Vitamin E and its health benefits

- Vitamin E
- 16 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Vitamin E ?
The body requires the fat-soluble vitamin vitamin E for a variety of vital processes. It also promotes a number of important physiological processes in the body in addition to acting as an antioxidant.1Overview | Researched based study from Nih.gov
It occurs naturally in many foods and is also available as supplements.

Facts
Facts on vitamin E
- Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley made the discovery of it in 1922.
- Eight distinct substances, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, make up vitamin E.
- As a potent antioxidant, it is frequently used in skincare products.
- Being a fat-soluble vitamin, it is stored in the body’s fatty tissues and, if taken in excess, can accumulate to hazardous levels.
Benefits
Benefits of vitamin E
Excellent antioxidant
- In the body, it mostly serves as an antioxidant.
- Its primary function is to shield cells from harm from dangerous substances called free radicals, which may cause oxidative stress and be a factor in chronic illnesses including cancer, heart disease, and dementia.1Biological role | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Immune system support
- By encouraging the creation of white blood cells that fight against infection and illness, it helps to strengthen the immune system.
Skin health
- It is thought to aid in defending the skin against pollutants and UV radiation damage. By lowering inflammation and encouraging collagen formation, it is also believed to delay the ageing process of the skin.1Biological role | Researched based study from Nih.gov
- Additionally, it could hydrate the skin and make wrinkles and fine lines less obvious.
Eye health
- It could aid in preventing age-related macular degeneration, which is one of the main factors in visual loss in older people.
Cardiovascular health
- It has been demonstrated that by enhancing blood flow and lowering inflammation, it can aid in the prevention of blood clot formation and lower the risk of heart disease.
Brain function
- Additionally, it could help keep people’ cognitive abilities intact and lower their risk of cognitive decline.1Biological role | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Sources

