Nutrition and Benefits of Bulgur

- Bulgur
- 17 Aug 2023
Overview
What is Bulgur?
Bulgur (Bulgur wheat) is a delicious nutrient-enriched whole grain. Commercially, Bulgur is made chiefly from durum wheat (Triticum durum), although other wheat varieties are also used.
Bulgur is the cracked, partially cooked, dried form of wheat. Bulgur has a mild nutty flavor and goes well as a side dish with various foods. Bulgur wheat is indigenous to West Asia, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean. It is the most versatile and easy to cook among the other whole grains.

Key Facts of Bulgur
- Bulgur is the staple food in many parts of the world
- Bulgur is a winter crop that grows best at temperatures ranging from 15 to 25-degree centigrade
- As part of American aid to famine areas, the United States sends Bulgur to the Far East countries
- Bulgur is a cheap food that superficially resembles rice in texture when cooked
- Turkey is the lead producer and exporter of Bulgur. Turkey can produce around one million tonnes and export 200,000 tonnes of Bulgur per year1Overview| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com ,2Overview| Researched based study from Sciencedirect.com .
Nutrition
Nutrition in Bulgur
The nutrition in 182 grams of cooked Bulgur is as follows:
- Calories-152
- Protein-6 gm (gram)
- Carbohydrate-34 gm
- Fat-below 1 gm
- Fiber- 8 gm
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid)-13% DV (Daily Value)
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)–8% DV
- Vitamin B9 (Folate)-8% DV
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)-9% DV
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)-9% DV
- Magnesium-14% DV
- Manganese-48% DV
- Iron-10% DV
- Zinc-9% DV
- Copper-15% DV
The % daily value (%DV) is the daily value percentage for each nutrient component in a food serving.
- The Bulgur whole grain contains a good amount of dietary fiber, magnesium, manganese, and iron and has fewer calories than other whole grains such as quinoa and brown rice.
The nutrients in Bulgur have the following functions in our body
- Manganese is a mineral necessary by the body for activating many enzymes of bodily processes and maintaining healthy bones
- Magnesium is essential for maintaining nerve and muscle function as well as blood pressure and sugar levels in our body
- Iron is a mineral needed for the proper growth and development of the body
- Zinc is a mineral that assists the immune system in fighting infections
- Copper helps sustain the nervous system and immune system
- Vitamin B5 helps the body to convert fat and carbohydrate into energy
- Vitamins B6 are needed to make the immune system function correctly and convert food into energy.
