Ear pain : What you need to know?

- Ear Pain
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Ear pain?
Ear pain (earache) is the dull, sharp, or burning sensation in one or both ears. It can occur for a short duration or continuously. Ear pain can arise all of a sudden or gradually. The ear pain can originate from the inside or the outside of our ear and treatment of the ear pain depends on the cause of the pain.1Overview| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Infants, toddlers (2-3 years), and young children below 14 years are more prone to ear pain than people of other age groups 3Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
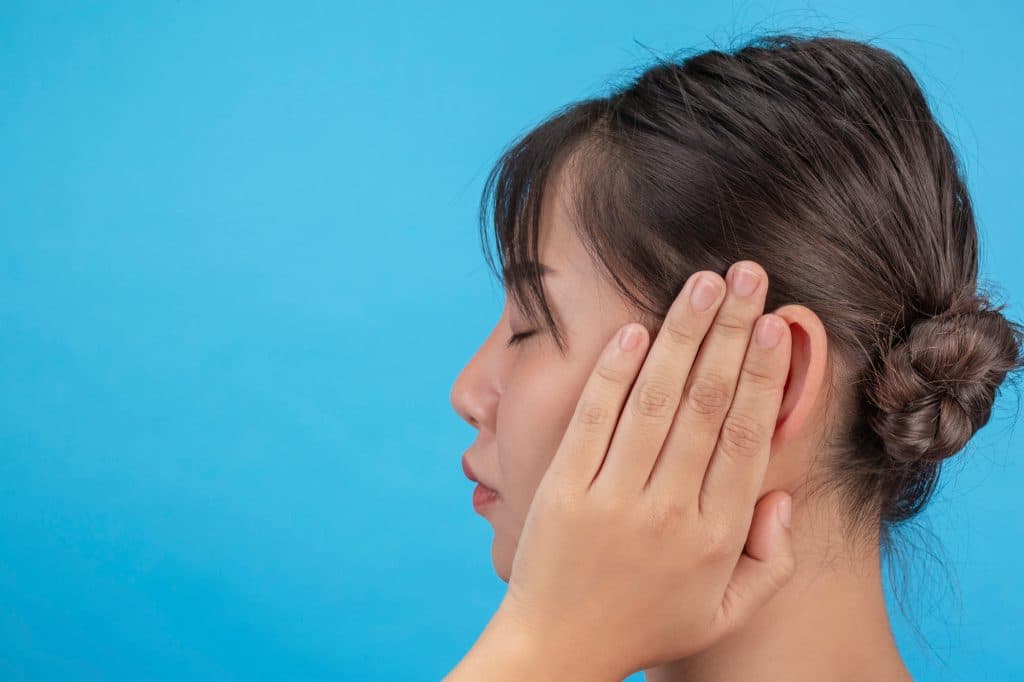

Facts of ear pain
- Ear pain is medically known as otalgia.
- Ear pain is more widespread in children, but it can happen in people of all age groups.
- Ear pain due to ear infections is common in children
- Ear ache is not life-threatening
- Rarely ear pain can be a sign of severe illness 2Overview| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Symptoms
Symptoms that can accompany Ear pain
Symptoms from injury or ear infection
- Decreased hearing
- Fluid from the ear
- Ear feels full
- Difficulty in chewing
- Jaw pain
- Clicking of the ears
- Fever
- Headache
- Hearing loss
Symptoms in children
- Difficulty responding to sound
- Difficulty in opening the mouth
- Rapid involuntary eye-movement
- Crying or getting irritated more than usual
- Difficulty sleeping
- Pulling off the ear
- Ear fullness
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of balance
- Fever
- Headache 3Symptoms| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Causes
Causes of Ear pain
The cause of ear pain might be due to the following reasons:
- An ear infection of the outer, middle, and inner ear
- A blocked eustachian tube that creates pressure behind the eardrum
- Pain in other places, such as teeth, jaw, and throat
- Any physical injury that is done by scratching the inner part of the ears with a cotton swab, finger, or other objects4Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Other common causes of ear pain are as follows:
- Pressure change while flying in an airplane
- Entering of foreign body in the ear
- Build up of earwax
- Water or shampoo entering the ear
- Harsh cleaning of the ear with a cotton swab
- Acute ear infection
- Persistent ear infection
- Sinus infection
- Sore throat
- Tooth infection 4Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Unusual causes of ear pain
- Ruptured eardrum
- Arthritis(joint inflammation) affecting the jaw
- Eczema(skin disease) in the ear canal
- Chronic facial nerve pain (trigeminal neuralgia)
- Temporomandibular joint syndrome (a condition affecting jaw movement) 4Causes| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Ear pain
Physical examination
- The doctor (ENT specialist) will first carry out a routine examination of the outer ear, the middle ear (ear canal), and the tympanic membrane (eardrum) with an instrument (otoscope).
