Exploring the Health benefits of Ginger

- Ginger
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
About Ginger
Ginger is a root used for centuries in various cultures for its flavor and potent medicinal properties. Its scientific name, Zingiber officinale, aptly reflects its origins in Southeast Asia, where it has been an integral part of traditional medicine and cuisine. It is a member of the same family as cardamom and turmeric, known as Zingiberaceae.1Overview| Researched based study from Foodprint.org Due to its distinct flavor and a variety of health advantages, ginger has experienced great global popularity.
This article will delve into nutrition, health benefits, available forms, culinary uses, side effects, precautions, and interactions associated with Ginger.

Nutrition
Nutrition in Ginger
The Food and Drug Administration of the United States (FDA) views ginger root as generally safe, and daily ingestion of up to 4 grams is considered safe.2Nutrition| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
One teaspoon (2 g) of raw ginger root may contain:
- Water – 1.58 g
- Calories – 1.6 Kcal
- Carbohydrates – 0.356 g
- Protein – 0.036 g
- Fiber – 0.04 g
- Fat – 0.015 g 3Nutrition| Researched based study from Usda.gov
Minerals:
- Potassium – 8.3 mg
- Calcium – 0.32 mg
- Iron – 0.012 mg
- Magnesium – 0.86 mg
- Phosphorus – 0.68 mg
- Sodium – 0.26 mg
- Zinc – 0.007 mg
- Copper – 0.005 mg
- Manganese – 0.005 mg
- Selenium – 0.014 µg
Vitamins:
- Choline – 0.576 mg
- Folate – 0.22 µg
- Vitamin C – 0.1 mg
- Niacin – 0.015 mg
- Pantothenic acid – 0.004 mg
- Vitamin B 6 – 0.003 mg
- Riboflavin – 0.001 mg
- Thiamin – 0.001 mg
Despite having few calories and few nutrients like vitamins and minerals, ginger is a fantastic source of antioxidants. It is typically ingested in small amounts, which might not be enough to absorb all its nutrients. However, Ginger has various active components like:
- Phenolic compounds – Gingerols, shogaols, and paradols.
- Terpene compounds – β-bisabolene, α-curcumene, and zingiberene, among others.4Nutrition| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Health benefits
Health benefits of Ginger
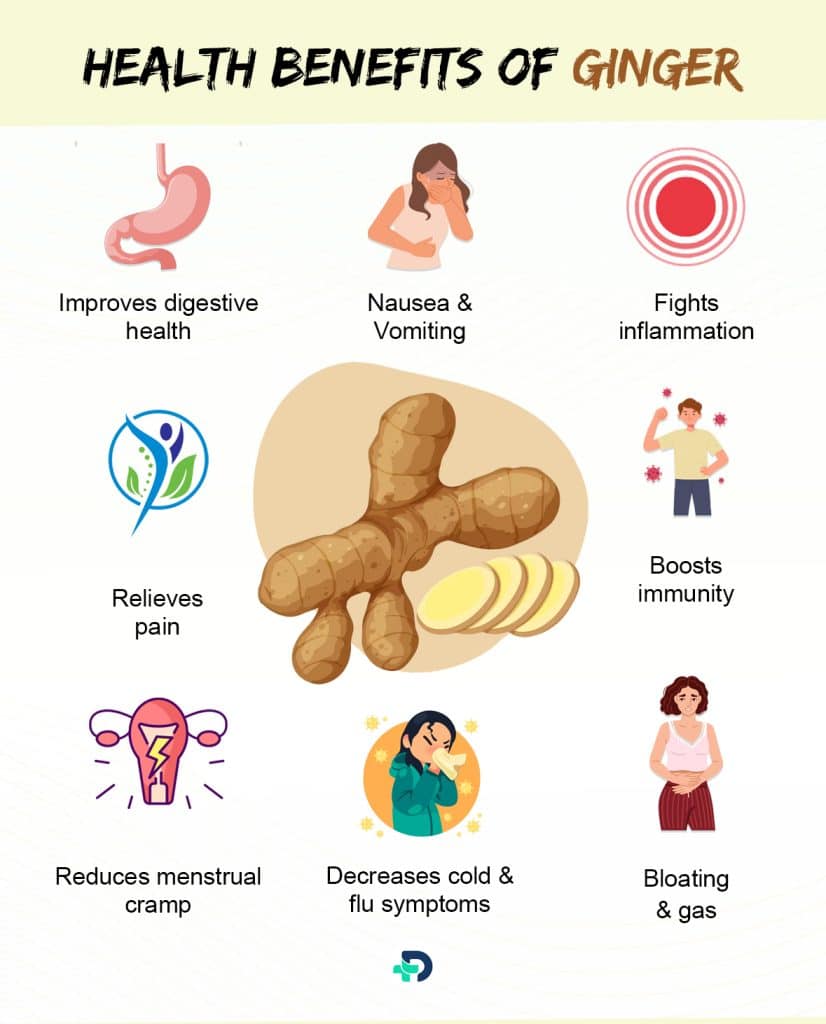
Adding Ginger to one’s diet is well known for its medicinal value and has the following health benefits:
- Improves digestive health
- Treats nausea and vomiting
- Fights inflammation
- Relives pain
- Boosts immunity
- Decreases cold and flu symptoms
- Reduces menstrual cramps
- Decreases bloating and gas
Improves digestive health:
- Digestive problems have long been treated naturally with ginger as it aids digestion by stimulating the production of digestive enzymes and increasing gastric motility.5Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Ginger can alleviate symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, and nausea.
Treats nausea and vomiting
- Studies have shown the effectiveness of Ginger in treating nausea and vomiting in pregnant women, cancer patients, or even in patients after surgery.6Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Fights inflammation