- Vitamin B9 (Folate) is necessary for normal cell functioning and tissue growth.
- Vitamin B3 helps properly utilize protein and fat and keeps the hair, skin, and nervous system healthy.
- Vitamin B1 is essential for healthy nerve, heart, and muscle function 3Nutrition| Researched based study from Usda.gov
Benefits
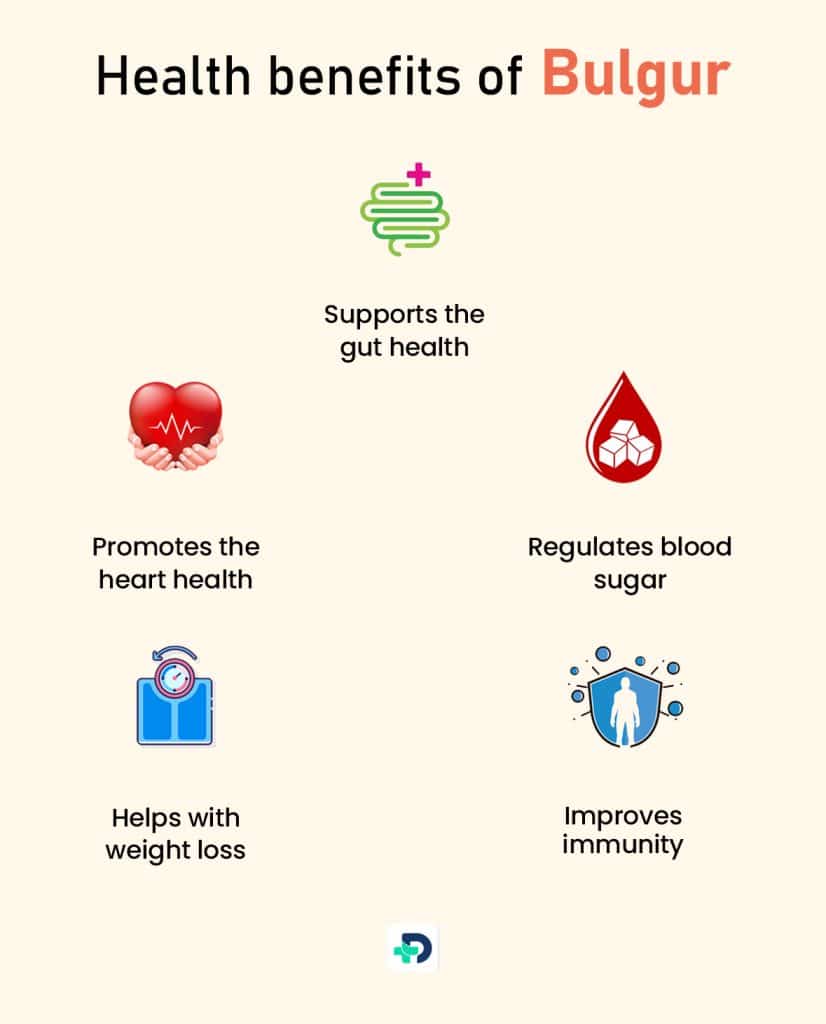
Health benefits of Bulgur
The health benefits of Bulgur are as follows:
- Helps in regulating blood sugar
- Promotes the heart health
- Supports the gut health
- Helps with weight loss
- Improves immunity
Regulates blood sugar
- Nutrients in Bulgur improve the insulin sensitivity. Insulin sensitivity is the ability of the insulin to clear glucose from the blood
- It decreases the risk of diabetes mellitus (type 2 diabetes) 4Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Promotes the heart health
- Nutrients in Bulgur lessen the cholesterol level in our body
- It lowers the homocysteine level in the blood. A high level of homocysteine indicates the development of heart diseases
- It reduces the risk of heart diseases
- It reduces the risk of death from coronary heart diseases 5Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Supports the gut health
- Bulgur nutrients promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut that supports proper digestive function.
- It regularizes the bowel movement and prevents constipation 6Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Helps with weight loss
- Bulgur nutrients keep the stomach full and make one feel less hungry
- It slows the absorption of sugar and fat in the small intestine
- It decreases the weight 7Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Improves immunity
- Nutrients in Bulgur neutralize the oxidative stress in the body
- It helps fight infections in the body
- It decreases the risk of breast and colon cancer 8Benefits| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Precautions
Precautions one needs be taken before consuming Bulgur
Bulgur contains a few compounds which may not suitable for everyone, hence one needs to be careful when including bulgur in their diet.
The compounds may rise complications are:
Gluten
- Gluten is a protein commonly found in most wheat varieties, including Bulgur. Gluten might only be suitable for some. Gluten might kill some of the beneficial bacteria needed for the gut in gluten-insensitive people. So, such people should opt for non-gluten foods.
Oxalates
- Bulgur also contains some oxalate compounds at high levels compared to other grain products. Oxalate is not harmful to healthy individuals. Oxalate can increase the calcium concentration in urine and complicate situations in people with kidney stones.
