Comprehensive Guide to Metformin: Usage, Side Effects and Interactions

- Metformin
- 29 Aug 2023
Introduction
What is Metformin?
Metformin is the drug that doctors prescribe for treating Type 2 diabetes (diabetes mellitus). Type 2 diabetes is when the body cannot utilize insulin properly, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Physicians might advise patients to take Metformin, exercise, and a balanced diet to control blood sugar levels. Metformin is a generic medication containing the same active component as the trade-name drug. Depending on the patient’s necessity, the doctor might prescribe Metformin with other drugs. The physician might also prescribe Metformin to treat other ailments apart from type 2 diabetes.
Here are some quick facts about Metformin:
- Metformin is available both in generic and trade-name medication.
- Some of the trade names for metformin medication are Fortamet, Glucophage, Riomet and Glumetza.
- In 1994, the FDA (The Food and Drug Administration, United States) approved Metformin. 1Facts| Researched based study from Science Direct
- In metformin drugs, Metformin is the chief ingredient. It belongs to a drug class called Biguanide.
- A drug class is a cluster of medication that works alike. 2Facts| Researched based study from National Institutes of Health

Mode of Action
How does Metformin work?
- The body maintains blood sugar in normal individuals by producing a chemical substance called insulin.
- Insulin is the component that helps the body convert glucose (sugar) into energy
- But in people with diabetes mellitus, the body cannot produce adequate insulin or become insulin resistant.
- Insulin resistance is the incapability of the body to respond to the body’s insulin and leads to elevated levels of sugar in the body
Metformin functions in the following ways to lower blood sugar levels in diabetes mellitus-
- By making the body more responsive to insulin and helping eliminate additional glucose.
- Reducing the blood sugar (glucose) produced by the liver.
- Reducing the body’s glucose absorption from foodstuffs. 3Mode of Action | Researched based study from Science Direct
Dosage
Dosage:
The doctor will prescribe the metformin dose depending on the patient’s situation. The physician will initially start with a minimal amount and then gradually increase and finally adjust the dose fit for the patient.
Here are some of the commonly recommended doses of Metformin in different age groups –
Type 2 diabetes dosage:
Adult dose (18 to 79 years) –
Immediate release tablet
- Initial dose- 500 milligrams twice daily or 850 mg once daily.
- Maximum dose- 2550 mg daily. (In divided doses thrice daily)
Extended-release tablet
- Initial dose-500mg daily
- Maximum dose- 2000mg daily(In divided doses)
Children dose (10 to 17 years) –
Immediate release tablet
- Initial dose-500mg daily. (Divided into two doses)
- Maximum dose- 2000mg daily. (In divided doses). 4Dosage| Researched based study from Science Direct
Uses
Uses of Metformin:
- Metformin is FDA approved drug for treating diabetes mellitus (Type 2 diabetes).
- In normal conditions, our body controls blood sugar by releasing insulin hormones. But in diseased individuals with diabetes mellitus, the body cannot produce sufficient insulin or cannot respond to insulin even if present. Consequently, the insulin hormone fails to work correctly, resulting in elevated sugar levels in the body.
- Metformin helps in the effective use of insulin in the body and thus helps control the blood sugar in the body.