- Ginger contains several bioactive compounds, including gingerol, with potent anti-inflammatory properties.
- Regular ginger use may help lessen inflammation and its symptoms, particularly in inflammatory bowel illnesses.4Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Relieves pain
- Ginger can fight inflammation, reducing reduce pain and swelling in inflammatory diseases like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.7Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Additionally, Ginger has been found to inhibit the production of certain compounds that promote pain transmission.
Boosts immunity
- In addition to its immune-boosting anti-inflammatory and antibiotic qualities, Ginger has antiviral and antibacterial qualities that can keep you healthy.8Health benefits| Researched based study from Clevelandclinic.org
Decreases cold and flu symptoms
- Regular consumption of Ginger may also reduce the severity and duration of respiratory infections like colds and flu.9Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Its warming properties help stimulate circulation and provide comfort during illness.
Reduces menstrual cramp
- Many women experience menstrual cramps, and consuming Ginger in various forms, such as ginger tea or capsules, has been shown to reduce the severity of menstrual pain and discomfort10Health benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Bloating and gas
- Including ginger in diet decreases gas and bloating in the digestive tract which usually results from constipation and fermentation.11Health benefits| Researched based study from Hopkinsmedicine.org
Forms
Available forms of Ginger
Ginger is available in the following forms:
- Fresh Ginger
- Dried ginger root
One can also find ginger extracts in the form of:
- Oils
- Tinctures 12Forms| Researched based study from Mountsinai.org
- Extracts
- Capsules
Uses
Culinary uses
Due to its distinctive flavor, Ginger is frequently utilized in cuisine worldwide. Here are some typical culinary applications for Ginger:
- Cooking – Ginger gives food a distinctive flavor and scent. It can be used in stir-fries, soups, curries, stews, and marinades to improve the taste of food.
- Baking – Ginger is a popular baking ingredient used to make muffins, ginger cakes, gingerbread, and cookies. It gives these delicacies a warm, spicy flavor.
- Beverages – ginger is used to make ginger tea that tastes great when served cold or hot. It is also used to flavor homemade syrups, smoothies, juices, and drinks.
- Sauces and dressings – it is used in salads and sauces. To make a delectable marinade or dipping sauce, mince or grate it, then mix it with vinegar, soy sauce, honey, or oil.
- Herbal infusions – To create a calming and fragrant herbal infusion, it can be steeped in hot water. It is frequently used to treat nausea or settle an upset stomach because of its well-known digestive benefits.
