Lantus: Uses, Side effects, and Interactions

- Lantus
- 22 Aug 2023
Overview
About Lantus
Lantus, or Insulin Glargine, has become a ground-breaking treatment choice. Millions of diabetics’ lives have transformed when this long-acting insulin which was approved in 2000. This medication gives patients more stable and regular control over their blood sugar levels, which lowers the risk of complications and enhances overall quality of life.
In this article, we will examine the key features of Lantus, indications, advantages, and potential drawbacks.

Uses
Uses of Lantus
It is mainly employed to treat diabetic mellitus. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are suggested. Its primary objective is to help control blood glucose levels by substituting or enhancing the body’s insulin.
Type 1 diabetes
- It is frequently used as a basal or long-acting insulin to keep blood sugar levels steady all day and all night.
- It provides a steady flow of insulin to mimic the body’s normal insulin production.
- It lowers blood sugar more steadily and predictably, lessening the chance of hypoglycemia.
Diabetes type 2
- It may be administered as a part of a patient’s treatment plan for type 2 diabetes patients whose blood glucose levels cannot be controlled by oral drugs alone.
- It is frequently used with oral antidiabetic medications. It aids in preventing hyperglycemia and its accompanying difficulties, including kidney damage, nerve damage, and eye problems1Uses| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Side effects
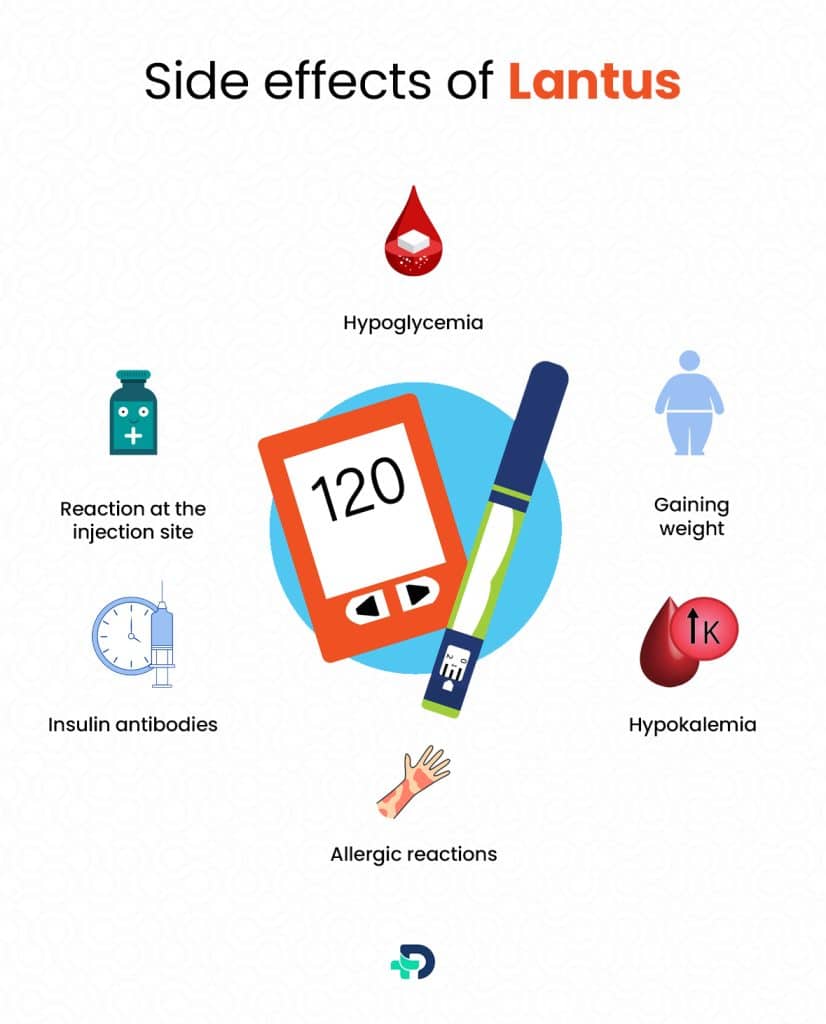
Lantus side effects
Although it is generally well tolerated, it may result in several side effects that can be divided into ordinary, less frequent, and uncommon.
Typical adverse effects include:
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or Low blood sugar is the most frequent side effect of insulin therapy. Possible signs include
- Sweating
- Shakiness
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Fast heart rate.
Regular blood sugar testing and early treatment with quick-acting carbs like glucose pills or juice are crucial.
Reaction at the injection site
There may be little to significant
- Redness
- Swelling
- Itching
- Pain at the injection site.
These responses can be reduced by rotating injection locations.
Gaining weight
- While using Lantus, some people may gain weight. The medication’s anabolic (tissue-building) actions are the cause of this.
Less common side effects may include:
Lipodystrophy
- Long-term use of the same injection site might cause alterations in the fat tissue, which can leave lumps or indentations there.
Hypokalemia
- Rarely, it may result in low potassium levels in the blood, which can produce symptoms including muscle weakness and irregular heartbeats.
Allergic reactions
Some people can experience rare allergic responses, including symptoms like:
- Itching
- Rash
- Swelling
- Breathing problems.
Whenever you suffer any of these, get medical help.
Uncommon side effects could include:
Significant hypoglycemia
- Extremely low blood sugar might cause confusion, coma, or seizures. If the dose is too high, this is more likely to occur.
