A Guide to Understanding Skin Lumps

- Skin Lumps
- 01 Sep 2023
Overview
Overview
Localized swellings or elevated patches of the skin that may vary in size, shape, and texture are referred to as skin lumps. They are also known as skin nodules or skin growths. They can be cancerous, non-cancerous, or inflammatory. 1Overview | Researched based study from MedlinePlus

Causes
What causes Skin Lumps?
Here are a few typical causes for skin lumps:
- Cysts: These are Fluid-filled sacs that form within the skin due to damaged or infected hair follicles. 2Causes | Researched based study from Better Health Channel
- Fibromas: Non-cancerous growths that vary in size and consist of connective or fibrous tissue are fibromas. They are commonly seen on the limbs and trunks.
- Warts: These are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and are elevated growths that develop on a variety of body regions, including the foot, hand and genitalia.
- Skin tags: Tiny, floppy growths that often appear when skin scrapes against itself or clothes.
- Boils: Painful, pus-filled lumps that originate from diseased sweat glands or hair follicles.
- Abscesses: Abscesses are localized infections that produce a pocket of pus beneath the skin, much like boils.
- Sebaceous cysts: Form due to clogged glands. They develop on the face, neck, or trunk and may be filled with a cheesy sticky substance.
- Hematomas: Blood collections beneath the skin as a result of trauma or injury is known as Hematoma.
- Granulomas: Inflammatory nodules that develop as a reaction to a variety of irritants, including foreign objects or certain illnesses.
- Lymph nodes: Lumps beneath the skin that might be felt to be enlarged. They can be due to any underlying illnesses or infections.
- Mole: While the majority of moles are harmless, changes in their color, size, or form may need additional examination.
- Skin cancer: Skin lumps may be a symptom of malignant growths including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- Allergy Responses: In certain instances, allergic responses might include skin swelling, lumps, or hives.
- Insect bites: A few types of insect stings or bites may result in small-scale swelling and the development of lumps or bumps.
- Keloids: Develop when scar tissue spreads beyond the site of the injury. Keloids are not dangerous and can be removed by the doctor.
- Lipomas: Soft tissue cancers called lipomas often progress slowly and are not generally harmful. The trunk and shoulders are often affected, and they have a mushy, rubbery texture.
- Cherry angiomas: Cherry angiomas are most likely the little, smooth red pimples that occur on your skin, particularly on your chest.
- Dermatofibromas: These firm lumps are commonly seen on the arms or legs and are circular, reddish-brown or purple in color. They are usually harmless.
- Folliculitis: As its name indicates, is an infection of the hair follicles that most often affects the scalp, face, and legs.
- Hives: Hives are skin lumps that emerge unexpectedly and are red, elevated, itchy, and painful.
Symptoms
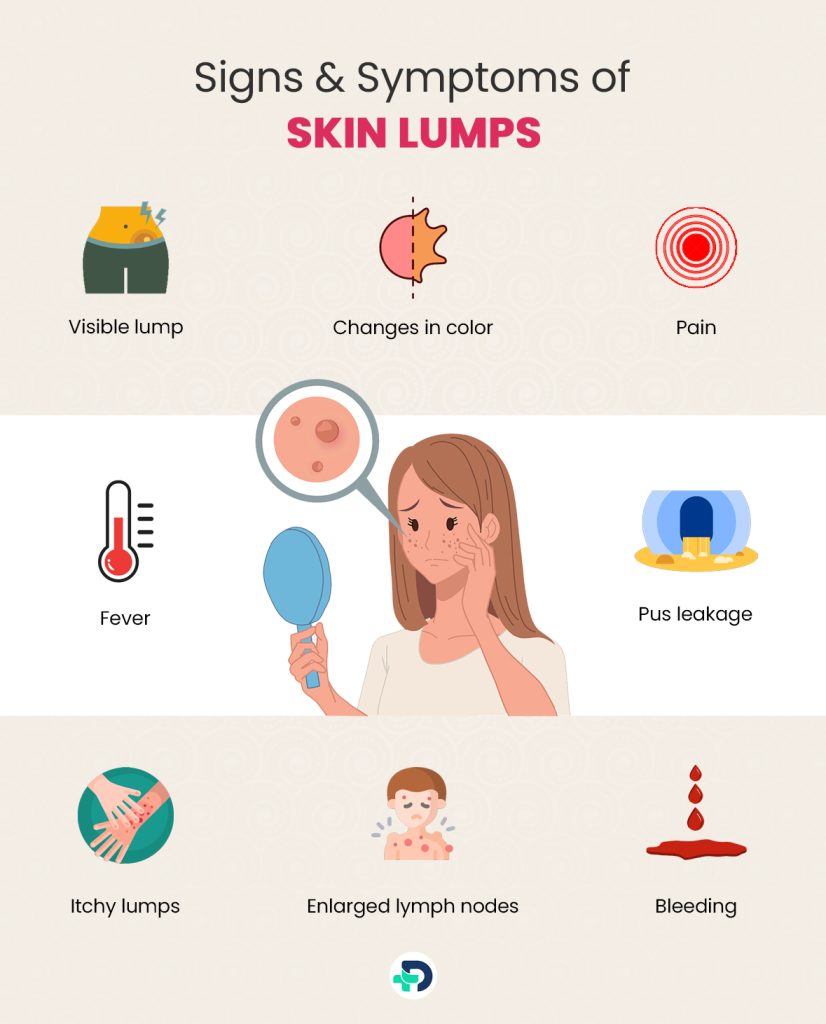
Signs and Symptoms of Skin Lumps