- Candied Ginger – By heating Ginger in sugar syrup and coating it with sugar, Ginger can be candied. Cakes, biscuits, and ice cream frequently have candied Ginger added as a garnish or ingredient.
- Asian cuisine – Ginger is common in many Asian cuisines, including Chinese, Japanese, Thai, and Indian. It is incorporated into several curries and cuisines like ginger chicken and Ginger fried rice.
- Condiments and spreads – Spreads and condiments with flavor can be created using it. For instance, Ginger can be combined with garlic, chili peppers, and other ingredients to develop ginger chutney or ginger garlic paste.
Side effects
Side effects of Ginger
While Ginger is generally safe for most people, in higher amounts, it could cause the following problems:
- Stomach discomfort
- Allergic symptoms
- Prolonged bleeding
- Irregular heartbeat
Symptoms of Mild stomach discomfort may include:
- Heartburn 13Side effects| Researched based study from Nccih.nih.gov
- Diarrhea
Symptoms of allergic reactions may include:
- Skin rashes and itching
- Breathing difficulty
- Swelling of face, tongue, lips, or throat
Precautions
Precautions
For the majority of people, ginger is generally safe. However, when consuming ginger, the following considerations should be made:
- Allergy to Ginger – though rare, eating Ginger or its extracts may cause allergic reactions in some individuals. People should discontinue its use and seek medical help in case of allergy.
- Stomach discomfort – to avoid any mild stomach discomfort or allergic reactions, it is recommended for people to start with small doses.
- Bleeding disorders – people with bleeding disorders like hemophilia or a low platelet count should consult with their doctors before consuming ginger or ginger supplements as it can prolong the bleeding in them.2Precautions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Gallstones – consuming ginger may contribute to gall stone formation and people with a history of gallstones or are at risk of developing them should consult their doctors before consuming Ginger as a supplement or in large amounts.2Precautions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Pregnant Women – Although Ginger is commonly safe to be used in pregnant women in small to moderate amounts to alleviate morning sickness and nausea, they need to consult with their healthcare provider before using ginger supplements or consuming Ginger in large quantities.
Interactions
Interactions of Ginger
- Blood-thinning medications – Blood thinners like warfarin and aspirin can interact with ginger, which also has blood-thinning effects. People who are taking any medication to prevent blood clots should Consult with their doctor before frequently taking ginger.14Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Diabetes medications – When used as a supplement with medications to control blood sugar levels, ginger can drop blood sugar and increase the risk of experiencing hypoglycemia or low blood sugar.15Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- Medications for blood pressure management – Ginger may lower blood pressure when taken with blood pressure-lowering drugs, increasing the possibility of low blood pressure.16Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Takeaway
Ginger is a versatile root with many culinary uses and potent health benefits. Incorporating Ginger into your diet in moderation can be a flavorful and healthy addition to support your overall well-being. This article may not include all of the drugs known to interact with ginger, so if taken as a supplement in large doses, people should discuss all of their current health issues and medications they are taking, which include prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, herbal drugs, and supplements.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Food Print
Real Food Encyclopedia - Ginger | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Ginger Root | Nutrition | Precautions
-
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
Ginger root, raw | Nutrition
-
National Library of Medicine
Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) | Nutrition
-
National Library of Medicine
Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials | Health Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Ginger in gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials | Health Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of a ginger extract on knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis | Health Benefits
-
Cleveland Clinic
6 Ginger Shot Benefits | Health Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of Ginger and Its Constituents on Airway Smooth Muscle Relaxation and Calcium Regulation | Health Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Effect of Zingiber officinale R. rhizomes (ginger) on pain relief in primary dysmenorrhea: a placebo randomized trial | Health Benefits
-
John Hopkins Medicine
Ginger Benefits | Health Benefits
-
Mount Sinai
Ginger | Forms
-
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Ginger | Side effects
-
National Library of Medicine
Effects of Oral Ginger Supplementation on the INR | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Dietary ginger as a traditional therapy for blood sugar control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Ginger lowers blood pressure through blockade of voltage-dependent calcium channels | Interactions