Epidermoid cysts: Things you need to know

- Epidermoid Cyst
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
What is an Epidermoid cyst?
An epidermoid cyst is a harmless bump beneath the skin. These cysts are usually firm or hard to the touch as they hold a substance called keratin. Keratin is the protein found in hair and the skin’s outer layer. It commonly appears on the face and shoulders; however, it can emerge in regions like the groin, fingers, or inside the mouth. The growth of the cysts is very slow and these can persist for a prolonged period without causing significant issues. An epidermoid cyst’s contents are mushy with an awful odor. These are the frequently encountered kind of cysts that occur in the skin. Epidermoid cysts frequently go away spontaneously without requiring treatment. However, if the cyst drains by itself, there is a possibility of its recurrence.1Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov

Symptoms
Symptoms of Epidermoid cyst
- The most common sign is a tiny, non-painful bump below the skin’s surface.
- The bump is most commonly detected on the human face, the throat, or the body.
- It frequently has a small opening in the middle of it.
- It normally develops gradually and painlessly.
Additional signs that may occur if the bump develops an infection or inflammation include:
- Inflammation of the skin
- Skin that is painful or uncomfortable
- Skin that is warmer in the afflicted area
- The substance that flows from the lump is grayish-white and unpleasantly odorous.2Symptoms| Researched based study from Medlineplus.gov
Causes
Causes of Epidermoid cyst
- The majority of epidermoid cysts are brought on by skin (epidermal) cells that travel beneath or are encased by the skin rather than discharging. These cells keep dividing then create an enclosure surrounding themselves (a lump) and release keratin, the natural fluid found in the skin. This is a dense, yellow fluid that the cyst may discharge. This condition can be either congenital or occur due to an injury to the skin.
- Epidermoid cysts are commonly found around hair follicles, which are small sacs containing hair strands. These follicles have openings that allow the release of natural oils for hair moisturizing. If a passageway becomes obstructed or if the follicle area becomes irritated, a cyst might develop.
- This frequently happens when the hair follicles experience harm due to a cut or injury.3Causes| Researched based study from Ucsd.edu
Prevalence
Prevalence
- Epidermoid cysts are the most frequent cysts that develop on the skin and usually appear between the ages of 30 and 40.
- It is uncommon to find these cysts before reaching adolescence.
- They are more commonly found in males compared to females.
- In newborns, small epidermal cysts known as milia are commonly observed.
- Around 1% of epidermoid cysts have been reported to undergo a malignant transformation.1Prevalence| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Epidermoid cyst
- The assessment of epidermoid cysts primarily relies on gathering information about the patient’s medical history and conducting a physical examination.
- Laboratory tests are generally not required for evaluating epidermoid cysts.
- Radiographic imaging techniques are not commonly used as part of the diagnostic process for these cysts.
- These cysts are typically diagnosed based on their characteristic appearance and clinical presentation, making radiographic studies unnecessary in most cases.1Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment
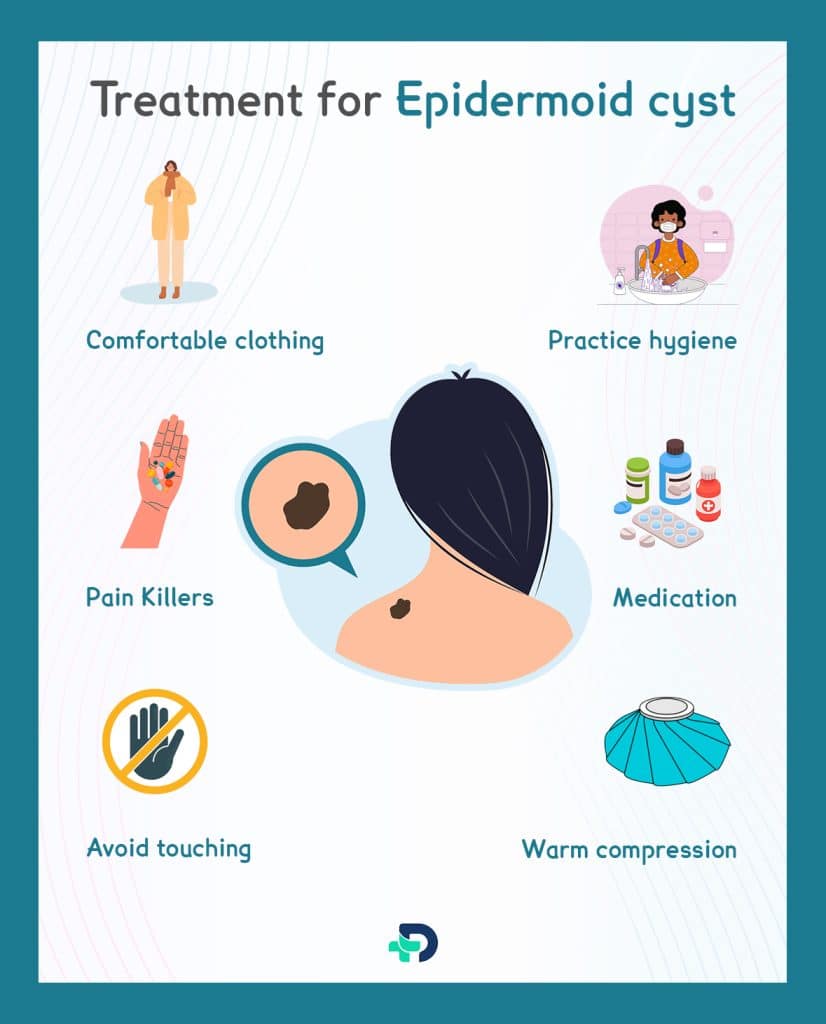
Treatment of Epidermoid cyst
Epidermoid cyst treatment is not immediate unless chosen by the patient voluntarily prior to a rise in symptom severity. The treatment procedure may include following:
Surgical intervention
- The ultimate treatment is surgery to remove the bump. This comprehensive approach is vital to prevent the epidermal inclusion cyst from returning. To remove the cyst, a small cut is made on the skin directly above it using a small surgical blade. The contents of the cyst are then squeezed out by applying gentle pressure on both sides of the cyst.
