Shoulder Pain: Symptoms, Causes & Management

- Shoulder Pain
- 10 Oct 2023
Introduction
Shoulder Pain
Any discomfort you experience near your shoulder joint is a shoulder pain. The complicated shoulder joint enables you to throw a ball, reach for something, or high-five someone. Your shoulder is more vulnerable to damage and injury as a result of how frequently you use it, which could lead to pain. 1 Introduction | Researched based study from Cleveland Clinic
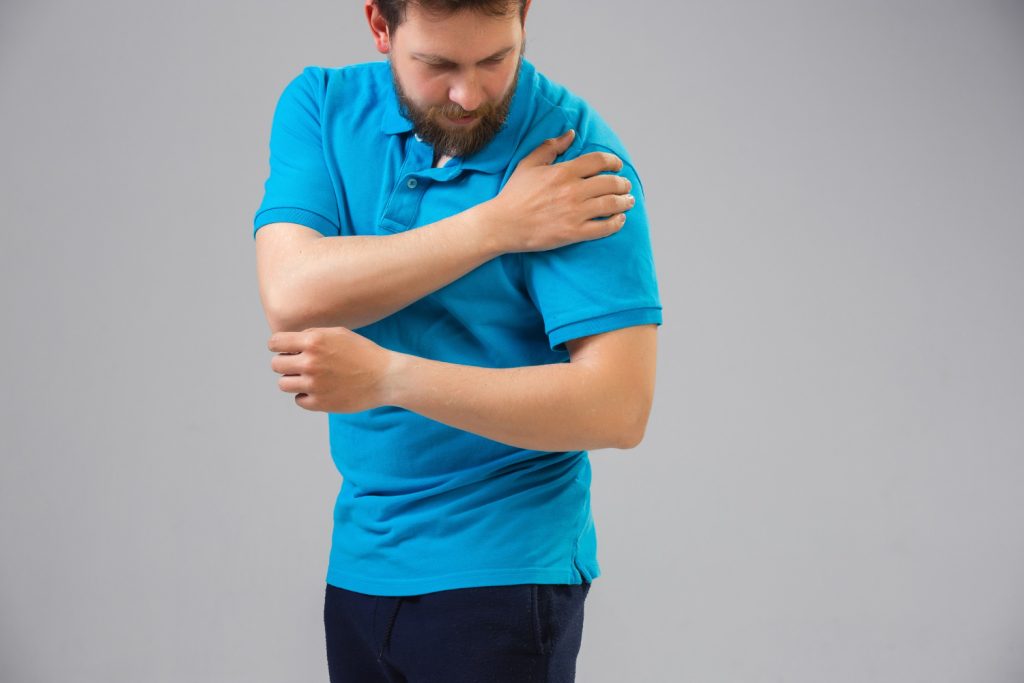

Symptoms
Symptoms of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain differs depending on the reason, but you may experience the following symptoms while moving or at rest:
- Shoulder warmth or redness
- Stiffness and weakening of the muscles
- Back, neck, or arm pain
- Restricted range of motion
- When you move your arm, you may feel a clicking, popping, or grinding feeling
If you experience sudden or severe discomfort, swelling, or deformity in your arm contact your doctor right away. 2 Symptoms | Researched based study from Dignity Health
Causes
Shoulder Pain Causes
The primary reason causing shoulder pain is, when the tendons of the rotator cuff tangle under the bony portion of the shoulder. Tendons enlarge or become damaged. It is additionally referred to as bursitis or rotator cuff tendonitis. Additional factors that could contribute to shoulder pain include:
- Arthritis
- Bursitis (an inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that typically cushions the joint and facilitates smooth movement)
- Separated shoulders
- Shoulder-regional bone spurs
- Shoulder fracture
- Shoulder dislocation
- Overuse or damage to surrounding tendons, such as the biceps muscles in the arms, can cause pain.
- Nerve damage that causes aberrant shoulder mobility
- Incorrect shoulder mechanics and posture
- Tendon tears in the rotator cuff 3 Causes | Researched based study from Penn Medicine
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Shoulder Pain
Since there are numerous possible causes of shoulder pain, your doctor will carefully review your symptoms, perform a physical exam, and occasionally order imaging tests to determine the exact problem.
Medical history
- A medical history can be a helpful tool in determining the reason of your discomfort because most shoulder issues are increased by certain activities and relieved by certain activities.
- The physician may ask you about when and how the discomfort started, whether it has happened before, and how it was treated, among other things, in order to evaluate both your overall health and the potential reasons of your shoulder problem.
Physical Examination
- Your physician will look for physical abnormalities such as edema, deformities, or weak muscles, as well as sore places.
- The examiner will evaluate your shoulder endurance and range of motion.
Imaging tests
- Your doctor may order certain tests to assist discover the cause of your discomfort and any underlying complications.
X-rays
- X-rays generate images of the bones and joints. They may indicate any changes caused by fractures or arthritis in the shoulder joint, such as bone spurs or a reduction in joint space.
- X-rays, on the other hand, do not disclose any changes or abnormalities with the soft tissues, including tendons and ligaments.
Ultrasound
- Ultrasounds are commonly used to detect inflammation, rips, or ruptures in the rotator cuff tendon.
- Although ultrasound can be a helpful tool in determining the source of your pain, it cannot be used to make a diagnosis.
- If an ultrasound is required, an x-ray will also be scheduled. The findings of the two tests combined will provide a more complete picture of the state of the joints and tendons.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- A diagnostic process that creates comprehensive images of organs and body structures using a mix of powerful magnets, radiofrequency technology, and a computer can frequently identify injury or disease in an adjacent ligament or muscle.
