Blackberry : What are the benefits?

- Blackberry
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Blackberry?
Blackberry is the delicious juicy fruit of a perennial plant belonging to the Rosaceae family. Blackberry is a versatile plant; fruit, leaf, and roots are used to make medicines. The fruit is densely packed with valuable nutrients and has multiple health benefits. Blackberries contain meager amounts of carbohydrates and fat.

Key facts of Blackberry
- Blackberries are considered a ‘superfood’ due to their nutrition
- The tiny bubbles of blackberries are known as drupelets and have a sweet and tangy flavor
- Blackberry is native to Europe, but it is cultivated in the United States throughout the year
- All hybrid varieties of blackberries provide significant amounts of vitamins and minerals, although some may be sweeter or tangier than the other
- Blackberries have high commercial value due to their use in various food products
- Mexico is the largest exporter of blackberries 1Overview| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Nutrition
Nutrition in Blackberry
A cup of raw strawberries contains the following:
- Calories-62
- Carbohydrate-14 gm (gram)
- Protein-2 gm
- Fat-below 1 gm
- Sugar-7 gm
- Fiber-8 gm
Blackberries are also a good source of the following
Vitamin K
- It is essential for blood clotting
- It helps in wound healing and bone metabolism
Vitamin A
- Vitamin A enhances the immune response and helps the body to fight infections
- It is responsible for producing the pigment in the retina of our eyes
Vitamin C
- It helps in the bone’s collagen formation
- It helps regenerate the skin
- It decreases the free radicals in the body
Vitamin E
- It protects the body from oxidative stress
- It helps maintain healthy eyes and skin
Manganese
- It is essential for healthy bone development
- It also supports the body in processing carbohydrates and cholesterol
Calcium
- It helps in blood clotting
- It helps in keeping our bones and teeth healthy
Glycemic Index in Blackberry
- Blackberries contain a low glycemic index(GI) of 25
- The glycemic index shows how each food one consumes affects the body’s blood glucose level
- A value equivalent to or lower than 55 is considered less likely to impact the body’s blood glucose level 2Nutrition| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Bioactives in Blackberry
Phenolics
- Phenolics are plant’s secondary metabolites involved in plant defense
- Secondary metabolites are natural compounds produced by plants
Flavonoids
- Flavonoids are organic compounds in plants responsible for color and flavor.
Anthocyanins
- Anthocyanins are water-soluble red, blue, or purple pigments present in plants.
Tannins
- Tannin is a natural water-soluble phenolic compound in the bark, fruits, and roots.
All the compounds mentioned above have antioxidant properties and protect the body against cell damage 2Nutrition| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Benefits
Benefits of Blackberry
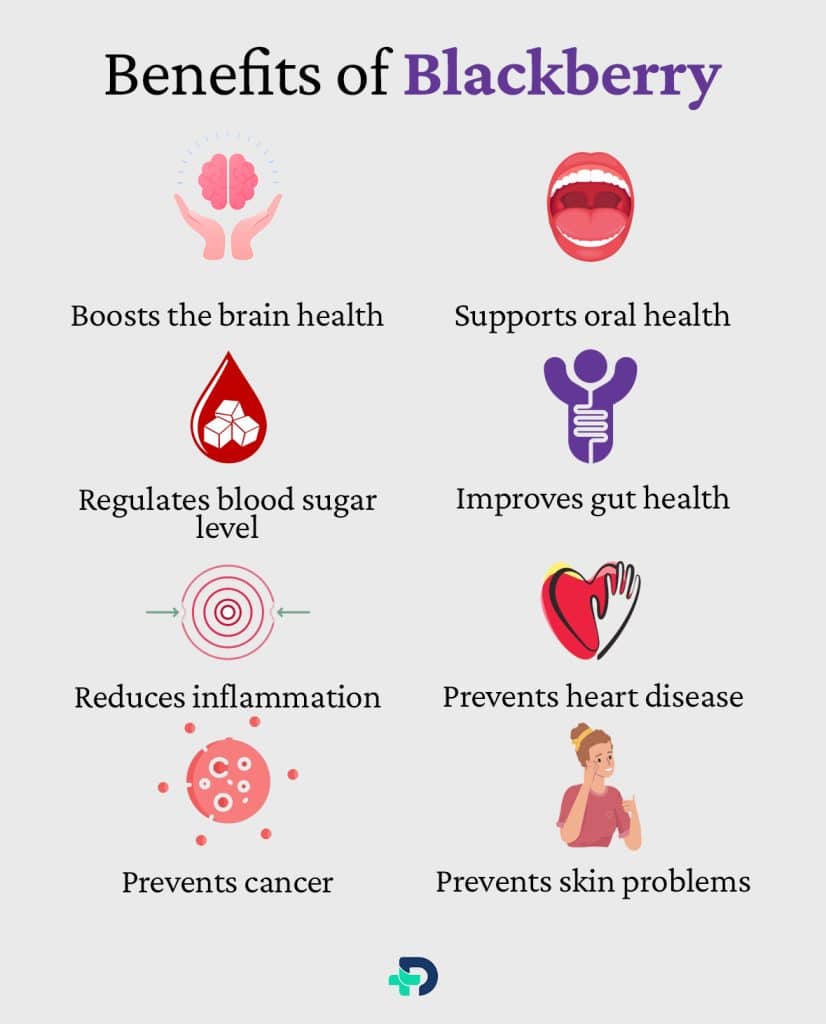
The health benefits of Blackberry are as follows:
- Boosts the brain health
- Supports oral health
- Regulates blood sugar level in diabetes
- Improves gut health
- Reduces inflammation
- Prevents heart disease
- Prevents cancer
- Prevents skin problems
Boosts the brain health
- Blackberry’s anthocyanin prevents age-related memory loss
- It reduces the brain inflammation
- It promotes the blood flow to the brain
- It improved the mental abilities and thinking capacity of mild dementia patients 3Benefits| Researched based study from Acs.org
However, more research is warranted to prove the effect of blackberries on brain health.