- Another surgical option involves using a small circular tool to create a hole in the skin. The intact cyst is then extracted by carefully applying pressure to guide it out through the incision made during the procedure.
- If there is a swollen lesion filled with fluid, it may require making a cut to release the fluid and remove any pockets inside.
Medication
- When an epidermoid cyst becomes inflamed, it can be treated by injecting steroids directly into it. This injection helps reduce the inflammation, which means there may be no need to drain the cyst.
- If a cyst starts to swell, become painful, grow larger, or get infected, the recommended treatment may involve taking antibiotics to fight the infection.
- The antibiotics used will be determined by the kind of bacteria contributing to the condition and its resistance to specific medications.4Treatment| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Home Remedies
Avoid touching
- It is important to resist the temptation of squeezing, popping, or cutting open a cyst by patients themselves. Engaging in such actions can lead to a worsening infection and the potential for scarring.
Warm compression
- In order to reduce discomfort in the affected area, one should submerge it in warm water or apply a warm pack using a thin, sterile cloth soaked in warm water. This should be done for a duration of 20 minutes each time.
Pain Killers
- In order to control pain, individuals can contemplate utilizing non-prescription pain relievers unless an alternative medication has been prescribed for this intent. Nevertheless, if they possess a past medical record of persistent Kidney or Liver disease, or if they have previously encountered a stomach ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding, it is vital to consult a healthcare provider prior to consuming these medications.
Practice hygiene
- To keep the area around the cyst clean, take regular showers every day. This helps prevent any buildup of dirt or bacteria that can worsen the condition.
Comfortable clothing
- Avoid wearing tight-fitting clothing in the area where the cyst is located. Loose-fitting clothes can help reduce friction and irritation, promoting better healing and comfort.4Treatment| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Complications
Complications
- Epidermoid cysts can cause discomfort or pain when they exert pressure on the nearby skin. These can also be aesthetically displeasing.
- Cysts that are inflamed have the possibility to become infectious. This infection has the ability to spread to the surrounding tissues or, in severe cases, enter the bloodstream.
- Even after undergoing surgery, if a cyst is not completely removed, there is a possibility of its reoccurrence.3Complications| Researched based study from Ucsd.edu
Prevention
Prevention
- There are no known methods to prevent the development of epidermoid cysts.
- However, one can reduce the risk of infection and scarring by avoiding actions such as forcefully pressing, bursting, inserting objects into, or self-surgically opening the cyst.
- These actions can often lead to infection and scarring.
- If the cyst becomes highly inflamed or infected, a healthcare professional should be consulted for proper care.5Prevention| Researched based study from Cedars-sinai.org
Prognosis
Prognosis of Epidermoid cyst
- Epidermal inclusion cysts are generally considered harmless cysts. However, although rare, they can undergo cancerous transformation.
- Among the cases where malignancy develops, approximately 70% of them are squamous cell carcinoma.
- It is important to note that while the occurrence of malignancy is uncommon, regular monitoring and proper medical evaluation of epidermal inclusion cysts are essential to detect any potential malignancy early and ensure appropriate management.1Prognosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Epidermoid cysts are generally not harmful. Epidermoid cysts are generally benign and develop slowly as small lumps beneath the skin. Some cysts may have a larger pore in the middle. They are the most prevalent form of cyst found in the skin. Occasionally, they may become inflamed, turn red, cause discomfort, or suddenly rupture.
- Medical professionals will assess whether surgical intervention is required and if there are any indications of the cysts turning malignant.
- Early detection and the right kind of care are essential in effectively managing epidermoid cysts. This approach is vital in achieving positive outcomes and enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
National Library of Medicine
Epidermoid Cyst | Overview | Prevalence | Diagnosis | Prognosis
-
Medline Plus
Epidermoid cyst | Symptoms
-
UC San Diego Health
Epidermoid Cysts of the Skin | Complications
-
National Library of Medicine
Epidermal Inclusion Cyst | Treatment
-
Cedars Sinai
Epidermoid Cysts of the Skin | Prevention