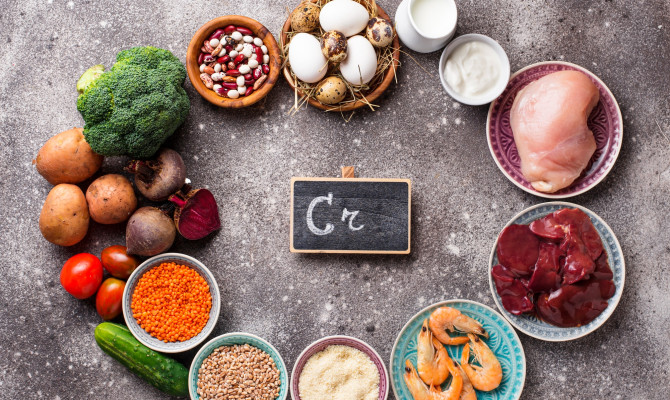
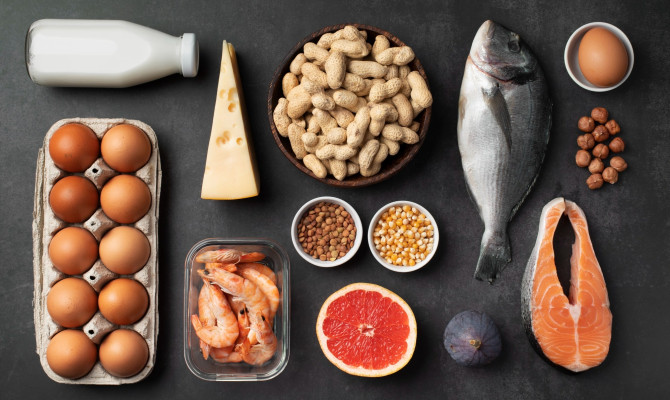
What are the dietary sources?
Plant-based sources of vitamin E are
Seeds and nuts
- Good sources include almonds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, and peanuts.1Sources | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Green leafy vegetables
- Collard greens, kale, and spinach are all high in vitamin E.
Vegetable oils
- Good sources include soybean oil, sunflower oil, safflower oil, etc.
Avocado
- A good source is an avocado.
Whole grains
- Such as oats, brown rice, and whole grains like wheat.
Fruits
- Several fruits, including papaya, kiwi, and mangoes, have trace quantities of vitamin E. 1Sources | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Animal based sources are
Egg whites
- One big egg provides almost 6% of the daily necessary amount of egg yolks, which makes them a decent source.
Liver
- Beef liver, chicken liver, and other organ meats are good sources of the recommended daily allowance, with a 3-ounce portion of beef liver providing around 10% of that amount.1Sources | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Fish
- There are small amounts in several fish varieties, including trout, salmon, and herring.
Meat
- Sources include chicken, pig, and beef, however the quantity varies depending on the cut of meat.1Sources | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Deficiency
Risk factors for vitamin E deficiency
In healthy people who eat a balanced, diverse diet, vitamin E deficiency is uncommon. On the other hand, some medical disorders, such as:
Disorders of fat absorption
- The body’s capacity to absorb dietary fat can be impacted by illnesses including Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, and liver disease.2Risk factors | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Low-fat diets
- The shortage can also be brought on by extremely low-fat diets or diets that drastically limit fat consumption.
Genetic disorders
- Deficiency may also result from rare hereditary conditions that alter the metabolism of vitamin E.2Risk factors | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
What are the symptoms of Vitamin E deficiencies?
- Weakened muscles-Loss of muscle mass and muscular wasting might result from the shortage.
- Poor coordination-It can have an impact on the neurological system and lead to balance and coordination issues.
- Vision issues-A lack of vitamin E can harm the retina, resulting in vision issues like blurry vision in low light and loss of peripheral vision.2Symptoms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Anemia-A condition when the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the tissues.2Symptoms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Immune system impairment-It can make the immune system less effective thus rendering infections more likely.
- Skin conditions-It may result in scaly, rough, and dry skin.
- Nerve damage-It is possible for nerve injury to take place, which can cause pain, tingling, and numbness in the hands and feet.2Symptoms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Forms
What are the various forms of vitamin E?
There are eight distinct forms of it in nature, which may be further broken down into tocopherols and tocotrienols.
- Alpha tocopherol is the most common and physiologically active form of vitamin E.
- Gamma-tocopherol, which is frequently present in foods and has particular anti-inflammatory qualities, is another.4Forms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
To obtain the maximum advantage from supplements, it’s crucial to select a combination of these kinds while shopping. Physically, it can be found in the following forms:
- Soft gels or capsules-supplements are frequently offered for sale as soft gels or capsules that may be swallowed.4Forms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Drops of liquid-additionally, it is offered in liquid form, which may be mixed with food or beverages.
- Oils or topical creams-its moisturizing and antioxidant characteristics make it a popular ingredient in skincare products like creams and oils.
- Foods fortified-it is frequently added to meals to boost their nutritious content, such as breads, morning cereals, and plant-based milk substitutes.4Forms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Multivitamin supplements-it may be found in multivitamin products, which combine vitamins and minerals. 4Forms | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage
Recommended dosage
- Babies (0–6 months): 4 mg per day.
- 7–12 month old infants: 5 mg per day.
- Children (ages 1-3): 6 mg per day.
- Kids (4–8 years old): 7 mg daily
- 9 to 13-year-olds: 11 mg daily
- Teenagers (14 to 18 years old): 15 mg daily
- For adults (19 years of age and older): 15 mg daily.1Dosage | Researched based study from Nih.gov
Overdose
Overdose signs
For adults, 1000 mg per day is the safe upper ingestion limit. Overdosing is possible if you take in more than this.5Overdose | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Overdose symptoms might include
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Bleeding
A significant vitamin E excess may cause a stroke and hemorrhage.
If you believe that you or someone you know has overdosed, get straight to the hospital.5Overdose | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Interactions
Medicine-related interactions
Blood-thinning drugs, such as warfarin
- These drugs’ effects may be enhanced by vitamin E, which also raises the risk of bleeding. 3Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins
- Vitamin E could lessen the impact, which might raise cholesterol levels.
Drugs for chemotherapy
- The supplements may lessen the efficiency of chemotherapy drugs, making them less efficient in killing cancer cells.3Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Immunosuppressive medications, such as cyclosporine
- May become less effective, which might increase the risk of organ rejection in transplant recipients.3Interactions | Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant characteristics are only a couple of the numerous confirmed potential health advantages of vitamin E.
- It comes in a number of forms. To prevent toxicity, it is important to ingest the recommended amounts in moderation.
- If you are on any medications or have any underlying medical issues, it is essential to see a healthcare expert before taking any supplements.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Institutes of Health
Vitamin E-Fact Sheet for Health Professionals | Overview | Biological role | Sources | Dosage
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin E Deficiency | Risk factors | Symptoms
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin E-drug interactions: molecular basis and clinical relevance | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Natural forms of vitamin E: metabolism, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and the role in disease prevention and therapy | Forms
-
National Library of Medicine
Vitamin E Toxicity | Overdose