Phytic acid
- Bulgur contains phytic acid, which is an anti-nutrient that can decrease the absorption of iron and zinc. However, sprouting bulgur wheat before consumption can reduce the quantity of phytic acid in it 9Precautions| Researched based study from Wiley.com
Side effects
Side effects of Bulgur
Most people can tolerate Bulgur well. However, some people might have the following side effects
- Itching
- Hives
- Skin rash
- Swelling of the lips, mouth, face, and tongue
- Difficult breathing
- Stomach gas (bloating) 9Side effects| Researched based study from Wiley.com
Contraindications
Who should not consume Bulgur
One should avoid adding bulgur in the diet in following conditions
- One with wheat allergy
- Who have a gluten-related disorder
- People with inflammatory bowel disease
- Having digestive problems
- With poor tolerance for high-fiber food
- Suffering from kidney disease like frequent kidney stones
- People with gout disease(a type of arthritis causing severe pain and swelling in the joints)
- People with celiac disease (a persistent digestive disorder that damages the small intestine) 10Contraindications| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Usage
Preparations of Bulgur
Bulgur is easy to prepare since it is already parboiled (partially boiled).
Preparation
- Add boiling water to Bulgur, stir it, and then cover it for around 15 minutes.
- After 15 minutes, remove the excess water.
- The Bulgur is ready to consume with any side food.
For coarser preparation
- One can combine one part of Bulgur with three parts of water, along with some olive oil and a small amount of salt
- Then let it boil for around 8 minutes and stir occasionally
- After 8 minutes, allow it to stand for five minutes, drain the excess water and serve.
Tips to include Bulgur in diet
- Sprinkle uncooked Bulgur in soup or stew and let it cook until it’s soft.
- Can use it with cereal or any other side dish.
- One can make a sweet salad with cooked Bulgur, pineapple, resins, and raspberry.
- Add Bulgur with low-salt chicken broth, tomato, and onions.
- Can cook the Bulgur with one’s favorite herb
- Use the cooked Bulgur as a filling for stuffed vegetables
- One can use the cooked bulgur wheat as a binder in the vegetable burger and meatballs
- Can also use Bulgur as a substitute for rice in any food recipe
Storage
Buying & Storage of Bulgur
Buying
- One can buy Bulgur from any grocery store or online all year round
- Always buy Bulgur that is well packaged and tightly sealed
- One must always check for the expiry date before purchasing
Storage
- One must store Bulgur in a cool and dry place away from direct sunlight
- Always keep it in an airtight container
- It lasts six months at room temperature, but when kept in the deep freeze, it can last up to a year.
- Cooked Bulgur must be stored in the refrigerator and consumed within one to two days 11Storage| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Takeaway
Key Takeaways
- Bulgur is a low-calorie, high-fiber, nutritious whole grain with many health benefits.
- Bulgur improves digestion and overall gut health
- Bulgur preparation is effortless and an excellent addition to various food items.
- Bulgur is an excellent addition to a healthy balanced diet.
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
Science Direct
Other food products | Overview
-
Science Direct
Effects of wheat cultivar, cooking method, and bulgur type on nutritional quality characteristics of bulgur | Overview
-
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
Bulgur, cooked | Nutrition
-
National Library of Medicine
Whole grain consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all cause and cause specific mortality: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Association between Grain and Legume Consumption and the Risk of Coronary Artery Obstruction among Jordanians Based on Angiography Results | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Mechanisms, Evaluation, and Management of Chronic Constipation | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Substituting whole grains for refined grains in a 6-wk randomized trial favorably affects energy-balance metrics in healthy men and postmenopausal women | Benefits
-
National Library of Medicine
Putting the whole grain puzzle together: health benefits associated with whole grains--summary of American Society for Nutrition 2010 Satellite Symposium | Benefits
-
Institute of Food Science & Technology
Biochemical and nutritional properties of wheat bulgur: A review | Side effects | Precautions
-
National Library of Medicine
Gluten-Free Products for Celiac Susceptible People | Contraindications
-
National Library of Medicine
Bulgur processes increase nutrition value: possible role in in-vitro protein digestability, phytic acid, trypsin inhibitor activity and mineral bioavailability | Storage