- Metformin is also off-label used to treat prediabetes. Prediabetes is when the blood sugar is above average but not large enough to be considered diabetes. Off-label use is medication for treating other conditions that are not FDA-approved. 5Uses| Researched based study from Science Direct
Side Effects
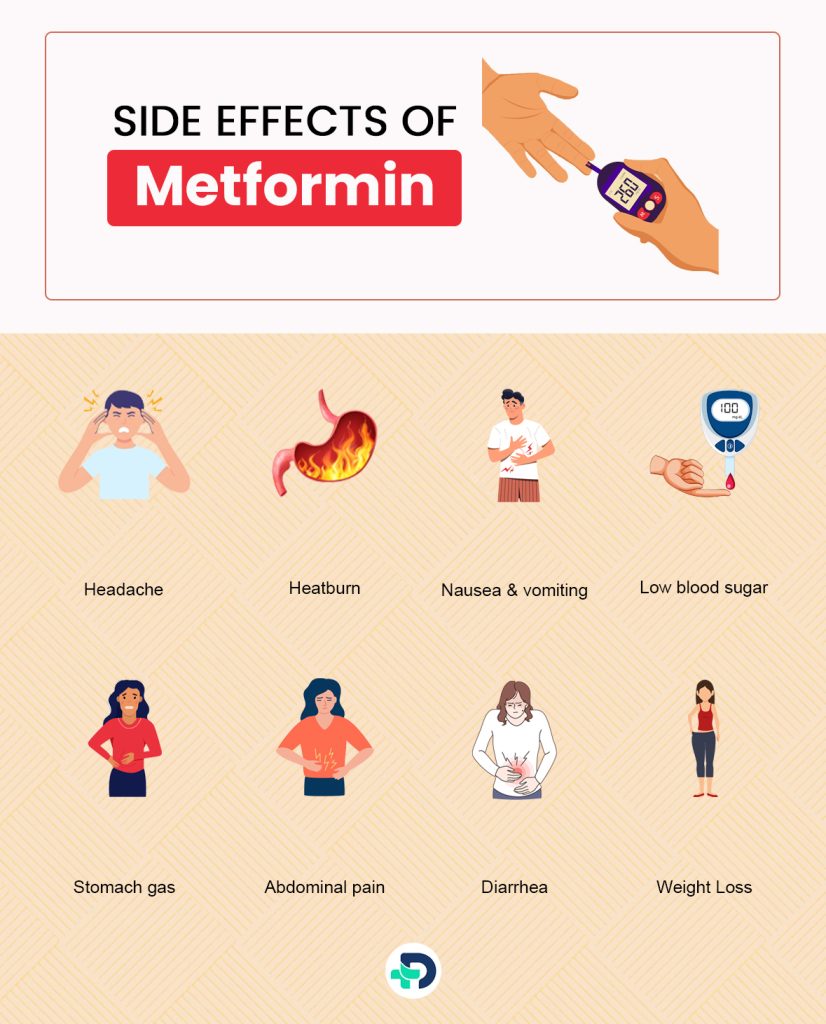
Side effects of Metformin:
Mild side effects –
- Headache
- Heartburn
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stomach gas. (Bloating)
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
Serious side effects –
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
Symptoms
Symptoms:
- Lightheadedness
- Sleepiness
- Headache
- Weakness
- Excessive sweating
- Irritability
- Hunger
- Confusion
- Body shaking
- Rapid heart rate
Lactic acidosis (a condition with excess lactic acid in the body)
Symptoms
- Muscle pain
- Extreme tiredness
- Drowsiness
- Weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Lightheadedness
- Belly pain
- Abnormal heart rate
- Shortness of breath
Low levels of vitamin B12
Symptoms
- Appetite loss
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Loss of sensation in feet and hands
Severe allergic reaction(In rare cases)
- Urticaria (Hives)
- Skin reddening
- Intense itching
- Swelling in eyelids, mouth, lips, and throat
- Trouble breathing 6Side effects | Researched based study from Science Direct
Formulations
Formulations:
Metformin comes as oral tablets and is available as an immediate or extended-release tablet.
Immediate release tablet
- Power (strength)-1000 milligrams (mg), 850 mg, 500mg
- Metformin immediate release drug start functioning instantly after the drug intake.
Extended-release tablet
- Power (strength)-1000mg, 750 mg, 500 mg. 7Formulations | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
- Metformin extended-release drug works after some time following the drug intake, while
Taking Metformin
- One can take Metformin tablets by mouth with a glass of plain water after food. Take the drug as per the physician’s advice, and one must not discontinue the drug prior doctor’s consultation as sudden stopping might cause an increase in the sugar level.
- Sometimes Metformin alone cannot control blood sugar levels. In that case, the doctor might advise other drugs such as Amaryl or Januvia along with Metformin to manage the condition.
Missed dose
- If one misses the metformin dose, take the dose immediately if there is enough time for the next dose. But if it is already time for the next dose, miss out on it and take the subsequent amount in time.
Overdose toxicity of Metformin
- One must not take Metformin in more amounts than the doctor advises.
- However, in case of unintentional overdose, one must instantly contact the Poison Control Center or emergency number based on the location, but if one experiences trouble breathing, call 911 or hurry to the nearest medical room.
