochlorothiazide
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Hydrochlorothiazide?
A drug named hydrochlorothiazide is used to treat edema or the body’s retention of fluid. Being a thiazide diuretic, it facilitates the body’s removal of extra water and salt by raising urine production.
We will delve into the specifics of hydrochlorothiazide in this article, looking at its medical applications, dosage and administration, potential side effects, precautions, and significant drug interactions. By thoroughly understanding this, patients and healthcare professionals can make educated decisions about using it and guarantee the best results.
Uses
Hydrochlorothiazide uses
Hydrochlorothiazide is widely prescribed in following health issues:
- Management of Hypertension
- Treatment of Edema
- Kidney stone treatment
Hypertension
- It is frequently recommended as a first-line treatment for hypertension. It lowers blood pressure by boosting the body’s ability to eliminate extra salt and water through increased urine production.
- It aids in lowering the stress placed on the artery walls by reducing the total fluid volume in the blood arteries, assisting in managing high blood pressure.
Edema
- Additionally, it is used to treat edema, which is the buildup of fluid in different bodily tissues. Congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, kidney diseases, and several drugs are among the factors that can cause edema.
- It aids in reducing fluid retention, alleviating swelling and discomfort related to it by encouraging diuresis (increased urine production).
Kidney stone
- In addition to these uses, it may also be recommended in some circumstances to prevent kidney stone formation, especially calcium-containing kidney stones. The drug aids in lowering the calcium level in urine, minimizing the chance of stone formation.1Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov ,2Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov ,3Uses| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage
Hydrochlorothiazide Dosage
For high blood pressure
- Adults typically start with a dose of 12.5 to 25 milligrams (mg), given once daily orally.
- Your doctor may change the dosage depending on how your blood pressure responds. Typically, the daily maximum dose is 50 mg.
For edema
- Adults should start with a 25 to 100 mg dose administered orally once daily or in divided doses to treat edema.
- Higher doses might be required in some circumstances, but they should always be given and closely monitored by a doctor.
For preventing kidney stones
- Adults take 25 to 100 mg orally once daily to prevent calcium stones.
- It’s crucial to take the medication exactly as your doctor has instructed.
- To avoid frequent nightly urination, the medication is commonly taken orally, with or without food, in the morning.
How to take Hydrochlorothiazide?
- Take the pills or capsules whole, with a glass of water.
- If you forget to take a dose, do so as soon as you remember, but omit it if it will be only a short while before your next scheduled dose.
- Never change the dosage or stop taking it without first visiting your doctor, as doing so could reduce the medication’s ability to treat your illness effectively.5Dosage| Researched based study from Fda.gov ,6Dosage| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Side effects
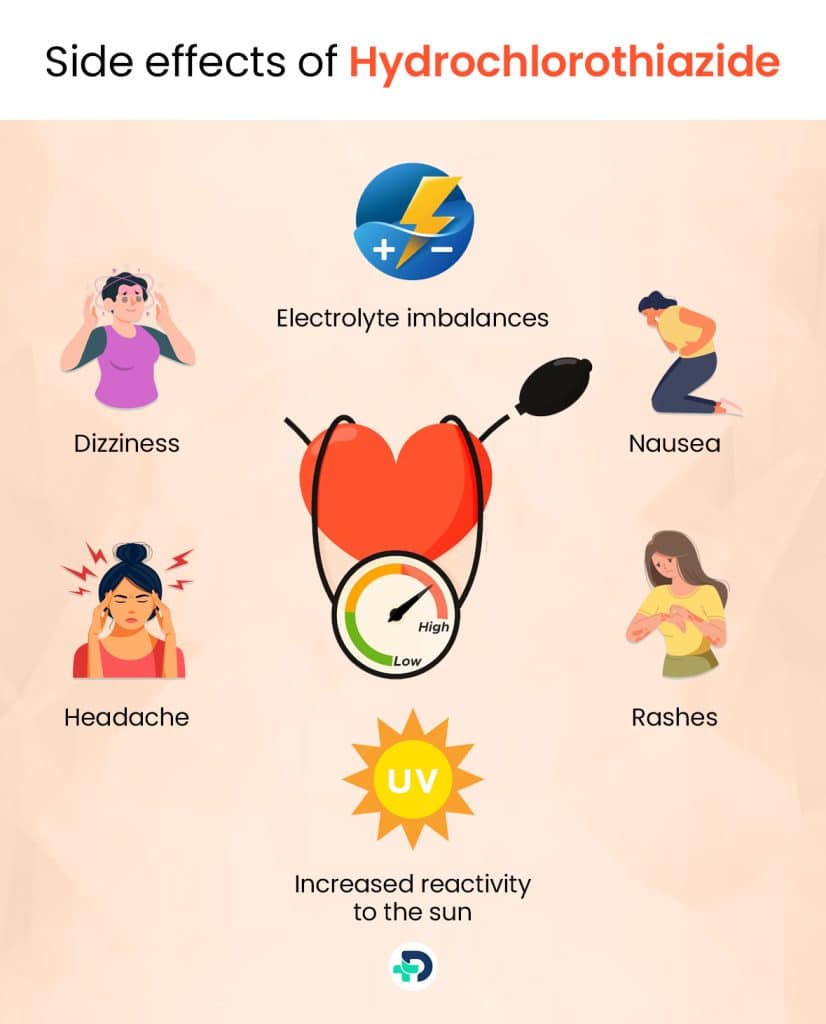
Hydrochlorothiazide side effects
It may result in side effects, just like other medications. It’s critical to be aware of any side effects and to tell your healthcare practitioner as soon as you have any worries. Typical adverse effects include:
- Increased urination
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Headache
- Nausea and stomach upset
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight
- Rash or allergic reactions
- Increased urination
Electrolyte imbalances
- It may impact the body’s specific electrolytes like potassium, sodium, and magnesium. Symptoms including weakness, weariness, and an erratic heartbeat may result.