The following typical warning signs and symptoms may be related to skin lumps:
- Visible lump
- Changes in color
- Pain 3Symptoms | Researched based study from Mount Sinai
- Fever, Redness and Warmth
- Pus leakage
- Itchy lumps
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Bleeding or Ulceration
If the lump changes in size, shape, color, or texture over time, it may be a sign of a more serious condition that needs to be treated by a doctor.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Skin Lumps
Physical Examination:
- The lumpy mass and its surroundings will be thoroughly physically examined by the doctor.
- They will evaluate its dimensions, form, color, texture, and any other features.
Dermoscopy:
- A method that utilizes a hand-held instrument with magnification and illumination to more closely inspect the skin’s surface.
Imaging investigations:
- To see the lump and its connection to neighboring structures, imaging investigations like ultrasound, X-ray, or MRI may be advised in certain circumstances.
Biopsy:
- A biopsy indicates the removal of a tiny sample of tissue from the lump and transporting it to a lab for testing.
Fine needle aspiration:
- A tiny needle is inserted into the lump to remove a small sample of tissue or fluid.
Patch testing:
- To determine if allergies might be the source of the lump or other skin abnormalities, a number of chemicals are applied to the skin.
Molecular Testing:
- When skin cancer is suspected, molecular testing may assist identify the kind and possible aggressiveness of the disease by examining the genetic composition of the lump’s cells.
PET-CT scan:
- The metabolic activity of a lump may be evaluated using a PET-CT scan.
Laboratory Tests:
- The doctor may prescribe blood tests, cultures, or another laboratory testing to learn more about the underlying ailment depending on the lump’s likely source.
How do you check for a lump?
To find new, changing, or strange lumps, you must carefully and systematically examine your body as follows:
- Find a bright room. Examine hard-to-see regions using a full-length and portable mirror.
- Undress to see your flesh. Check your scalp, back and between your toes.
- Examine your sides, front and back in a body length mirror. Use a portable mirror to see your back and feet.
- Start from your head and proceed down. Cover everything by following a pattern. Palpate the skin with your fingertips as you go.
- Observe color, texture, and size variations. Find new lumps, bumps, or growths.
- Check moles for color, size, form, and borders. Skin cancer may cause changes in these properties.
- Touch your neck, armpit, and groin lymph nodes. Swollen and painful Lymph nodes suggest an infection.
- Check your palms, soles and fingers and toes.
Self-examination may help identify concerns, but it’s not a replacement for medical review. New, changing, or worrying skin lumps should be checked by a doctor.
Treatment
Treatment of Skin Lumps
The different ways to treat different types of skin lumps:
Medication:
- Antibiotics
- Corticosteroids
- Topical medications
Laser treatment:
- Used to destroy specific cells or tissues by aiming at them.