- Following, he will examine the nose, mouth, and sinuses and might also look at the back molars to see signs of recurrent teeth clenching.
Then the doctor might perform the following tests:
Nasal endoscopy
- Nasal endoscopy is a procedure to see the inside of the nose and the sinuses. It is done with an endoscope.5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Vestibular function test
- The vestibular function test is a series of tests to identify whether the ears are functioning correctly.
- It evaluates the balance system in the inner ear
CT (Computed tomography) scan
- A CT scan might be recommended if the doctor suspects an infection of the large bone (mastoid bone) behind the ear.5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
- It uses X-rays and computers to get a detailed picture of the inside of our body.
MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging)
- MRI might be recommended if the doctor suspects a tumor for the ear pain
- It uses a magnetic field and computer to get images of the internal structures of our body.
Blood tests
The doctor might recommend blood tests if he suspects a severe infection.
ESR (Erythrocyte sedimentation rate)
- It is a test to check the inflammation in the body
White blood cell count
- It is a test to check the infection level in the body. A high WBC count indicates infection in the body
C-reactive protein
- It is a test to check the inflammation in the body. Increased level of C-reactive protein indicates inflammation in the body 5Diagnosis| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Treatment
Treatment of Ear pain
Treatment of ear infection includes both medicines and surgery , selection of treatment depend on root cause and severity of pain.it may include following:
Over-the-counter medication
NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Ibuprofen
- Diclofenac
- Tylenol (pain reliever)
Oral antibiotics (treats bacterial infection)
- Azithromycin
- Cephalexin
Eardrops
Antibiotic eardrops-It contains the following active ingredients-
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ofloxacin
- Tobramycin
- Gentamicin
Antifungal eardrops-It contains the following active ingredients-
- Miconazole
- Clotrimazole
For pain from wax build up
Wax-softening eardrops-It contains the following ingredients-
- Carbamide peroxide
- Glycerin
- Sodium bicarbonate
Surgery
- Doctors might indicate a surgical operation for ear pains due to tumors, such as severe mastoiditis. Mastoiditis is the infection of the mastoid bone behind the ear.
- It might also be indicated to treat persistent middle ear infections and eustachian tube malfunctioning 6Treatment| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Home remedies
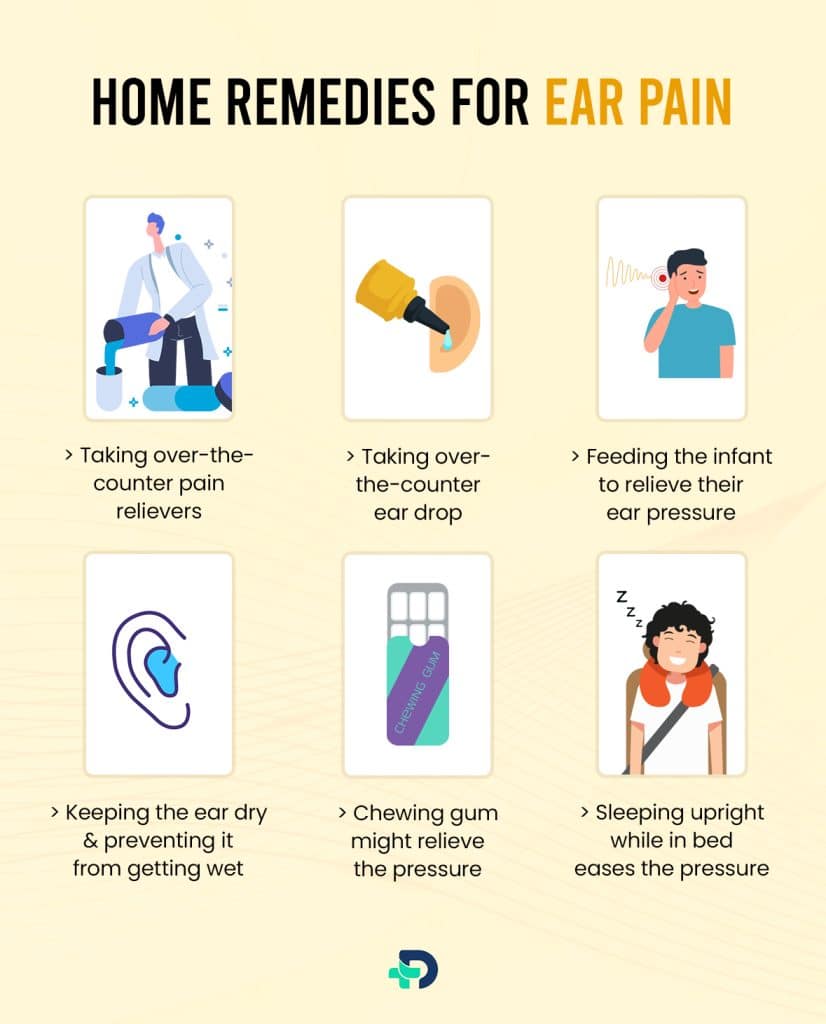
Home Remedies for Ear pain
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers
- Taking over-the-counter ear drop
- Applying a cold compress and warm compress in the ear alternatively to relieve the pain
- Keeping the ear dry and preventing it from getting wet
- Sitting upright to relieve ear pressure that is causing pain