Dizziness
- Some people may feel dizzy when taking the medication for the first time, especially when standing up fast. The blood pressure decline may be the cause of this.
Headache
- It might happen as a result of taking hydrochlorothiazide.
Nausea and an uneasy stomach
- People sometimes notice gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain.
Increased reactivity to the sun
- Your skin can become more vulnerable to sunburn or rashes due to this. Precautions like applying sunscreen and donning protective gear should be taken.
Allergic responses or rashes
- Rarely, it may cause allergic reactions or skin rashes. These may need immediate medical intervention and range from moderate to severe.4Side effects| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov ,5Side effects| Researched based study from Fda.gov ,6Side effects| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Precautions
Warnings and Precautions
Before taking hydrochlorothiazide one need to discuss following things with their healthcare professional:
Allergies
- Let your doctor know if you have any well-known allergies, particularly diuretics. Include any allergic reactions to other medications in your disclosure as well.
Kidney disease
- The kidneys remove it from the body, and diminished renal function can impact this process.
A liver condition
- A compromised liver might change its metabolism, which could reduce its efficiency or have negative repercussions.
Diabetes
- If you have diabetes, careful blood glucose monitoring may be required as it can influence blood sugar levels.
Gout
- It has been linked to the aggravation or activation of the autoimmune illness and can aggravate or induce bouts of gout by raising uric acid levels.
Allergy or asthma
- In those with a history of allergies or asthma, it may raise the risk of allergic reactions.
Breastfeeding and becoming pregnant
- If you are pregnant, intend to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding, let your healthcare practitioner know. As it could potentially harm the fetus or pass into breast milk, it is typically not advised during pregnancy or breastfeeding.5Precautions| Researched based study from Fda.gov ,6Precautions| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Interactions
Hydrochlorothiazide Interactions
Hydrochlorothiazide interactions with Medicines
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- If you need to take an NSAID, talk to your doctor about the proper monitoring. Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen may reduce the effectiveness of hydrochlorothiazide and raise the risk of kidney issues.
Lithium
- It might cause toxicity by raising the body’s levels of lithium. If you take lithium with hydrochlorothiazide, close monitoring of your lithium levels is vital since lithium can lead to electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium levels, which can exacerbate the harmful effects of digoxin on the heart. Regular electrolyte and level monitoring is necessary if you are taking both drugs.
Diabetes drugs
- Blood sugar levels may be impacted, necessitating dosage modifications for diabetes treatments such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic.
Cholestyramine and colestipol
- These medications can bind to the drug, increasing the danger of electrolyte imbalances and lowering potassium levels.
Other antihypertensive medicines
- Its ability to reduce blood pressure can be strengthened by taking it along with other antihypertensive medications. Dosage modifications and careful monitoring may be necessary to avoid dangerously low blood pressure.5Interactions| Researched based study from Fda.gov ,6Interactions| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Hydrochlorothiazide Interactions with Food
High potassium foods
- Bananas, oranges, tomatoes, avocados, spinach, potatoes, and some legumes should be avoided or consumed in moderation by those with hypertension to prevent potassium depletion.
Grapefruit
- It may interact with hydrochlorothiazide, changing how well the drug is absorbed and raising the amount in the body.
Alcohol
- Drinking alcohol might exacerbate the blood pressure-lowering effects, which could lead to fainting, lightheadedness, or dizziness. It can also raise the risk of dehydration, a possible side effect.
Salt substitutes
- Some salt substitutes have high potassium levels, which could interfere with a medication’s ability to lower potassium levels. It’s crucial to read the label of any salt substitutes you use and choose ones that are low in potassium or to discuss suitable replacements with your doctor.7Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Hydrochlorothiazide | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Thiazide Diuretics | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Hydrochlorothiazide | Uses
-
National Library of Medicine
Thiazide effects and side effects: insights from molecular genetics | Side effects
-
FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE TABLETS, USP | Dosage | Side effects | Interactions
-
FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
MICROZIDE® (hydrochlorothiazide, USP) Capsules | Dosage | Side effects | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of Dietary Sodium and Hydrochlorothiazide on the Antiproteinuric Efficacy of Losartan | Interactions