- Treats different kinds of skin lumps, such as some kinds of warts, birthmarks, and small skin tumors.
Surgical Removal:
- During surgical removal, a knife or other surgical tools are used to cut the lump out of the skin. 4Treatment | Researched based study from Queensland Health
- It is often used for cysts, lipomas, and some kinds of skin cancer, among other skin growths.
Excision and Biopsy:
- The whole lump and a small amount of healthy tissue around it are cut out.
- The tissue that was cut out is then sent to a lab for a histopathological test to find out composition of the lump.
Chemotherapy and radiation treatment:
- Most of the time, these methods are used to get rid of skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- The type, stage, and site of the cancer will determine whether chemotherapy or radiation is better.
Hyfrecation:
- A hyfrecator is a very accurate tool that sends low-energy electrical bursts through tissue to stop it from bleeding.
Natural remedies to manage skin lumps
For some types of skin lumps, natural remedies might help relieve pain or speed up the healing process. However, it’s important to remember that these remedies are not a replacement for a medical exam and treatment. 5Treatment | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Here are some harmless ways to treat some types of skin lumps:
Warm Compresses:
- For some types of abscesses or boils, putting a warm, damp cloth on the lump can help ease the pain and speed up the draining.
Apple Cider Vinegar:
- Because it kills germs, apple cider vinegar is used frequently.
- A wart might get better over time if you put a weak solution on it.
Aloe Vera:
- Aloe vera juice can be soothing and can be used to reduce discomfort caused by some lumps on the skin.
Turmeric:
- Turmeric is good for reducing inflammation and killing germs.
- Some types of infections could be helped by making a mix of turmeric and water and putting it on the lump.
Essential Oils:
- Some essential oils, like lavender and chamomile, have calming effects and can be put on the skin by mixing them with a carrier oil.
Calendula Cream:
- Made from marigold flowers, calendula cream is known for its calming effects and might help with minor skin irritations.
Coconut Oil:
- Coconut oil can help keep your skin fresh and reduce inflammation.
- Dry or sensitive skin might feel less painful if you put a thin layer on it.
Prevention
Ways to Prevent Skin Lumps
Preventing skin lumps requires proper skin cleanliness, infection prevention, and general health. These steps may lower your risk of skin lumps:
- Clean your skin with gentle soap and water especially on friction-prone regions including underarms, groin, and skin-to-skin contact.
- Use a moderate, hypoallergenic moisturizer to avoid dryness and irritation.
- Avoid tight clothing as they may cause discomfort, skin tags, and friction cysts.
- Sunscreen, protective gear, and wide-brimmed hats protect skin from UV radiation. UV exposure may cause skin cancer.
- Avoid tobacco and drinking to avoid skin problems, including skin cancer.
- Stay Hydrated as water keeps skin healthy and supple.
- Eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains help skin health.
- Use insect repellent to avoid skin responses and illnesses from insect bites.
- Check your skin often for new lumps, tags, moles, or lesions.
- Avoid picking and scratching to avoid introducing germs and causing illnesses.
- Some illnesses, including warts, may create skin lumps. Ask your doctor for vaccination.
- Avoid sharing personal belongings in gyms and locker rooms, where skin diseases are more frequent.
- Manage chronic conditions like diabetes and eczema to avoid skin problems.
Complications
Complications of Skin Lumps
Here are a few complications of skin lumps:
- Infection
- Cosmetic issues
- Impaired function
- Bleeding and ulceration
- Nerve compression
- Cancer
Takeaway
Takeaway
In conclusion, lumps on the skin are rather frequent and might indicate anything from a completely normal process to a more serious underlying disease. Many different conditions, such as cysts, infections, lipomas, moles, and malignant skin tumors, may give birth to these lesions. Understanding skin lumps, detecting them early, and treating them effectively are all essential. 6Takeaway | Researched based study from National Library of Medicine
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
MedlinePlus
Overview
-
Better Health Channel
Causes
-
Mount Sinai
Symptoms
-
Queensland Health
Treatment
-
National Library of Medicine
Treatment | Natural Remedies
-
National Library of Medicine
Takeaway