- Sleeping upright while in bed eases the pressure
- Feeding the infant to relieve their ear pressure
- Distracting the child by playing a favorite movie or making them focus on other things that they enjoy
- Doing neck exercises several times a day might relieve ear pain caused due to tense muscles around the ear canal.
- Chewing gum might relieve the pressure in case of ear pain caused due to traveling to high altitudes.
- Applying ginger juice around the outer ear canal might relieve ear pain. However, one must not put the juice into the ear canal.
- Eating raw garlic might reduce ear pain. However, people taking antibiotics must consult a physician before taking raw garlic as it might interact with the drug 7Home remedies| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Prevention
Prevention of Ear pain
- Protect the ear from small objects or insects
- One must adequately dry the ears after bathing or swimming
- Keep away from dust and pollen
- Avoid the persistent use of cotton swabs or earwax-softening agents.
- Wear earplugs for swimming
- Avoid putting the finger or towel into the ear after swimming
- One must clean the ears softly and with care
- One must avoid digging into the ear canal
- Keep away from the smoking environment
- One with frequent ear wax buildup must visit a doctor every six to twelve months to clear it up 8Prevention| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com
Consultation
When to seek emergency medical attention?
One must immediately seek medical attention under the following conditions:
- A child with a persistent fever of 101 degrees Fahrenheit or above .
- Severe pain that stops suddenly (can be due to eardrum rupture)
- Severe ear pain that does not improve within 24 to 48 hours
- Ear pain with fever and sore throat
- Pain when touching or pulling the ear lobe
- Buzzing sound in the ears
- Hearing loss
- Swelling or rash in the ear canal
- Extreme tiredness
- Severe headache
- Drooping (hanging) of the facial muscles
- Swelling around the ear
- Pus or blood drainage from the ears 9Consultation| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Ear pain is an uncomfortable ear sensation due to infection or other reasons.
- Some ear pain resolves on its own after improving the health condition
- Ear pain that lasts for more than two days with fever, chill must contact a health professional to get the correct treatment and prevent unwanted complications
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Earache | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Otalgia | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Acute earache | Symptoms | Overview
-
National Library of Medicine
Ear Pain: Diagnosing Common and Uncommon Causes | Causes
-
National Library of Medicine
Diagnosis of ear pain | Diagnosis
-
National Library of Medicine
Earache | Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Feeding young infants with their head in upright position reduces respiratory and ear morbidity | Home remedies
-
Science Direct
Ear pain | Prevention
-
National Library of Medicine
Ear infections | Consultation