Insulin antibodies
- The body may produce antibodies that inhibit insulin, which could lessen its efficiency.1Side effects| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Dosage
Lantus dosage & administration
The dosage may change based on a person’s unique circumstances, including blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and overall diabetes care strategy. It is prescribed by medical professionals, and the dosage is modified to suit the requirements of each patient.
- Due to increased insulin resistance, some people may need higher insulin doses, whereas others more sensitive to it may only need lesser dosages.
- Type one diabetes and type two diabetes may require different dosages. The severity of the ailment may also affect the dose.
- When adjusting the dosage, your doctor will also consider any additional diabetes drugs or treatments you are taking.
- Your healthcare professional will also consider lifestyle factors such as diet, activity, and others since these might affect the amount of insulin needed1Dosage| Researched based study from Fda.gov
How should Lantus be administered?
Subcutaneous injections are used to give it, which is injected right beneath the skin. It can be purchased as a liquid in prefilled disposable insulin pens or as a vial for syringe use. How to administer it is as follows:
Using a pen
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Check the insulin’s appearance by removing the pen cap; it should be clear and colorless.
- Select a place for an injection. The buttocks, upper arms, and abdomen are frequent injection locations. To avoid lipodystrophy, alternate the injection sites.
- After using an alcohol swab to clean the area, let it dry.
- Tap the pen while holding it with the needle pointed up to eliminate any air bubbles.
- Set the dosage to the prescribed number of units.
- Pinch the skin where it has been cleaned in order to fully enter the needle at a 90-degree angle.
- To inject the drug, completely press the injection button.
- Count slowly from 10 before removing the needle from the skin to ensure the entire dose is administered.
- Put the pen cap back on, and properly discard the discarded needle.
Using the syringe and a vial
- Use soap and water to wash your hands thoroughly.
- Draw the prescribed amount of air into the syringe.
- Inject air into the vial by inserting a needle inside the rubber stopper.
- The viral infection and inject the appropriate dosage into the syringe
- Pick an injection site, clean it with alcohol, and let it air dry.
- Patch the skin there, then stab the needle at a 90-degree angle.
- To inject, depress the plunger.
- Gently count to 10 before removing the needle from the skin to be sure the complete amount has been administered.
- Throw away the used needle and syringe.1Dosage| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Drug interactions
Drug interactions
It may interact with some medications, reducing their effectiveness or producing unwanted consequences. To ensure safe and efficient management, you must inform your doctor about all your drugs, dietary supplements, and herbal products.
Hypoglycemic medications
- The risk of hypoglycemia can be increased when taking Lantus and other diabetes drugs, such as sulfonylureas or meglitinides.1Interactions| Researched based study from Fda.gov
Beta-blockers
- Some beta-blockers used to treat disorders, including heart disease and hypertension, might conceal hypoglycemia’s symptoms, making it more difficult to identify low blood sugar levels. This can raise some questions for people with diabetes on Lantus.6Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Thiazolidinedione
- When used with Lantus, several medications, sometimes called TZDs, may improve insulin sensitivity and raise the risk of hypoglycemia.4Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Corticosteroids
- They may increase blood sugar levels, which could offset insulin’s effects. Diabetes patients who need corticosteroid therapy should be closely watched, and insulin dosage modifications may be required.5Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
ACE inhibitors and ARBs
- Frequently prescribed for hypertension and kidney illness, these drugs may impact blood glucose levels7Interactions| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov
Different medications
- Lantus may interact with several medications, such as antipsychotics, antiviral treatments, and thyroid medications. Always disclose all of the medications you are taking to your healthcare provider in order to avoid any interactions.
Pregnancy and Lantus
Pregnancy and Lantus
It is crucial to discuss insulin use with your doctor if you are pregnant or want to become pregnant. Maintaining good blood sugar control throughout pregnancy is essential for both the mother’s and the unborn child’s health.
When using Lantus while pregnant, keep the following things in mind:
Pre-existing diabetes
- Your doctor will work with you to alter your insulin dosage and blood sugar monitoring if you have diabetes before becoming pregnant to maintain stable blood glucose levels during the pregnancy.
- Pregnancy problems brought on by uncontrolled diabetes might affect both the mother and the fetus.
Gestational diabetes
- Pregnant women can occasionally develop gestational diabetes. In these circumstances, insulin therapy may be recommended to control it.
- A change in insulin need is possible.
- During pregnancy, significantly, as the pregnancy advances, insulin needs can change.
Congenital disability risk
- There is no evidence linking the usage of insulin-like Lantus to a higher incidence of birth abnormalities.2Pregnancy and Lantus| Researched based study from Nlm.nih.gov 3Pregnancy and Lantus| Researched based study from Diabetes.org Generally speaking, using insulin while pregnant is safe
Any feedback on this article?
 This Articles content was accurate
This Articles content was accurate Very Informative Article
Very Informative Article I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
 This article contains inaccurate content
This article contains inaccurate content This article was not helpful
This article was not helpful I have a question or a comment
I have a question or a comment
We appreciate your helpful feedback!
Checkout our social pages
References
-
FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION
LANTUS® | Overview | Uses | Side effects | Dosage | Administration | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Insulin Glargine Safety in Pregnancy | Pregnancy and Lantus
-
American Diabetes Association
Insulin Glargine during Pregnancy | Pregnancy and Lantus
-
National Library of Medicine
Clinically and pharmacologically relevant interactions of antidiabetic drugs | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Challenges With Insulin in the Inpatient Setting | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Beta adrenergic antagonists and antianginal drugs | Interactions
-
National Library of Medicine
Simple Reason for Hypoglycemia: ACE Inhibitor-induced Severe Recurrent Hypoglycemia in a Nondiabetic Patient | Interactions