Supports oral health
- Blackberry extract prevents and controls the gum diseases
- It prevents the teeth cavities 4Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Regulates blood sugar level
- The soluble fibers in Blackberry break down in the intestine and enter the bloodstream. It controls the body’s blood sugar level and helps in diabetes management.
- It lowers the cholesterol in the body 5Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Improves gut health
- The insoluble fibers in blackberries pass through the digestive tract but do not get digested.
- It keeps the food and the waste moving
- It prevents constipation and stomach gas (flatulence) 6Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Reduces inflammation
- Blackberries reduce pain and swelling
- It helps the body to fight infection 7Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- However, further research is wanted to prove the effect of blackberries on inflammation.
Prevents heart disease
- Anthocyanin in blackberries lowers the blood cholesterol
- It decreases the risk of plaque (fat deposit) formation in the arteries 8Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
However, further research is warranted to prove the effect of Blackberry on heart diseases.
Prevents cancer
- Blackberry’s anthocyanin nullifies the free radicals that damage our body’s DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- It prevents abnormal cell growth 9Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov However, more research is wanted to prove the effect of Blackberry on cancer.
Prevents skin problems
- Blackberry’s phenolic compounds improve the body’s blood circulation
- It reduces pain and swelling caused due to blocked pores 10Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Dosage of Blackberry
- The proper dose of Blackberry depends on factors such as the person’s age and medical condition.
- To date, there is inadequate scientific evidence to determine the appropriate dose of Blackberry.
- One must always keep in mind that natural products can also be harmful. Following the product label or consulting a healthcare professional before consuming is always advisable 11Dosage| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Side effects
Side effects of Blackberry
Blackberry is well tolerated by most people when consumed in food levels. However, some people might encounter the following side effects :
- Itching
- Hives
- Swelling in the lips, mouth, and tongue
- Runny nose
- Watery eyes
- Vomiting
- Breathing difficulty
- Lightheadedness
- Rapid heartbeat 12Side effects| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Precautions
Precaution one should take while having Blackberry
- Nursing mothers, pregnant women, and young children should not consume the roots, stalk, and leaves of Blackberries due to the lack of information on the safety and efficiency of these groups.
- One should consume Blackberries in moderate amounts as excess consumption can lead to diarrhea in some people.
Who should avoid Blackberry
- People allergic to berries
- People allergic to aspirin drug
- People susceptible to kidney stones
- People with intestinal surgeries 13Precautions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Interaction
- There is no information on the drug’s interaction with blackberries to date. However, people with medical conditions must consult a healthcare professional before taking them as supplements.
Forms
Available forms of Blackberry
Blackberry is available in the following forms:
- Raw fruit
- Capsule form
- Tablet form
- Powder form
Usage
Usage of Blackberry
Picking & buying of Blackberry
Picking
- One should pick blackberries that are deep black, firm, and shiny.
- One should collect in several small containers instead of a single large one to avoid crushing the drupelets.
Buying
- Blackberries are available in grocery stores, farmer’s markets, or supermarkets between May to September.
Tips for incorporating Blackberry into the diet
- To make a salad, one can combine it with raspberries, blueberries, and strawberries.
- Add it as toppings for ice cream and yogurt
- Use it in pies as fillings
- Can use blackberries alongside peas and vinegar in chicken fries.
- Mix it with lemon and yogurt in frozen desserts
- One can add milk and other fruits to smoothies
- Have it with goat cheese and Roman lettuce to make a sweet salad
- One can add to green beans and top with oregano
- Sprinkle with Italian sausage and basil on pizza
- One can blend it with red wine grapes (Cabernet) to make a tangy sauce for salmon 14Usage| Researched based study from Researchgate.net
Storage of Blackberry
- One should keep blackberries in a closed container in a refrigerator or a cool place.
- One should consume it within three days as it has less self-life.
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Blackberry is a nutritious fruit with many health good nesses
- More research studies are needed to support some of the benefits of Blackberry.
- Blackberries are easy to add to one’s diet, but one should always consume them in a balanced manner with other fruits
- One interested in including blackberry supplement in one’s diet must consult a healthcare professional to know the exact dose and to prevent unwanted side effects
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Blackberry - an overview | Overview
-
Science Direct
Nutritional and bioactive value of Rubus berries | Nutrition
-
ACS Publications
Berry Fruit Enhances Beneficial Signaling in the Brain | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Antibacterial Effects of Blackberry Extract Target Periodontopathogens | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Dietary berries, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: an overview of human feeding trials | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Recent Studies on Berry Bioactives and Their Health-Promoting Roles | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Phytochemicals Determination, and Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Activities of Blackberry Fruits | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Anti-inflammatory effect of purified dietary anthocyanin in adults with hypercholesterolemia: a randomized controlled trial | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Epigenetic Effects of Blackberry Extract on Human Colorectal Cancer Cells | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
The Potential of Plant Phenolics in Prevention and Therapy of Skin Disorders | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
The blackberry fruit: a review on its composition and chemistry, metabolism and bioavailability, and health benefits | Benefits
-
Science Direct
Evaluation of Rubus grandifolius L. (wild blackberries) activities targeting management of type-2 diabetes and obesity using in vitro models | Side effects
-
National Library of Medicine
Rubus Fruticosus L.: Constituents, Biological Activities and Health Related Uses | Precautions
-
Research Gate
The Blackberry Fruit: A Review on Its Composition and Chemistry, Metabolism and Bioavailability, and Health Benefits | Usage