Some symptoms of overdose are as follows-
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- High lactic acid in the body (lactic acidosis)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Extreme tiredness
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Diarrhea 8Overdose| Researched based study from Science Direct
Precautions
Precautions:
- There is insufficient information or research on whether Metformin is safe during pregnancy.
- Few studies indicate that Metformin passes in small amounts in breast milk, but there is limited information on the adverse effects of Metformin on the breastfed child.
- So pregnant women, nursing mothers, and those planning to start a family must consult the doctor before taking the metformin treatment plan. The doctor might suggest other medication that would suit better for the condition. 9Precautions| Researched based study from National Institutes of Health 10Precautions| Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Considerations
Consideration before taking Metformin:
Talk with the doctor about any health issues before starting the Metformin drug.
The conditions to consider before taking Metformin are as follows-
- Allergic to Metformin or any other food or drug
- Dehydration
- Heart issues
- Liver disease
- Kidney problem
- Diabetic ketoacidosis. (Fatal diabetic complication)
- Anemia. (Inadequate healthy red blood cells in the body)
- Alcoholism. (Addicted to alcohol)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome. (Enlarged ovaries with cyst due to hormonal imbalance)
- Serious infection
- Type 1 diabetes. (High sugar due to the destruction of insulin-secreting pancreatic cells)
- Forthcoming surgery
- Nursing mothers
- Pregnant women 11Considerations| Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Interactions
Interactions of Metformin:
Blood pressure medication
- Taking Metformin and blood pressure medication viz; Nifedipine together might interfere with the drug’s effectiveness and might increase the drug’s side effects.
Glaucoma (eye disease) medication
- Taking metformin and glaucoma medication viz; dorzolamide together might increase the possibility of elevated levels of lactic acid in the body.
Diabetic drugs
- Taking Metformin with other diabetic medication might cause the blood sugar level to go too low. So the doctor might reduce the doses of other diabetic medication while prescribing Metformin.
Anti-seizure medication
- Taking Metformin with anti-seizure medication viz; Topiramate together might increase the risk of lactic acid accumulation in the body.
Some other examples of drugs that Metformin might interact with are as follows-
- Insulin (Diabetic drug)
- Phenytoin (Anti-seizure medicine)
- Chlorpromazine (Anti-depressant drug)
- Cimetidine (Heartburn medication)
- Isoniazid (Tuberculosis drug)
- Levothyroxine (Thyroid drug)
- Prednisone (Steroid drug)
- Dolutegravir (Human Immunodeficiency Virus drug) 12Interactions | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
However, other drugs might also interact with Metformin not mentioned in the list above. So, one must always speak to the physician about any medication one uses before taking the metformin treatment to avoid unwanted interactions.
Storage
Storage:
- Keep the medications in a sealed container at 15 to 30 degrees centigrade temperatures.
- Store the drug away from direct sun rays and away from kids and youngsters
- Avoid storing the drug in moist areas such as the washroom. 1Storage | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Alternatives
Alternatives to Metformin:
There are also other medications to treat Type 2 diabetes. Some may prove better than others. However, one willing to have an alternative to Metformin must talk with the physician to get the best match.
Some examples of other medications for treating Type 2 diabetes are as follows-
- Tradjenta
- Actos
- Invokana
- Januvia
- Glucotrol
- Farxiga
- Amaryl 13Alternatives | Researched based study from National Institutes of Health
Takeaways
Key Takeaways:
- Metformin is an FDA-approved medication to treat Type 2 diabetes (diabetes mellitus).
- People with medical issues must consult a healthcare professional before taking metformin medication to avert complexities.
- Metformin is a long-term medication; people must not stop it themselves as it might increase blood sugar levels again.
- Metformin has prominent side effects, and overdose can lead to fatal conditions. So, one must take the precise doses as advised by the physician.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Facts | Storage
-
National Institutes of Health
Facts
-
Science Direct
Mode of action
-
Science Direct
Dosage
-
Science Direct
Uses
-
Science Direct
Side effects
-
National Institutes of Health
Formulations
-
Science Direct
Overdose
-
National Institutes of Health
Precautions
-
National Institutes of Health
Precautions
-
National Institutes of Health
Considerations
-
National Institutes of Health
Interactions
-
National Institutes of Health
Alternatives