Januvia: Uses, Dosage, Side effects and Interactions

- Januvia
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Januvia?
Januvia is a prescription medicine that contains an active ingredient called sitagliptin, which belongs to a group of medicines called anti-hyperglycemic agents (a class of drugs used to lower blood sugar levels in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus). It is generally not recommended for use in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and has limited use in patients suffering from pancreatitis, a condition that occurs due to inflammation of the pancreas.1Overview| Researched based study from Fda.gov

Uses
Januvia Uses & Indications
Type 2 diabetes Management
- Adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus can use Januvia alone or in combination with other anti-diabetic drugs (such as insulin, metformin, or sulphonylureas) as a supplement to diet and exercise to help lower blood sugar levels.2Uses| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Diabetes mellitus type 2: what is it?
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the body produces insufficient insulin and the insulin that is generated does not work efficiently. Sugar is generally produced in excess in the body due to the condition which leads to increased blood sugar (glucose) levels in the body resulting in medical conditions such as kidney damage, or heart disease if not controlled/treated.2Uses| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Dosage
Januvia Dosage forms and strengths
Available dosage
- Januvia comes as a round, film-coated tablet with 221, 112, and 277 denoted on one side of the tablet as 25mg, 50mg, and 100mg dosage, respectively.2Dosage| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
How is Januvia administered?
- When taking this drug, always follow your doctor’s recommendations. Speak to your doctor if you have any queries about the administration.
- The normal dosage is one oral 100 mg film-coated tablet taken once daily.
- You can take this medication with or without food and it is important to follow the diet and activity plan as suggested by your doctor while taking Januvia medicine.2Dosage| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Side effects
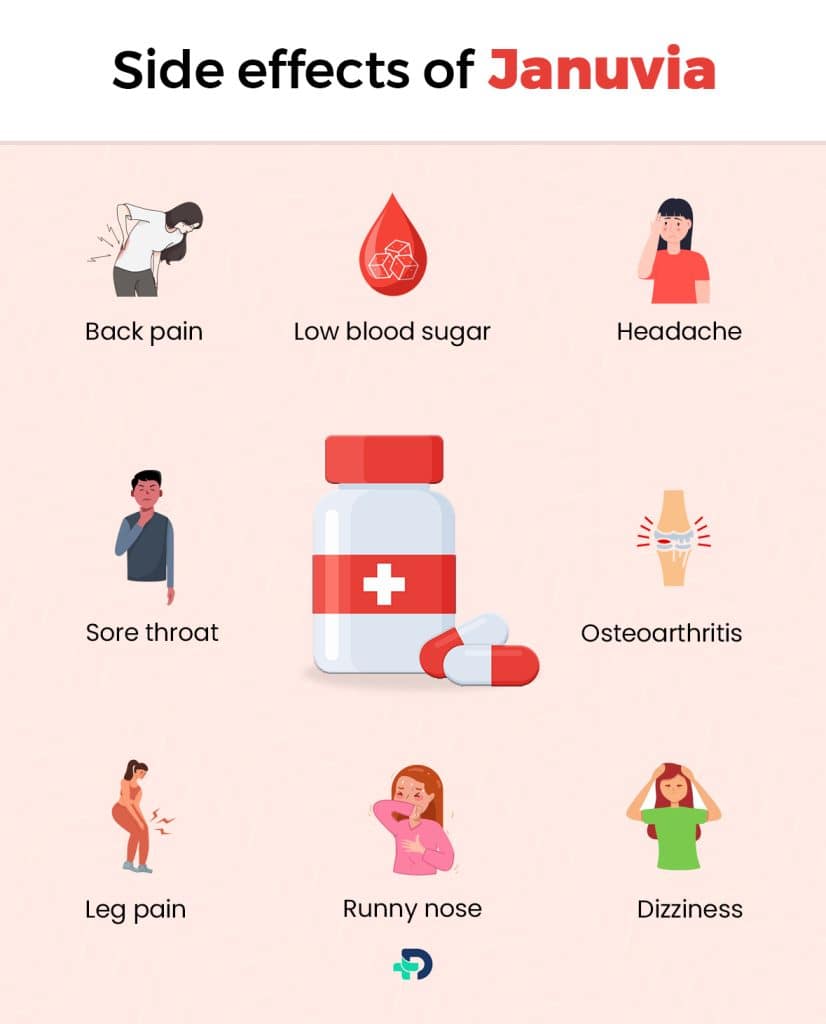
Side effects of Januvia
If any of these signs are bothersome or do not go away, consult your physician for guidance:
Common side effects
- Low blood sugar
- Headache
- Upper respiratory infection
- Stuffy/runny nose
- Sore throat
- Osteoarthritis (degenerative disease)
- Arm/leg pain.