Computed tomography scan (CT scan)
- A diagnostic imaging process which makes use of computer technology as well as X-rays to generate axial, or horizontal, pictures (commonly referred to as slices) of the body.
- A CT scan produces high-resolution images of any area of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans provide more information than standard X-rays.
- To assess nerve function, your doctor might request a test like an EMG (electromyogram).
Arthrogram
- During this x-ray scan, a dye is injected into the shoulder to improve visibility of the joint and the muscles and tendons that surround it. Additionally, an MRI might be used.
Arthroscopy
- Your surgeon uses a fiber-optic camera to see within the joint during this surgical operation.
- Arthroscopy can disclose soft tissue injuries that are not obvious on physical examination, x-rays, or other tests.
- Arthroscopy may be utilized to address the issue in addition to assisting in identifying the source of the pain. 4 Diagnosis | Researched based study from American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons , 5 Diagnosis | Researched based study from Johns Hopkins Medicine
Prevention
How to Prevent Shoulder Pain?
Accidental injuries cannot always be avoided, but there are steps you can do to lower your risk and safeguard your shoulder. As an example:
- When participating in an activity, pay attention to your body’s signals; if something aches, take a break till you recuperate.
- Warm up before engaging in any activity that needs pitching or dangling from your arms.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and amount of activity as directed by your doctor.
- Practice activities to strengthen the muscles around your shoulder if your doctor suggests it to protect the joint.
- To strengthen your shoulder as well as prevent repetitive usage injuries at work, utilize correct ergonomics. 2 Prevention | Researched based study from Dignity Health
Management
Shoulder Pain Treatment
The cause of the shoulder pain must be addressed before beginning any form of treatment. And while one course of treatment could be effective for one problem, it might not be effective and might even be harmful for another. You must consult a qualified medical professional before beginning a treatment regimen.
Not all of the treatments on this list are suitable for all conditions. But given your circumstance, some might assist in reducing shoulder pain.
Rest
- The first line of treatment for many common types of shoulder discomfort is to rest the joint and let the inflammation or irritation to subside.
- When resting the joint, use cautious; prolonged rest might cause joint stiffness.
Physical therapy:
- A key component of treating shoulder pain is physical therapy.
- To improve your strength, regain mobility, and assist you in getting back to your pre-injury level of activity, your physical therapist may employ a variety of methods.
Application of Ice and Heat pack:
- Most frequently, ice packs are used to lessen the discomfort and swelling associated with a recent shoulder injury.
- Injuries to the shoulder caused by overuse, such as bursitis or rotator cuff tendonitis, can also be treated with them.
- In such instances, ice can be applied right away following performing the overhead training to decrease the onset of inflammation.
- Heating patches are also used to treat chronic shoulder pain, even though generally prior overhead workouts. Heat can help with pain relief, stiffness relief, and muscle relaxation.
- Before using ice or heat, check with a physician or physical therapist. It’s crucial to create a detailed strategy for the sequence and length of each treatment to ensure optimum healing.
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) and steroid injections are the two most often utilized treatments to reduce shoulder discomfort and swelling.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Some NSAIDs are accessible over-the-counter and are frequently used for managing shoulder problems such arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis.
- It is vital to utilize them just for a limited amount of time and underneath the supervision of your healthcare professional.
- NSAIDs contain some dangers, so tell your doctor if you are pregnant or have any health issues, such as high blood pressure, asthma, or a history of kidney disease, liver illness, or stomach ulcers.
Steroid Injection
- A steroid injection involves your healthcare professional injecting cortisone, a potent steroid medicine that lowers inflammation, into your shoulder.
- An injection can help lessen pain and make it easier to participate in physical therapy sessions.
Surgery
- Some shoulder disorders may necessitate surgery. Most patients with shoulder discomfort, however, will react to simple therapy measures such as activity modification, rest, exercise, and medication.
- Certain kinds of shoulder problems, such as recurrent dislocations as well as certain rotator cuff injuries, may not benefit from exercise. In some cases, operation may be considered rather early.
- An arthroscopy is often used to eliminate scar tissue or heal damaged tissues, whereas traditional open procedures can be used for extensive reconstructions or shoulder restoration. 4 Management | Researched based study from American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons , 6 Management | Researched based study from Better Health Channel
Takeaway
Shoulder Pain: Exercises & Medical Counsel are Required
- Most people experience discomfort in their shoulders at a certain moment in their lives. This ball and socket joint has an unusual structure that provides it a wide range of motion but also makes it vulnerable to stress, pain, and injury, especially for athletes.
- You can recover with natural solutions for shoulder pain. They may also reduce the likelihood of further shoulder injuries. Simple exercises you may do at home, medication, and medical counsel can all work to strengthen your shoulder joint and decrease discomfort.
- People who experience severe discomfort or pain that does not improve with self-care should visit a doctor. For shoulder dislocations and other severe injuries, you should also consult a doctor right once.
- Shoulder discomfort could be caused by an undetectable condition. Underlying problems in the patient can cause acute discomfort in the shoulder muscles that radiates to the arm. It might be anything from heart illness to spinal abnormalities to liver problems to diabetes.
- Physical therapy has proven to be more effective than surgery in addressing shoulder discomfort. A physical therapist provides a beneficial conservative strategy with long-term good benefits and functionality restoration that is economical and does not require you avoid work.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Cleveland Clinic
Introduction
-
Dignity Health
Symptoms | Prevention
-
Penn Medicine
Causes
-
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Diagnosis | Management
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Diagnosis
-
Better Health Channel
Management