Uncommon side effects
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Itching
- Vomiting
- Back pain
- Bullous pemphigoid (a type of skin blister).2Side effects| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Serious side effects (that might lead to discontinuation of treatment with Januvia)
- Pancreatitis (inflamed pancreas) with associated symptoms such as severe & persistent pain in the abdomen, with/without nausea, or vomiting
- Serious allergic (hypersensitivity) reaction associated with symptoms that include rash, hives, blisters on the skin, swelling of the face, lips, tongue/throat, difficulty in breathing, or swallowing.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Januvia is not indicated for use:
- In patients hypersensitive/allergic to sitagliptin, and/or other ingredients of the medicine
- In children and adolescents (aged below 18 years)
- If you are a pregnant woman.
- If you are nursing (breastfeeding) an infant.2Contraindications| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Precautions
Warnings and precautions
Inform your doctor before using Januvia medicine if any of these applies to you:
- Have/had pancreatitis (inflamed pancreas)
- Suffering from alcoholism
- Suffering from type 1 diabetes, or diabetic ketoacidosis (a complication of diabetes marked with high blood sugar, nausea/vomiting, and/or rapid weight loss)
- Have/had kidney problems
- Have/had liver problems
Patients suffering from alcoholism
- Patients who are alcoholic should take Januvia with caution since alcohol can increase the risk of pancreatitis that occurs due to an inflamed pancreas generally associated with symptoms such as upper abdominal pain, fever, rapid pulse, and/or nausea/vomiting.
Patients suffering from diabetic ketoacidosis
- Patients who suffer from diabetic ketoacidosis, a serious complication of diabetes, should take Januvia with caution after consulting the doctor since this condition can lead to adverse effects such as high blood sugar, nausea, vomiting, and/or rapid weight loss in affected individuals.
Patients suffering from kidney problems
- Patients who suffer from kidney problems such as renal impairment should take Januvia with caution after consulting the doctor to avoid undesirable effects.
Patients suffering from liver problems
- Patients who suffer from liver problems such as hepatic impairment should take Januvia with caution after consulting the doctor to avoid undesirable effects.1Precautions| Researched based study from Fda.gov ,2Precautions| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Use in specific populations
Pregnant women
- If you are pregnant, or planning to become pregnant then it is advisable to avoid this medicine since it may cause some undesirable effects in an unborn baby. To avoid undesirable effects during pregnancy, consult your doctor for advice.
Nursing mothers
- Breastfeeding mothers should not take Januvia medicine since it is not known whether the medicine passes through breastfed milk, which could have negative effects on nursing infants.
When used in children
- Since Januvia is ineffective under the age of 18, it is not advised for use in children and adolescents. For further information, speak with your doctor.
When used in geriatric patients
- Elderly patients (aged 65 years and above) should take Januvia medicine with caution after consulting the doctor to avoid undesirable effects in this age group.1Precautions| Researched based study from Fda.gov ,2Precautions| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Interactions
Januvia Interactions
Drug-Drug interaction
A lot of drugs can interact with Januvia, and some drugs should be avoided while taking the medicine. To avoid undesirable effects, inform your physician about all the medicines you take before taking Januvia medicine which may include a few listed below:
- Digoxin (a medicine used to treat irregular heartbeat and other heart problems)
- Other antidiabetic medicines (used to lower blood sugar levels) Ex. metformin, insulin, and sulphonylureas.2Interactions| Researched based study from Medicines.org.uk
Takeaway
Takeaway tips
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the body produces insufficient insulin and the insulin that is generated does not work efficiently.
- Adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus can be advised Januvia alone or in combination with other anti-diabetic drugs (such as insulin, metformin, or sulphonylureas) which act as a supplement to diet and exercise to help lower their blood sugar levels.
- The common side effects associated with the use of Januvia are low blood sugar, headache, upper respiratory infection, stuffy/runny nose, and/or sore throat
- Patients who are allergic/hypersensitive to sitagliptin, an anti-hyperglycemic medication used to reduce blood sugar levels, should not take Januvia medicine.
- Januvia should be avoided in pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Januvia should be used with caution in patients suffering from kidney, and liver problems and should consult a doctor before taking the medicine to avoid undesirable effects.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
Januvia | Overview | Precautions
-
Electronic medicines compendium (EMC)
Sitagliptin | Uses | Dosage | Side effects | Contraindications | Interactions